中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (25): 4079-4086.doi: 10.12307/2024.193
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
间充质干细胞及细胞外囊泡治疗肺纤维化的现状与未来
王艳阳1,2,刘 婵1,2,余丽梅1,2,何志旭1,2,3
- 1遵义医科大学附属医院贵州省细胞工程重点实验室,贵州省遵义市 563000;2遵义医科大学组织损伤修复与再生医学省部共建协同创新中心,贵州省遵义市 563000;3贵州省儿童医院遵义医科大学附属医院小儿内科,贵州省遵义市 563000
-
收稿日期:2023-07-08接受日期:2023-08-24出版日期:2024-09-08发布日期:2023-11-24 -
通讯作者:何志旭,主任医师,教授,博士生导师,遵义医科大学附属医院贵州省细胞工程重点实验室,贵州省遵义市 563000;遵义医科大学组织损伤修复与再生医学省部共建协同创新中心,贵州省遵义市 563000;贵州省儿童医院遵义医科大学附属医院小儿内科,贵州省遵义市 563000 -
作者简介:王艳阳,女,1999年生,河南省焦作市人,汉族,遵义医科大学在读硕士,主要从事干细胞治疗学研究。 -
基金资助:2022年国家自然科学基金面上项目(32270848),项目负责人:何志旭;2020年教育部协同创新中心建设项目:组织损伤修复与再生医学省部共建协同创新中心(教科技函[2020]39号),项目负责人:何志旭;2020年贵州省科技支撑计划项目(黔科合支撑【2020】4Y192号),项目负责人:何志旭
Current status and future of treatment of pulmonary fibrosis by mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles
Wang Yanyang1, 2, Liu Chan1, 2, Yu Limei1, 2, He Zhixu1, 2, 3
- 1Key Cell Engineering Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Ministry of Tissue Damage Repair and Regenerative Medicine Jointly Established a Collaborative Innovation Center, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 3Guizhou Children’s Hospital; Department of Pediatrics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2023-07-08Accepted:2023-08-24Online:2024-09-08Published:2023-11-24 -
Contact:He Zhixu, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Key Cell Engineering Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; Ministry of Tissue Damage Repair and Regenerative Medicine Jointly Established a Collaborative Innovation Center, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; Guizhou Children’s Hospital; Department of Pediatrics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Wang Yanyang, Master candidate, Key Cell Engineering Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; Ministry of Tissue Damage Repair and Regenerative Medicine Jointly Established a Collaborative Innovation Center, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:2022 National Natural Science Foundation (General Program), No. 32270848 (to HZX); 2020 Ministry of Education Collaborative Innovation Center Construction Project: Ministry of Tissue Damage Repair and Regenerative Medicine Jointly Established a Collaborative Innovation Center, No. [2020]39 (to HZX); 2020 Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Support Plan Project, No. [2020]4Y192 (to HZX)
摘要:
文题释义:
间充质干细胞:是一类多能性的成体干细胞,起源于间充质组织,主要存在于骨髓、脂肪组织、脐带以及其他组织中。这些干细胞具有自我更新和多向分化能力,可以分化为多种细胞类型,包括成骨细胞、软骨细胞、脂肪细胞和肌肉细胞等,已广泛应用于组织工程、再生医学和疾病治疗等领域。细胞外囊泡:是一类由细胞释放到细胞外的小型膜包裹的囊泡,其直径通常在30-1 000 nm之间。细胞外囊泡包含了细胞内部的生物活性分子,如蛋白质、核酸(RNA和DNA)、脂质等。这些囊泡可以通过与周围细胞进行物质交换,传递包含的生物信息,从而调节目标细胞的生物学功能和信号传导。细胞外囊泡在细胞间的通讯和信息传递中起着重要的作用,被认为是一种重要的细胞间通讯介质,对于维持组织稳态和参与疾病发生发展具有重要意义。
目的:综述间充质干细胞及其细胞外囊泡在肺纤维化治疗方面的应用,以期全面了解其治疗机制、疗效评估和面临的问题,为未来进一步研究和临床应用提供参考和指导。
方法:中文检索词为“间充质干细胞”“间充质干细胞细胞外囊泡”“肺纤维化”;英文检索词为“mesenchymal stem cells”
“mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles”“pulmonary fibrosis”,检索中国知网和PubMed电子期刊数据库,通过人工阅读排除重复文献等,最终纳入112篇文献,重点对58篇中英文文献进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:①间充质干细胞及其细胞外囊泡可以通过多种机制抑制纤维化过程,如调节炎症反应、抑制成纤维细胞增殖和促进受损组织修复,临床试验的初步结果也显示出一定的治疗效果,包括改善患者的肺功能和生活质量。②然而,间充质干细胞及其细胞外囊泡治疗肺纤维化仍面临一些挑战。在治疗过程中需要解决细胞迁移和组织内定位等问题,以其能够准确到达受损肺组织。另外,长期安全性问题也有待进一步研究改进。对于其转化医学发展,细胞采集、细胞分离、细胞培养、细胞收获和细胞鉴定等标准化程序还需要被细化。③尽管面临这些挑战,但通过科研工作者和医务人员的共同努力,这些问题有望得到逐步解决。未来,可以通过优化治疗方案和探索个体化治疗进一步提高治疗效果。同时,深入研究间充质干细胞及其细胞外囊泡的治疗机制,有望开发出更为高效和安全的治疗策略。
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-3682-3618 (王艳阳);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8263-129X (何志旭)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
王艳阳, 刘 婵, 余丽梅, 何志旭. 间充质干细胞及细胞外囊泡治疗肺纤维化的现状与未来[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(25): 4079-4086.
Wang Yanyang, Liu Chan, Yu Limei, He Zhixu. Current status and future of treatment of pulmonary fibrosis by mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 4079-4086.
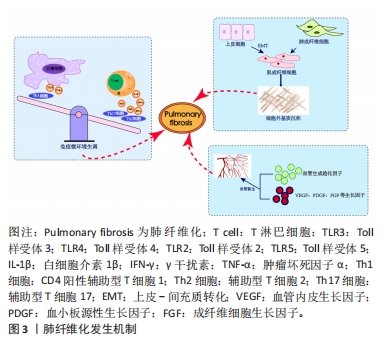
2.1.1 免疫微环境改变 肺纤维化最初被描述为一种以炎症反应为始的疾病[19],研究证明炎症反应几乎参与了所有的伤口愈合发生与纤维化进程[20],其中在纤维化进程中炎症微环境发生的主要变化包括:①免疫细胞群与炎症因子。新近研究通过单细胞测序技术揭示肺纤维化过程中免疫细胞群的主要改变以巨噬细胞与T细胞为主[21]。巨噬细胞分为促进炎症的M1型巨噬细胞和抗炎的M2型巨噬细胞,M1型巨噬细胞负责肺泡上皮损伤后的调节过程,分泌肿瘤坏死因子α等肺纤维化相关炎症因子。M2型巨噬细胞主要在伤口愈合过程、肺部炎症反应中发挥关键作用,分泌白细胞介素10等肺纤维化过程的重要因子。各种调节细胞因子、趋化因子、递质和免疫调节细胞通过改变M1、M2型巨噬细胞的极化过程来作用于肺部疾患,从而影响肺纤维化的发展过程[22-23]。在T细胞群中,Th1细胞参与吞噬细胞依赖性炎症,分泌大量白细胞介素2等,Th2细胞参与慢性炎症疾病和组织修复,分泌大量白细胞介素4等[24]。正常伤口有效愈合通常以占主导地位的Th1反应为特征,而免疫平衡转为以Th2细胞为主导会导致慢性炎症,最终导致纤维化[25],不平衡的Th1/Th2免疫反应被认为是特发性肺纤维化发病机制的核心。研究发现,Th17分化受阻可以减轻博莱霉素诱导的肺纤维化[24,26]。②Toll样受体与炎性小体等免疫活性物质。Toll样受体是参与非特异性免疫(天然免疫)的一类重要蛋白质分子,表达在巨噬细胞、树突状细胞和上皮细胞表面。研究表明,Toll样受体3、Toll样受体4缺乏会促进肺纤维化中异常的炎症反应和纤维增殖反应,Toll样受体2、Toll样受体5在肺纤维化动物模型中表达增加[27-30]。在肺纤维化发生中现有研究比较多的炎性小体是NLRP3与AIM2炎性小体,NLRP3在肺泡上皮细胞中被激活,可以通过转化生长因子β1调节上皮-间质转化参与肺纤维化进程[31-32]。CHO等[33]通过临床试验证明,AIM2炎性小体在特发性肺纤维化患者的外周血单核细胞中会增加,AIM2炎性小体激活有助于产生和释放促纤维化递质。
2.1.2 上皮、间质细胞群改变导致的间质沉积 肺纤维化过程中,肌成纤维细胞大量产生导致间质沉积的途径包括:①间质细胞种群发生变化:成纤维细胞向肌成纤维细胞的过渡是伤口愈合过程中的正常事件,其特征是平滑肌肌动蛋白达增加。肌成纤维细胞是产生闭合伤口收缩力所必需的要素,这与胶原蛋白沉积有关[34],肌成纤维细胞数量的增加会导致纤维化的进展,单细胞测序结果揭示了在肺纤维化发生发展中,肌成纤维细胞特异性表面标志物表达在平滑肌细胞等多种细胞中,所有间充质细胞中与细胞外基质相关的基因都上调[35]。②肺上皮细胞发生上皮-间质转化。临床样本与实验动物肺部组织病理染色中间充质与上皮细胞标志物的共定位证实了上皮-间质转化的发生[36-38] ,单细胞测序揭示肺纤维化肺上皮细胞的特点是气道上皮细胞比例增加,肺泡上皮细胞大幅下降,出现的异常基底细胞表达上皮-间质转化的标志物[21],肺纤维化过程中,转化生长因子β、血小板衍生生长因子受体、成纤维细胞生长因子和多种信号通路都能促进间充质基因的表达和上皮基因的下调[4,39]。
2.1.3 血管生成 血管生成是伤口修复的正常特征,能够提供组织愈合所需的细胞和营养。研究发现,在肺纤维化过程中,纤维化区域内出现广泛新生血管[40]。血管生成的稳态由血管生成促进和抑制因素共同调节,例如血管生成趋化因子5、血管生成趋化因子8与血管生成趋化因子10的表达不平衡,可以使血管生成增加,抑制血管生成趋化因子受体2可以减弱博莱霉素诱导的肺纤维化程度[41-42];也有研究证明血管生成素生物轴与肺纤维化血管重塑的调节明确相关[43]; 血管内皮生长因子、血小板衍生生长因子和成纤维细胞生长因子也都与肺纤维化的发病机制相关[44],血管内皮生长因子是最有效的血管生成刺激因素之一,在肺纤维化发生发展过程中发挥重要作用[45-46]。
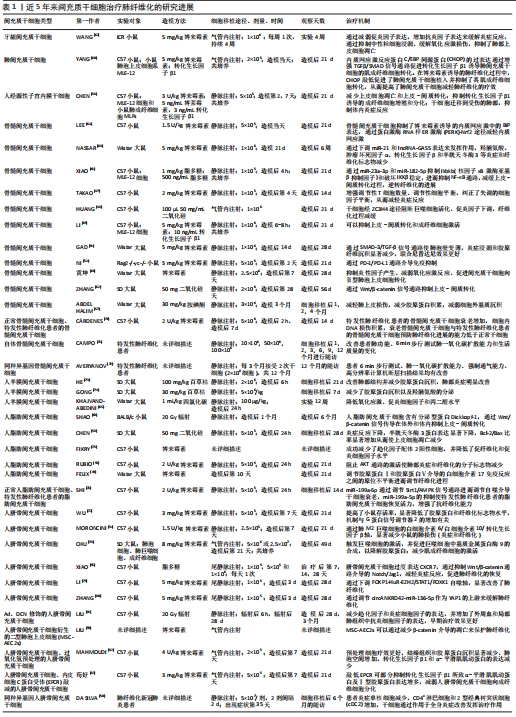
2.2 MSCs治疗肺纤维化的研究进展 在中国知网、PubMed数据库筛选出近5年内涉及MSCs治疗肺纤维化的相关研究37篇[47-83],其中包括34个临床前研究,3个临床研究,研究所涉及的具体细节按照MSCs种类进行分类,造模方法、细胞移植途径、剂量、时间等具体细节见表1。关于MSCs治疗肺纤维化的机制,迄今为止研究最充分的是炎症改善,不同来源MSCs可以通过调整中性粒细胞比例、T细胞数量、Treg平衡来对抗炎症[47-50],现有的通路研究包含SMAD-3/TGF-β信号通路、PD-1/PD-L1通路、AKT通路、IL-6/IL-10/TGF-β轴、Wnt/β-catenin通路[51-55],通过不同的作用机制最终使得促炎因子下调,抗炎因子上调;其次是上皮间质细胞群的改善[56]:其中包括肺上皮细胞的凋亡减轻[57-59],成纤维细胞的激活或增殖被抑制[60],上皮-间质转化的改善[61],现有研究多数集中在通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路减缓上皮-间质转化的发生[62-63];最后是氧化应激过程的改善[64-65]。大多数情况下,上述改变并不单一发生,多种机制发生综合作用[66],最终完成纤维化的改善。
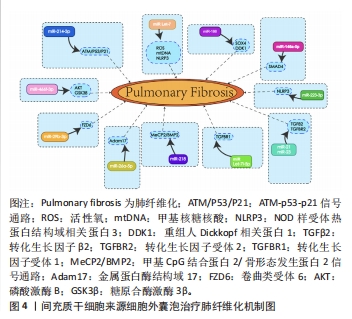
2.3 MSC-EVs治疗肺纤维化研究进展 在中国知网、PubMed数据库筛选近5年来涉及MSC-EVs治疗肺纤维化相关研究21篇[84-104],实验涉及的具体细节见表2,其作用机制主要通过细胞外囊泡介导的miRNA引起靶向通路改变进而产生抗纤维化效应,多数研究阐明具体发挥作用的miRNA及其靶基因,汇总图见图4,其作用的发挥也主要是通过抑制相关炎症因子,从而减轻肺部纤维病变,同时促进肺部组织修复。值得关注的是,较多研究着力于上皮-间质转化的延缓,其中较为重要的是不同来源的MSCs能通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的改变抑制上皮-间质转化的发生[84-85],至于其他研究,发挥具体作用的miRNA及其相应靶基因还有待进一步探讨。

| [1] NALYSNYK L, CID-RUZAFA J, ROTELLA P, et al. Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: review of the literature. Eur Respir Rev. 2012; 21(126):355-361. [2] KING TE JR, PARDO A, SELMAN M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 2011; 378(9807):1949-1961. [3] WAKWAYA Y, BROWN KK. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Epidemiology, Diagnosis and Outcomes. Am J Med Sci. 2019;357(5):359-369. [4] MOSS BJ, RYTER SW, ROSAS IO. Pathogenic Mechanisms Underlying Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2022;17:515-546. [5] CHIOMA OS, DRAKE WP. Role of Microbial Agents in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Yale J Biol Med. 2017;90(2):219-227. [6] GENTILE F, AIMO A, FORFORI F, et al. COVID-19 and risk of pulmonary fibrosis: the importance of planning ahead. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2020;27(13):1442-1446. [7] CAPLAN AI. Mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 1991;9(5):641-650. [8] ANDRZEJEWSKA A, LUKOMSKA B, JANOWSKI M. Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stem Cells: From Roots to Boost. Stem Cells. 2019;37(7):855-864. [9] VASANTHAN J, GURUSAMY N, RAJASINGH S, et al. Role of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Regenerative Therapy. Cells. 2020;10(1):54. [10] MISHRA VK, SHIH HH, PARVEEN F, et al. Identifying the Therapeutic Significance of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells. 2020;9(5):1145. [11] SAMSONRAJ RM, RAGHUNATH M, NURCOMBE V, et al. Concise Review: Multifaceted Characterization of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Use in Regenerative Medicine. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(12):2173-2185. [12] LI DY, LI RF, SUN DX, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in pulmonary fibrosis: a meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):461. [13] LAI P, WENG J, GUO L, et al. Novel insights into MSC-EVs therapy for immune diseases. Biomark Res. 2019;7:6. [14] HARRELL CR, JOVICIC N, DJONOV V, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles as New Remedies in the Therapy of Inflammatory Diseases. Cells. 2019;8(12):1605. [15] RANI S, RYAN AE, GRIFFIN MD, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Extracellular Vesicles: Toward Cell-free Therapeutic Applications. Mol Ther. 2015;23(5):812-823. [16] FERNÁNDEZ-FRANCOS S, EIRO N, COSTA LA, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells as a Cornerstone in a Galaxy of Intercellular Signals: Basis for a New Era of Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(7):3576. [17] MEYER KC. Pulmonary fibrosis, part I: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and diagnosis. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2017;11(5):343-359. [18] WANG YY, ZHANG CY, MA YQ, et al. Therapeutic effects of C-28 methyl ester of 2-cyano-3,12-dioxoolean-1,9-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO-Me; bardoxolone methyl) on radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:3163-3178. [19] AMERICAN THORACIC SOCIETY. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161(2 Pt 1):646-664. [20] WICK G, GRUNDTMAN C, MAYERL C, et al. The immunology of fibrosis. Annu Rev Immunol. 2013;31:107-135. [21] ADAMS TS, SCHUPP JC, POLI S, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals ectopic and aberrant lung-resident cell populations in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Adv. 2020;6(28):eaba1983. [22] LOCATI M, MANTOVANI A, SICA A. Macrophage activation and polarization as an adaptive component of innate immunity. Adv Immunol. 2013;120:163-184. [23] ZHANG L, WANG Y, WU G, et al. Macrophages: friend or foe in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Respir Res. 2018;19(1):170. [24] HEUKELS P, MOOR CC, VON DER THÜSEN JH, et al. Inflammation and immunity in IPF pathogenesis and treatment. Respir Med. 2019;147:79-91. [25] WICK G, BACKOVIC A, RABENSTEINER E, et al. The immunology of fibrosis: innate and adaptive responses. Trends Immunol. 2010;31(3):110-119. [26] PARK SJ, HAHN HJ, OH SR, et al. Theophylline Attenuates BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting Th17 Differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1019. [27] LIANG J, ZHANG Y, XIE T, et al. Hyaluronan and TLR4 promote surfactant-protein-C-positive alveolar progenitor cell renewal and prevent severe pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Nat Med. 2016;22(11):1285-1293. [28] MILLIEN VO, LU W, SHAW J, et al. Cleavage of fibrinogen by proteinases elicits allergic responses through Toll-like receptor 4. Science. 2013;341(6147):792-796. [29] O’DWYER DN, ARMSTRONG ME, TRUJILLO G, et al. The Toll-like receptor 3 L412F polymorphism and disease progression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188(12):1442-1450. [30] MCELROY AN, INVERNIZZI R, LASKOWSKA JW, et al. Candidate Role for Toll-like Receptor 3 L412F Polymorphism and Infection in Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205(5):550-562. [31] TIAN R, ZHU Y, YAO J, et al. NLRP3 participates in the regulation of EMT in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Cell Res. 2017;357(2):328-334. [32] JÄGER B, SEELIGER B, TERWOLBECK O, et al. The NLRP3-Inflammasome-Caspase-1 Pathway Is Upregulated in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Acute Exacerbations and Is Inducible by Apoptotic A549 Cells. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:642855. [33] CHO SJ, MOON JS, NIKAHIRA K, et al. GLUT1-dependent glycolysis regulates exacerbation of fibrosis via AIM2 inflammasome activation. Thorax. 2020;75(3): 227-236. [34] TOMASEK JJ, GABBIANI G, HINZ B, et al. Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3(5):349-363. [35] TSUKUI T, SUN KH, WETTER JB, et al. Collagen-producing lung cell atlas identifies multiple subsets with distinct localization and relevance to fibrosis. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1920. [36] CHILOSI M, CALIÒ A, ROSSI A, et al. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition-related proteins ZEB1, β-catenin, and β-tubulin-III in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Mod Pathol. 2017;30(1):26-38. [37] WILLIS BC, LIEBLER JM, LUBY-PHELPS K,et al. Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelial cells by transforming growth factor-beta1: potential role in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 2005;166(5):1321-1332. [38] MARMAI C, SUTHERLAND RE, KIM KK, et al. Alveolar epithelial cells express mesenchymal proteins in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011;301(1):L71-L78. [39] MAHER TM, OBALLA E, SIMPSON JK, et al. An epithelial biomarker signature for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an analysis from the multicentre PROFILE cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5(12):946-955. [40] BARRATT S, MILLAR A. Vascular remodelling in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. QJM. 2014;107(7):515-519. [41] KEANE MP, ARENBERG DA, LYNCH JP 3RD, et al. The CXC chemokines, IL-8 and IP-10, regulate angiogenic activity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Immunol. 1997;159(3):1437-1443. [42] RUSSO RC, GUABIRABA R, GARCIA CC, et al. Role of the chemokine receptor CXCR2 in bleomycin-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009;40(4):410-421. [43] MARGARITOPOULOS GA, ANTONIOU KM, KARAGIANNIS K, et al. Investigation of angiogenetic axis Angiopoietin-1 and -2/Tie-2 in fibrotic lung diseases: a bronchoalveolar lavage study. Int J Mol Med. 2010;26(6):919-923. [44] AMANO H, MATSUI Y, HATANAKA K, et al. VEGFR1-tyrosine kinase signaling in pulmonary fibrosis. Inflamm Regen. 2021;41(1):16. [45] ANDO M, MIYAZAKI E, ITO T, et al. Significance of serum vascular endothelial growth factor level in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lung. 2010; 188(3):247-252. [46] MURRAY LA, HABIEL DM, HOHMANN M, et al. Antifibrotic role of vascular endothelial growth factor in pulmonary fibrosis. JCI Insight. 2017;2(16):e92192. [47] TAKAO S, NAKASHIMA T, MASUDA T, et al. Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells cultured in serum-free media demonstrate enhanced antifibrotic abilities via prolonged survival and robust regulatory T cell induction in murine bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):506. [48] HUANG J, HUANG J, NING X,et al. CT/NIRF dual-modal imaging tracking and therapeutic efficacy of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells labeled with Au nanoparticles in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(8): 1713-1727. [49] FELIX RG, BOVOLATO ALC, COTRIM OS, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells and adipose-derived stem cell-conditioned medium modulate in situ imbalance between collagen I- and collagen V-mediated IL-17 immune response recovering bleomycin pulmonary fibrosis. Histol Histopathol. 2020;35(3):289-301. [50] DA SILVA KN, PINHEIRO PCG, GOBATTO ALN, et al. Immunomodulatory and Anti-fibrotic Effects Following the Infusion of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in a Critically Ill Patient With COVID-19 Presenting Lung Fibrosis: A Case Report. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:767291. [51] GAD ES, SALAMA AAA, EL-SHAFIE MF, et al. The Anti-fibrotic and Anti-inflammatory Potential of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Nintedanib in Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis in Rats. Inflammation. 2020; 43(1):123-134. [52] NI K, LIU M, ZHENG J, et al. PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway Mediates the Alleviation of Pulmonary Fibrosis by Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Humanized Mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018;58(6):684-695. [53] RUBIO GA, ELLIOT SJ, WIKRAMANAYAKE TC, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells prevent bleomycin-induced lung and skin fibrosis in aged mice and restore wound healing. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(8):5503-5512. [54] MORONCINI G, PAOLINI C, ORLANDO F, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells from human umbilical cord prevent the development of lung fibrosis in immunocompetent mice. PLoS One. 2018;13(6):e0196048. [55] XIAO K, LIU C, WANG H, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing CXCR7 facilitate treatment of ARDS-associated pulmonary fibrosis via inhibition of Notch/Jag1 mediated by the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165:115124. [56] CHEN X, WU Y, WANG Y, et al. Human menstrual blood-derived stem cells mitigate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis through anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammatory effects. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):477. [57] ABDEL HALIM AS, AHMED HH, AGLAN HA, et al. Role of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in alleviating pulmonary epithelium damage and extracellular matrix remodeling in a rat model of lung fibrosis induced by amiodarone. Biotech Histochem. 2021;96(6):418-430. [58] CHEN S, CUI G, PENG C, et al. Transplantation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates pulmonary fibrosis of silicosis via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis effects in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):110. [59] LIU J, PENG D, YOU J, et al. Type 2 Alveolar Epithelial Cells Differentiated from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Mouse Pulmonary Fibrosis Through β-Catenin-Regulated Cell Apoptosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2021; 30(13):660-670. [60] YANG X, SUN W, JING X, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress modulates the fate of lung resident mesenchymal stem cell to myofibroblast via C/EBP homologous protein during pulmonary fibrosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):279. [61] XIAO K, HE W, GUAN W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells reverse EMT process through blocking the activation of NF-κB and Hedgehog pathways in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(10):863. [62] ZHANG E, YANG Y, CHEN S, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis potentially by attenuating Wnt/β-catenin signaling in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):311. [63] SHAO L, ZHANG Y, SHI W, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells can repair radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis via a DKK-1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Tissue Res. 2021;384(1):87-97. [64] LEE EJ, CÁRDENES N, ÁLVAREZ D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells reduce ER stress via PERK-Nrf2 pathway in an aged mouse model. Respirology. 2020;25(4):417-426. [65] KHAJVAND-ABEDINI M, BAHMANI M, ZIAMAJIDI N, et al. The Restoring Effect of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Cell-Conditioned Medium (hMSC-CM) against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Male Wistar Rats. Int J Inflam. 2022;2022:7179766. [66] 黄坤,周勇,刘美芳,等. 甘草酸二铵联合骨髓间充质干细胞治疗大鼠肺纤维化急性加重的实验研究[J].中国呼吸与危重监护杂志,2020,19(1):64-69. [67] WANG X, ZHAO S, LAI J, et al. Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Antifibrotic Effects of Gingival-Derived MSCs on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;23(1):99. [68] NASSAR SZ, ABDELMONSIF DA, ALI RG, et al. Sodium hydrosulfide and bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells combined therapy for bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats: Implication of micro RNA-21 and Lnc GAS5. Life Sci. 2022;309:120988. [69] LI X, LI C, TANG Y, et al. NMDA receptor activation inhibits the antifibrotic effect of BM-MSCs on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018;315(3):L404-L421. [70] CÁRDENES N, ÁLVAREZ D, SELLARÉS J, et al. Senescence of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):257. [71] CAMPO A, GONZÁLEZ-RUIZ JM, ANDREU E, et al. Endobronchial autologous bone marrow-mesenchymal stromal cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a phase I trial. ERJ Open Res. 2021;7(2):00773-2020. [72] AVERYANOV A, KOROLEVA I, KONOPLYANNIKOV M, et al. First-in-human high-cumulative-dose stem cell therapy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with rapid lung function decline. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(1):6-16. [73] HE F, WANG Y, LI Y, et al. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats by inhibiting the inflammatory response. Life Sci. 2020;243:117290. [74] GONG L, WANG X, XU S, et al. Human Amnion-Derived MSCs Alleviate Acute Lung Injury and Hinder Pulmonary Fibrosis Caused by Paraquat in Rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:3932070. [75] FIKRY H, SALEH LA, GAWAD SA. Therapeutic effect of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AD-MSCs) compared to pirfenidone on corticosteroid resistance in a mouse model of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Histol Histopathol. 2022;37(11):1065-1083. [76] Shi L, Han Q, Hong Y, et al. Inhibition of miR-199a-5p rejuvenates aged mesenchymal stem cells derived from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and improves their therapeutic efficacy in experimental pulmonary fibrosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):147. [77] WU X, GOU H, ZHOU O, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells combined with pirfenidone upregulates the expression of RGS2 in the pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Respir Res. 2022;23(1):270. [78] CHU KA, WANG SY, YEH CC, et al. Reversal of bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis by a xenograft of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton’s jelly. Theranostics. 2019;9(22):6646-6664. [79] LI R, ZHANG H, ZHANG J, et al. hucMSCs treatment ameliorated pulmonary fibrosis via downregulating the circFOXP1-HuR-EZH2/STAT1/FOXK1 autophagic axis. Stem Cells. 2023:sxad053. [80] ZHANG H, ZHU Q, JI Y, et al. hucMSCs treatment prevents pulmonary fibrosis by reducing circANKRD42-YAP1-mediated mechanical stiffness. Aging (Albany NY). 2023;15(12):5514-5534. [81] LIU D, KONG F, YUAN Y, et al. Decorin-Modified Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Attenuate Radiation-Induced Lung Injuries via Regulating Inflammation, Fibrotic Factors, and Immune Responses. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018;101(4):945-956. [82] MAHMOUDI T, ABDOLMOHAMMADI K, BASHIRI H, et al. Hydrogen Peroxide Preconditioning Promotes Protective Effects of Umbilical Cord Vein Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Experimental Pulmonary Fibrosis. Adv Pharm Bull. 2020;10(1):72-80. [83] 苟好. EPCR基因敲低的人脐带间充质干细胞治疗博来霉素所致小鼠肺纤维化及机制初探[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2018. [84] ZHANG X, YE L, TANG W, et al. Wnt/β-Catenin Participates in the Repair of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome-Associated Early Pulmonary Fibrosis via Mesenchymal Stem Cell Microvesicles. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16:237-247. [85] ZHANG E, GENG X, SHAN S, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition potentially via attenuating Wnt/β-catenin signaling to alleviate silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2021;31(9):655-666. [86] LEI X, HE N, ZHU L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Radiation-Induced Lung Injury via miRNA-214-3p. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021;35(11):849-862. [87] YANG S, LIU P, GAO T, et al. Every road leads to Rome: therapeutic effect and mechanism of the extracellular vesicles of human embryonic stem cell-derived immune and matrix regulatory cells administered to mouse models of pulmonary fibrosis through different routes. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):163. [88] SUN L, ZHU M, FENG W, et al. Exosomal miRNA Let-7 from Menstrual Blood-Derived Endometrial Stem Cells Alleviates Pulmonary Fibrosis through Regulating Mitochondrial DNA Damage. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:4506303. [89] TAN JL, LAU SN, LEAW B, et al. Amnion Epithelial Cell-Derived Exosomes Restrict Lung Injury and Enhance Endogenous Lung Repair. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018; 7(2):180-196. [90] MANSOURI N, WILLIS GR, FERNANDEZ-GONZALEZ A, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes prevent and revert experimental pulmonary fibrosis through modulation of monocyte phenotypes. JCI Insight. 2019;4(21):e128060. [91] ZHOU J, LIN Y, KANG X, et al. microRNA-186 in extracellular vesicles from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviates idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis via interaction with SOX4 and DKK1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):96. [92] LI Y, SHEN Z, JIANG X, et al. Mouse mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-466f-3p reverses EMT process through inhibiting AKT/GSK3β pathway via c-MET in radiation-induced lung injury. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41(1):128. [93] WAN X, CHEN S, FANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles suppress the fibroblast proliferation by downregulating FZD6 expression in fibroblasts via micrRNA-29b-3p in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(11):8613-8625. [94] ROZIER P, MAUMUS M, MARIA ATJ, et al. Lung Fibrosis Is Improved by Extracellular Vesicles from IFNγ-Primed Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Murine Systemic Sclerosis. Cells. 2021;10(10):2727. [95] BANDEIRA E, OLIVEIRA H, SILVA JD, et al. Therapeutic effects of adipose-tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles in experimental silicosis. Respir Res. 2018;19(1):104. [96] HOU L, ZHU Z, JIANG F, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviated silica induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice via circPWWP2A/miR-223-3p/NLRP3 axis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023;251:114537. [97] XU C, ZHAO J, LI Q, et al. Exosomes derived from three-dimensional cultured human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate pulmonary fibrosis in a mouse silicosis model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):503. [98] SHI L, REN J, LI J, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells alleviate pulmonary fibrosis by means of transforming growth factor-β signaling inhibition. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):230. [99] 杨静,胡华钟,张书勤,等.脐带间充质干细胞来源的外泌体通过抑制上皮间质转化缓解肺纤维化[J].南方医科大学学报,2020,40(7):988-994. [100] 韩艳煦. 磁化脐带间充质干细胞外泌体对特发性肺纤维化的治疗研究[D].长春:东北师范大学,2021. [101] ZHAO J, JIANG Q, XU C, et al. MiR-26a-5p from HucMSC-derived extracellular vesicles inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition by targeting Adam17 in silica-induced lung fibrosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023;257:114950. [102] ZHAO Y, DU L, SUN J, et al. Exosomal miR-218 derived from mesenchymal stem cells inhibits endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition by epigenetically modulating of BMP2 in pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023. doi: 10.1007/s10565-023-09810-z. [103] XU C, HOU L, ZHAO J, et al. Exosomal let-7i-5p from three-dimensional cultured human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells inhibits fibroblast activation in silicosis through targeting TGFBR1. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022;233:113302. [104] 李晗.缺氧预处理人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过miRNA-146a-5p调控SMAD4减轻肺纤维化的研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2023. [105] FURLANI D, UGURLUCAN M, ONG L, et al. Is the intravascular administration of mesenchymal stem cells safe? Mesenchymal stem cells and intravital microscopy. Microvasc Res. 2009;77(3):370-376. [106] WEISS ARR, DAHLKE MH. Immunomodulation by Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Mechanisms of Action of Living, Apoptotic, and Dead MSCs. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1191. [107] DJOUAD F, PLENCE P, BONY C, et al Immunosuppressive effect of mesenchymal stem cells favors tumor growth in allogeneic animals. Blood. 2003;102(10): 3837-3844. [108] SIRITHAMMAJAK S, MANOCHANTR S, TANTRAWATPAN C, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from the Placenta and Chorion Suppress the Proliferation while Enhancing the Migration of Human Breast Cancer Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:4020845. [109] HU C, ZHAO L, ZHANG L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based cell-free strategies: safe and effective treatments for liver injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):377. [110] ZHANG H, XIAO B, JIANG L, et al. Inhibition of mesenchymal stromal cells’ chemotactic effect to ameliorate paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Toxicol Lett. 2019;307:1-10. [111] LAN YW, CHOO KB, CHEN CM, et al. Hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells attenuate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):97. [112] LV Y, YU C, LI X, et al. ROS-activatable nanocomposites for CT imaging tracking and antioxidative protection of mesenchymal stem cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis therapy. J Control Release. 2023;357:249-263. |
| [1] | 余伟杰, 刘爱峰, 陈继鑫, 郭天赐, 贾易臻, 冯汇川, 杨家麟. 机器学习在腰椎间盘突出症诊治中的优势和应用策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [2] | 陈凯佳, 刘景云, 曹 宁, 孙建波, 周 燕, 梅建国, 任 强. 组织工程技术在股骨头坏死治疗中的应用及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [3] | 林泽玉, 徐 林. 痛风致骨破坏机制的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| [4] | 冯睿钦, 韩 娜, 张 蒙, 谷馨怡, 张丰识. 1%富血小板血浆联合骨髓间充质干细胞促进周围神经损伤的修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [5] | 邱晓燕, 李碧欣, 黎敬弟, 范垂钦, 马 廉, 王鸿武. MAFA-PDX1过表达慢病毒感染人脐带间充质干细胞向胰岛素分泌细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1000-1006. |
| [6] | 刘麒薇, 张俊辉, 杨 袁, 王金娟. 脐带间充质干细胞治疗多囊卵巢综合征的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [7] | 刘建宏, 廖世杰, 李波香, 唐生平, 韦帧翟, 丁晓飞. 细胞外囊泡携带非编码RNA调控破骨细胞的活化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1076-1082. |
| [8] | 潘小龙, 樊飞燕, 应春苗, 刘飞祥, 张运克. 中药抑制间充质干细胞衰老的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [9] | 刘瀚峰, 王晶晶, 余云生. 人造外泌体治疗心肌梗死:应用现状及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1118-1123. |
| [10] | 诸葛晓萱, 李 策, 包广洁, 康 宏. 缝隙连接蛋白43经典与非经典作用在疾病治疗中的潜在价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1130-1136. |
| [11] | 马树微, 何 生, 韩 冰, 张缭云. 间充质干细胞来源外泌体治疗动物急性肝衰竭的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [12] | 张克凡, 石 辉. 细胞因子治疗骨关节炎的研究现状及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [13] | 李佳琪, 黄元礼, 李 妍, 王春仁, 韩倩倩. 非交联透明质酸分子质量降解的机制及影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 747-752. |
| [14] | 徐 溶, 王豪杰, 耿梦想, 孟 凯, 王 卉, 张克勤, 赵荟菁. 多孔聚四氟乙烯人工血管制备及功能化改性研究的进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 759-765. |
| [15] | 陈小芳, 郑国爽, 李茂源, 于炜婷. 可注射海藻酸钠水凝胶的制备及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 789-794. |
间充质干细胞(mesenchymal stem cells,MSCs)一词由CAPLAN[7]于1991年提出,属于成体干细胞,但是其具有较强的自我更新和多向分化的能力[8],它们存在于许多不同的组织和器官中,例如脂肪组织、骨髓、皮肤、脐血等[9],MSCs具有良好的免疫调节和免疫抑制作用[10],还参与组织的发育和修复[11]。近年来发现MSCs具有修复脏器纤维化的能力,在再生应用领域受到越来越多的关注。研究发现不同来源 MSCs对博来霉素、脂多糖、二氧化硅、百草枯等诱导的肺纤维化模型有明确的实验疗效[12]。
间充质干细胞来源细胞外囊泡(mesenchymal stem cells extracellular vesicles,MSC-EVs)根据起源、直径、膜标志物的差异被分为3种类型,分别为外泌体、微囊泡、凋亡小体,MSC-EVs富含信使RNA(mRNA)、microRNA(miRNA)、细胞因子、趋化因子、免疫调节因子等生物活性分子[13-14],细胞外囊泡可以通过介导细胞间通讯的方式发挥生物学效应[15]。近来发现,MSCs可以通过旁分泌作用释放细胞外囊泡,发挥抑制炎症反应、调节免疫功能和对抗组织纤维化的作用[15-16]。
该文章就肺纤维化发生机制、MSCs及MSC-EVs治疗肺纤维化的机制作一综述,讨论了现有研究的优缺点以及现实应用的瓶颈与展望,为临床肺纤维化的治疗提供依据以及为后续治疗新药研究提供潜在的干预靶点。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2023-08-01 进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2000 年8月至2023 年8月,以及年代久远的经典文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网电子期刊数据库和PubMed电子期刊数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词:“间充质干细胞”“间充质干细胞细胞外囊泡”“肺纤维化”;英文检索词:“mesenchymal stem cells”“mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles”“ pulmonary fibrosis”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述、述评、经验交流和病例报告。
1.1.6 检索策略 中国知网和PubMed数据库检索策略见图1。
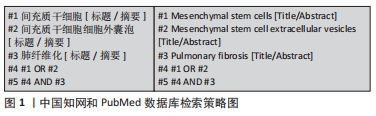
1.1.8 检索文献量 初步检索到中文文献78篇,英文文献172篇。
1.2 纳入标准 ①描述肺纤维化研究进展的文献;②各种干细胞及其细胞外囊泡治疗肺纤维化疾病的文献;③同一领域选择新近文献或者在权威杂志发表的文献。
1.3 排除标准 与研究主题不相符或者重复陈旧性文献。
1.4 文献质量评估和数据的提取 根据文章题目及摘要进行初步筛选,排除与研究主题不符、发表年代久远以及重复文献,纳入112篇文献,重点对研究内容相关度高的58篇文献进行综述分析,其中中国知网数据库5篇,PubMed数据库53篇,具体检索流程见图2。
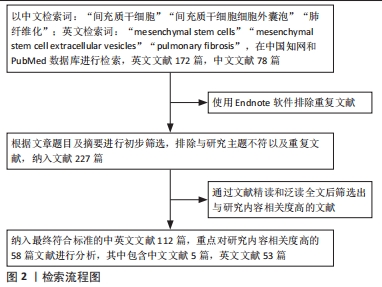
目前,肺移植是唯一有效的肺纤维化治疗策略,但由于其复杂性、多层次管理和捐赠器官供应有限,肺纤维化仍然是临床医生以及科研工作者面临的重大挑战。近年来MSCs和MSC-EVs的研究进展为肺纤维化治疗提供了大量的理论和实践基础,但仍有一些局限性以及需要研究的难题:①尽管通过现有单细胞测序等新兴技术的辅助,但在纤维化过程中使用MSCs和MSC-EVs发生的动态变化等方面的研究仍然有限。②现有实验缺乏标准化的治疗方案:有研究发现,不同的干细胞供体、移植剂量、移植时间等都会影响疗效[70-71,78,81,86,89,95],从而导致研究结果的可比性和可复制性有限。关于MSCs和MSC-EVs的最佳来源、供体条件、培养条件、给药途径、剂量、给药间隔等影响因素,仍待进一步研究以优化其治疗效果、改进临床干预试验的设计,从而确保MSCs治疗的安全性和循证性,要根据具体的实验安排或患者疾病体征选择相对有效的给药方法。③基础研究的最终目标是临床转化,为临床患者减轻痛苦。在转化层面上,MSCs与普通细胞一样,需要进行细胞采集、细胞分离、细胞培养、细胞收获和细胞鉴定等标准化程序,国家药品监督管理局在2023年4月最新发布的试行版《人源干细胞产品药学研究与评价技术指导原则》在一定程度上做到了规范干细胞的生产工艺与质量标准,而细胞外囊泡实现转化的标准制备方法与质量管理原则还待进一步探索与研究。另外,干细胞移植的致瘤问题也急需解决。进入临床普遍应用应严格掌握其绝对适应证,以发挥其积极的正面效用。
现有研究所证明的MSCs和MSC-EVs治疗肺纤维化的优缺点对比明显。MSCs的优点有:①MSCs可以分化为不同类型的细胞,从而能发挥组织修复和再生等功能;②MSCs具有优异的抗炎和免疫调节作用,从而减少炎症损伤造成的纤维化反应;③富含丰富生长因子和细胞因子,可以针对抑制纤维化过程以及促进组织修复过程发挥重要作用。MSCs的缺点有:①由于其自身有一定的免疫特性,移植后可能会引发宿主的免疫反应从而导致免疫排斥反应;②长期安全性与致瘤性还待进一步评估,有动物实验以及临床研究证实干细胞输入动物以及人体后,会造成不同程度的的血管栓塞,甚至造成死亡[71,105],MSCs移植可能导致体内肿瘤生长[106-108]。MSC-EVs的优点有:①较好的生物相容性,其以无细胞治疗的方式有效避免了免疫排斥反应;②较高的稳定性:有研究证明干细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡相比于干细胞,存储和运输条件更加稳定,在使用时质量和数量更方便控制[109],是一种相对有效的有前景的治疗手段,值得进一步的研究探索;③MSC-EVs相对于MSCs本身较小,可以更容易穿透组织和细胞屏障,从而更好地传递其包含的生物活性分子。MSC-EVs的缺点有:①现有科学方法从细胞培养物中分离和纯化大量的MSC-EVs仍然存在技术上的挑战,而且其获得量相比于MSCs十分有限,普遍适用难度较大,不同来源和制备方式的细胞外囊泡可能具有不同的功能和效果,因此需要更多的研究来确定公认的最佳制备方法;②由于其现有研究较少,具体作用机制尚不完全清楚,导致了现阶段进一步转化发展的抑制。
现有研究证明MSCs和MSC-EVs对于不同模型或不同疾病所致的肺纤维化存在一定的治疗效果和机制上的差异,这些差异可以归因于动物模型的差异、疾病病理机制的差异、造模药物浓度以及时间所造成的炎症程度、组织损伤程度差异以及细胞外囊泡和间充质干细胞来源不同等因素导致的。实验设计和方法的差异也会对实验结果造成影响。因此,在进行治疗效果评估时,需要综合考虑这些因素,并进行更多的研究以进一步了解和优化治疗策略。
综上所述,MSCs和MSC-EVs治疗肺纤维化的研究取得了一些进展,但仍需要进一步深入研究来解决现有的问题和挑战。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 这篇综述与其他相关综述的不同之处在于清晰多角度地探究了MSCs和MSC-EVs在肺纤维化治疗中的应用,系统详细地总结了造模药物、剂量、干预时间、干预用量以及作用机制,相较于其他综述可能更侧重于总结已有的临床研究结果和治疗效果,该综述着重于探讨治疗机制上的多样性和复杂性。
该综述也着眼于探讨目前治疗中面临的问题与挑战,如临床试验中的质控问题、移植途径和干细胞的致瘤性等。这种全面性的总结使读者能够更好地了解该治疗方法的局限性,也为未来的研究和临床应用提供了指导。
此外,该综述通过广泛收集和整理文献,采用系统性的文献综述方法,确保了文章的可信度和准确性,其所引用的高质量研究成果和临床试验结果进一步增强了文章的权威性。作者对文献中的实验数据和临床试验结果进行了全面的分析和总结,使得读者能够全面了解MSCs和MSC-EVs治疗肺纤维化的疗效和潜力。
3.3 综述的局限性 该综述对MSCs和MSC-EVs在肺纤维化治疗方面进行了深入细致的探讨,局限性主要在于知识的时效性和研究进展的快速更新。随着科学研究的不断进展,肺纤维化治疗领域可能会出现新的发现和突破,其中包括新的治疗方法、新的药物或新的治疗机制等,因此某些最新的研究成果和治疗进展可能未能被充分纳入,这使得该综述在时效性方面存在一定的局限性,读者在阅读时需要对新的研究进展保持警觉。由于MSCs和MSC-EVs治疗肺纤维化还处于不断发展和探索阶段,其转化临床应用和效果尚未完全成熟。该综述所涉及的临床试验结果和治疗效果可能受到样本量较小、研究设计不足等因素的影响,因此需要更多大规模、多中心的临床研究来验证其有效性和安全性。
3.4 综述的重要意义 首先,通过对已有文献和研究成果的综合整理和分析,为科研工作者和临床医务人员提供了一份全面的参考资料。读者可以深入了解MSCs和MSC-EVs在肺纤维化治疗中的现有应用以及潜在价值,掌握其治疗机制和可能的临床效果,这将有助于激发更多的科学家投身于该领域的研究,推动肺纤维化治疗的创新和进步。其次,该综述探讨了目前面临的问题和挑战,如剂量确定、移植途径等。这些问题的深入分析使得科研工作者能够更好地认识到该治疗方法的局限性和现实难题,从而引导未来研究的重点和方向。通过针对这些问题的研究和解决,将有助于优化治疗方案,提高治疗效果,以便更好地应用于临床实践。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 对于MSCs和MSC-EVs治疗肺纤维化的现有研究困难,可以从以下方面来采取措施:①通过对发病机制、治疗机制以及细胞间通讯等领域的研究,可以为未来的临床研究和应用提供更可靠的科学依据。②随着新技术的研究发展,在以往单纯干细胞或单纯细胞外囊泡疗效研究的基础上,学者们开始研究不同条件预处理的MSCs和MSC-EVs治疗肺纤维化的效果,其中包括炎症因子、基因工程编辑、缺氧、磁化等条件预处理,达到了进一步优化治疗效果的目
的[59,81,83,94,100,110-112],还可以通过引入特定的趋化因子或受体来促进MSCs或MSC-EVs的迁移,并利用纳米技术或特定的载体来实现靶向定植、定向释放等。③联合运用多种疗法:干细胞联合临床药物治疗疗效优于两者单一治疗的疗效[66],这也是未来将MSCs或MSC-EVs用于临床转化的又一理论支撑,除了作为单独的细胞疗法,MSCs或MSC-EVs还可以被利用为载体,用于输送其他生物活性物质,如基因、药物或治疗性蛋白质等。这种组合治疗的策略有望实现更精确的治疗效果,并提高肺纤维化患者的生存率和生活质量。④临床数据支持:进一步的临床研究也是必要的,需要系统的大量临床试验数据以评估MSCs或MSC-EVs治疗肺纤维化的长期疗效和安全性,来推动这些治疗方法的临床应用。同时,长期随访研究可以帮助评估治疗的持久性和潜在的不良影响。
综上所述,MSCs或MSC-EVs治疗肺纤维化经过漫长的研究发展,近年来已取得了瞩目的成就。相信通过科研工作者及医务人员共同的努力,进一步探索研究其相关细节,MSCs或MSC-EVs会早日广泛用于临床疾病的治疗。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
间充质干细胞:是一类多能性的成体干细胞,起源于间充质组织,主要存在于骨髓、脂肪组织、脐带以及其他组织中。这些干细胞具有自我更新和多向分化能力,可以分化为多种细胞类型,包括成骨细胞、软骨细胞、脂肪细胞和肌肉细胞等,已广泛应用于组织工程、再生医学和疾病治疗等领域。细胞外囊泡:是一类由细胞释放到细胞外的小型膜包裹的囊泡,其直径通常在30-1 000 nm之间。细胞外囊泡包含了细胞内部的生物活性分子,如蛋白质、核酸(RNA和DNA)、脂质等。这些囊泡可以通过与周围细胞进行物质交换,传递包含的生物信息,从而调节目标细胞的生物学功能和信号传导。细胞外囊泡在细胞间的通讯和信息传递中起着重要的作用,被认为是一种重要的细胞间通讯介质,对于维持组织稳态和参与疾病发生发展具有重要意义。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
现有研究证明间充质干细胞及其细胞外囊泡对于不同模型或不同疾病所致的肺纤维化存在一定的治疗效果和机制上的差异。这些差异可以归因于由于动物模型的差异、疾病病理机制的差异、造模药物浓度以及时间所造成的炎症程度、组织损伤程度差异以及细胞外囊泡和间充质干细胞来源不同等因素导致的。实验设计和方法的差异也会对实验结果造成差异。因此,在进行治疗效果评估时,需要综合考虑这些因素,并进行更多的研究以进一步了解和优化治疗策略。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||