[1] CAI H, GUO H. Mesenchymal stem cells and their exocytotic vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(3):2085.
[2] ADELIPOUR M, LUBMAN DM, KIM J. Potential applications of mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes in regenerative medicine. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2023;23(6):491-507.
[3] YANG G, FAN X, LIU Y, et al. Immunomodulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023;19(5):1214-1231.
[4] BROWN M, WORRELL C, PARIANTE CM. Inflammation and early life stress: an updated review of childhood trauma and inflammatory markers in adulthood. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021;211:173291.
[5] AKDIS M, BURGLER S, CRAMERI R, et al. Interleukins, from 1 to 37, and interferon-γ: receptors, functions, and roles in diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127(3):701-721, e1-e70.
[6] KITAGAWA T, HATTORI T, SENTANI K, et al. Relationship between interleukin-1β gene expression in epicardial adipose tissue and coronary atherosclerosis based on computed tomographic analysis. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2021; 15(2):175-179.
[7] STRENN N, PÅLSSON E, LIBERG B, et al. Influence of genetic variations in IL-1B on brain region volumes in bipolar patients and controls. Psychiatry Res. 2021;296: 113606.
[8] LU J, MIAO Z, JIANG Y, et al. Chrysophanol prevents IL-1β-Induced inflammation and ECM degradation in osteoarthritis via the Sirt6/NF-κB and Nrf2/NF-κB axis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;208:115402.
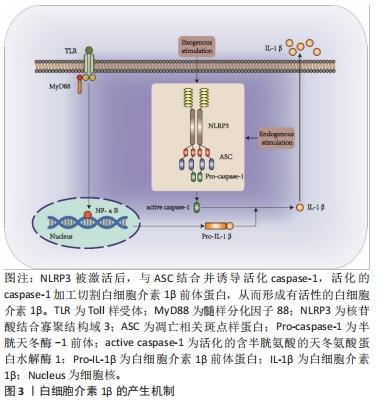
[9] ZHANG J, LIU X, WAN C, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome mediates M1 macrophage polarization and IL-1β production in inflammatory root resorption. J Clin Periodontol. 2020;47(4):451-460.
[10] CRISTINA DE BRITO TOSCANO E, LEANDRO MARCIANO VIEIRA É, BONI ROCHA DIAS B, et al. NLRP3 and NLRP1 inflammasomes are up-regulated in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and may contribute to overexpression of caspase-1 and IL-β in sclerotic hippocampi. Brain Res. 2021;1752:147230.
[11] LI Z, HU J, BAO C, et al. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and elevation of interleukin-1β secretion in infection by sever fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):2573.
[12] SCHRODER K, TSCHOPP J. The inflammasomes. Cell. 2010;140(6):821-832.
[13] WAN P, ZHANG S, RUAN Z, et al. AP-1 signaling pathway promotes pro-IL-1β transcription to facilitate NLRP3 inflammasome activation upon influenza A virus infection. Virulence. 2022;13(1):502-513.
[14] LATZ E, XIAO TS, STUTZ A. Activation and regulation of the inflammasomes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(6):397-411.
[15] NOURI BARKESTANI M, NASERIAN S, KHODDAM F, et al. Optimization of IL-1RA structure to achieve a smaller protein with a higher affinity to its receptor. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):7483.
[16] ZAREZADEH MEHRABADI A, AGHAMOHAMADI N, KHOSHMIRSAFA M, et al. The roles of interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein in certain inflammatory conditions. Immunology. 2022;166(1):38-46.
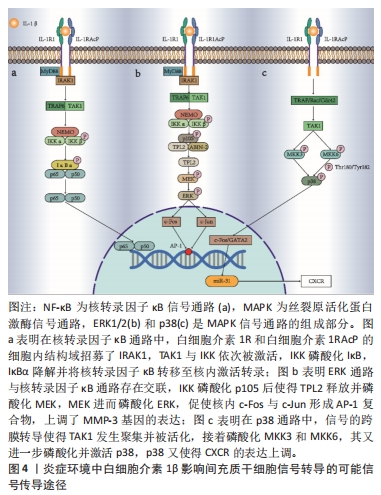
[17] JEFFERIES C, BOWIE A, BRADY G, et al. Transactivation by the p65 subunit of NF-kappaB in response to interleukin-1 (IL-1) involves MyD88, IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1, TRAF-6, and Rac1. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21(14):4544-4552.
[18] TIAN S, LI YL, WANG J, et al. Chinese Ecliptae herba (Eclipta prostrata (L.) L.) extract and its component wedelolactone enhances osteoblastogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via targeting METTL3-mediated m6A RNA methylation. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;312:116433.
[19] TSENG WC, LEE PY, TSAI MT, et al. Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate acute kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury via enhancing renal tubular autophagy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):367.
[20] ZHANG S, XIE Y, YAN F, et al. Negative pressure wound therapy improves bone regeneration by promoting osteogenic differentiation via the AMPK-ULK1-autophagy axis. Autophagy. 2022;18(9):2229-2245.
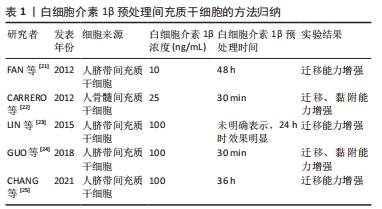
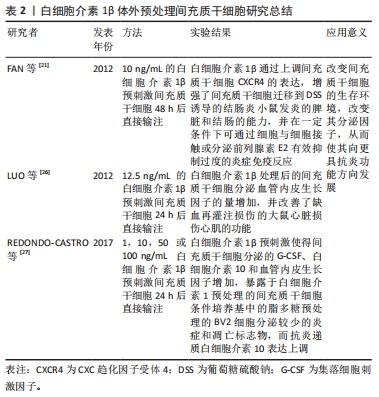
[21] FAN H, ZHAO G, LIU L, et al. Pre-treatment with IL-1β enhances the efficacy of MSC transplantation in DSS-induced colitis. Cell Mol Immunol. 2012;9(6):473-481.
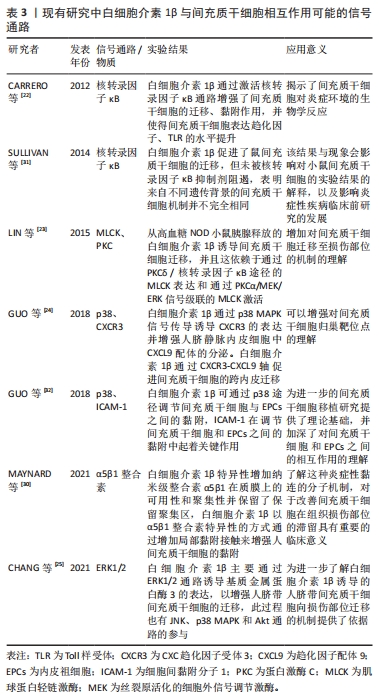
[22] CARRERO R, CERRADA I, LLEDÓ E, et al. IL1β induces mesenchymal stem cells migration and leucocyte chemotaxis through NF-κB. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2012;8(3): 905-916.
[23] LIN CY, ZU CH, YANG CC, et al. IL-1β-induced mesenchymal stem cell migration involves MLCK activation via PKC signaling. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(10):2011-2028.
[24] GUO YC, CHIU YH, CHEN CP, et al. Interleukin-1β induces CXCR3-mediated chemotaxis to promote umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transendothelial migration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):281.
[25] CHANG CH, LIN YL, TYAN YS, et al. Interleukin-1β-induced matrix metalloproteinase-3 via ERK1/2 pathway to promote mesenchymal stem cell migration. PLoS One. 2021;16(5):e0252163.
[26] LUO Y, WANG Y, POYNTER JA, et al. Pretreating mesenchymal stem cells with interleukin-1β and transforming growth factor-β synergistically increases vascular endothelial growth factor production and improves mesenchymal stem cell-mediated myocardial protection after acute ischemia. Surgery. 2012;151(3):353-363.
[27] REDONDO-CASTRO E, CUNNINGHAM C, MILLER J, et al. Interleukin-1 primes human mesenchymal stem cells towards an anti-inflammatory and pro-trophic phenotype in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):79.
[28] XIE F, TENG L, LU J, et al. Interleukin-10-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent hypertrophic scar formation via regulating the biological characteristics of fibroblasts and inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2022;2022:6368311.
[29] LI Y, LU L, XIE Y, et al. Interleukin-6 knockout inhibits senescence of bone mesenchymal stem cells in high-fat diet-induced bone loss. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;11:622950.
[30] MAYNARD SA, PCHELINTSEVA E, ZWI-DANTSIS L, et al. IL-1β mediated nanoscale surface clustering of integrin α5β1 regulates the adhesion of mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):6890.
[31] SULLIVAN CB, PORTER RM, EVANS CH, et al. TNFα and IL-1β influence the differentiation and migration of murine MSCs independently of the NF-κB pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(4):104.
[32] GUO J, ZHANG H, XIA J, et al. Interleukin-1β induces intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression, thus enhancing the adhesion between mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(4):1976-1982.
[33] SADRI F, REZAEI Z, FEREIDOUNI M. The significance of the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway in the normal development. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49(4):3307-3320.
[34] WANG R, WEI W, RONG S, et al. Intravenous injection of SDF-1α-overexpressing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells has a potential protective effect on myocardial ischemia in mice. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;17(4):348-360.
[35] CAPECE D, VERZELLA D, FLATI I, et al. NF-κB: blending metabolism, immunity, and inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2022;43(9):757-775.
[36] BRIKOS C, WAIT R, BEGUM S, et al. Mass spectrometric analysis of the endogenous type I interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor signaling complex formed after IL-1 binding identifies IL-1RAcP, MyD88, and IRAK-4 as the stable components. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6(9):1551-1559.
[37] WESCHE H, KORHERR C, KRACHT M, et al. The interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP) is essential for IL-1-induced activation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) and stress-activated protein kinases (SAP kinases). J Biol Chem. 1997;272(12):7727-7731.
[38] DIEP S, MADDUKURI M, YAMAUCHI S, et al. Interleukin-1 and nuclear factor kappa B signaling promote breast cancer progression and treatment resistance. Cells. 2022;11(10):1673.
[39] BARNABEI L, LAPLANTINE E, MBONGO W, et al. NF-κB: at the borders of autoimmunity and inflammation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:716469.
[40] TSENG HC, LEE IT, LIN CC, et al. IL-1β promotes corneal epithelial cell migration by increasing MMP-9 expression through NF-κB- and AP-1-dependent pathways. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57955.
[41] YU JS, HUANG T, ZHANG Y, et al. Substrate-specific recognition of IKKs mediated by USP16 facilitates autoimmune inflammation. Sci Adv. 2021;7(3):eabc4009.
[42] LANG V, SYMONS A, WATTON SJ, et al. ABIN-2 forms a ternary complex with TPL-2 and NF-kappa B1 p105 and is essential for TPL-2 protein stability. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(12):5235-5248.
[43] GANTKE T, SRISKANTHARAJAH S, LEY SC. Regulation and function of TPL-2, an IκB kinase-regulated MAP kinase kinase kinase. Cell Res. 2011;21(1):131-145.
[44] SENGER K, PHAM VC, VARFOLOMEEV E, et al. The kinase TPL2 activates ERK and p38 signaling to promote neutrophilic inflammation. Sci Signal. 2017;10(475):eaah4273.
[45] WON KJ, PARK JS, JEONG HY. Repression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha by AP-1 underlies dyslipidemia associated with retinoic acid. J Lipid Res. 2019;60(4): 794-804.
[46] BENBOW U, BRINCKERHOFF CE. The AP-1 site and MMP gene regulation: what is all the fuss about? Matrix Biol. 1997;15(8-9):519-526.
[47] NISSINEN L, KÄHÄRI VM. Matrix metalloproteinases in inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840(8):2571-2580.
[48] HUGHES CE, NIBBS RJB. A guide to chemokines and their receptors. FEBS J. 2018; 285(16):2944-2971.
[49] MAO CY, WANG YG, ZHANG X, et al. Double-edged-sword effect of IL-1β on the osteogenesis of periodontal ligament stem cells via crosstalk between the NF-κB, MAPK and BMP/Smad signaling pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(7):e2296.
[50] KAMMERER T, FAIHS V, HULDE N, et al. Hypoxic-inflammatory responses under acute hypoxia: In Vitro experiments and prospective observational expedition trial. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):1034.
[51] DUHEN T, CAMPBELL DJ. IL-1β promotes the differentiation of polyfunctional human CCR6+CXCR3+ Th1/17 cells that are specific for pathogenic and commensal microbes. J Immunol. 2014;193(1):120-129.
[52] CANNON A, THOMPSON CM, BHATIA R, et al. Contribution of CXCR3-mediated signaling in the metastatic cascade of solid malignancies. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021;1876(2):188628.
[53] GARCÍA-HERNÁNDEZ L, GARCÍA-ORTEGA MB, RUIZ-ALCALÁ G, et al. The p38 MAPK components and modulators as biomarkers and molecular targets in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;23(1):370.
[54] YUAN L, BU S, DU M, et al. RNF207 exacerbates pathological cardiac hypertrophy via post-translational modification of TAB1. Cardiovasc Res. 2023;119(1):183-194.
[55] RAINGEAUD J, WHITMARSH AJ, BARRETT T, et al. MKK3- and MKK6-regulated gene expression is mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16(3):1247-1255.
[56] CUADRADO A, NEBREDA AR. Mechanisms and functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem J. 2010;429(3):403-417.
[57] KIM E, AHUJA A, KIM MY, et al. DNA or protein methylation-dependent regulation of activator protein-1 function. Cells. 2021;10(2):461.
[58] ZHONG L, SIMONEAU B, HUOT J, et al. p38 and JNK pathways control E-selectin-dependent extravasation of colon cancer cells by modulating miR-31 transcription. Oncotarget. 2017;8(1):1678-1687.
[59] 张玉娟,原一桐,杜若琛,等. miR-31促进骨髓MSCs的增殖和迁移[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(1):66-71.
[60] HONG JM, LEE JW, SEEN DS, et al. LPA1-mediated inhibition of CXCR4 attenuates CXCL12-induced signaling and cell migration. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):257.
[61] WANG CC, LU JW, CHIANG KH, et al. Anti-inflammatory and chondro-protective effects of acidic polysaccharide from enteromorpha prolifera in experimental models of osteoarthritis in-vitro and in-vivo. Cartilage. 2022;13(4):157-170.
[62] KIM E, AHUJA A, KIM MY, et al. DNA or protein methylation-dependent regulation of activator protein-1 function. cells. 2021;10(2):461.
[63] WANG C, XU M, FAN Q, et al. Therapeutic potential of exosome-based personalized delivery platform in chronic inflammatory diseases. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023;18(1):100772.
[64] LIU W, SUN Y, HE Y, et al. IL-1β impedes the chondrogenic differentiation of synovial fluid mesenchymal stem cells in the human temporomandibular joint. Int J Mol Med. 2017;39(2):317-326.
[65] DING J, GHALI O, LENCEL P, et al. TNF-alpha and IL-1beta inhibit RUNX2 and collagen expression but increase alkaline phosphatase activity and mineralization in human mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2009;84(15-16):499-504. |