中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (13): 2082-2089.doi: 10.12307/2024.154
• 干细胞基础实验 basic experiments of stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
骨髓增生异常综合征与急性髓系白血病之间免疫浸润相关基因的筛选及验证
邓发滑1,胡华丽1,王斯奇1,许建霞1,禄婷婷1,2,黄 海1,2,韦四喜1,2
- 1贵州医科大学医学检验学院临床生化教研室,贵州省贵阳市 550004;2贵州医科大学附属医院临床检验中心,贵州省贵阳市 550004
Screening and verification of genes related to immune infiltration between myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia
Deng Fahua1, Hu Huali1, Wang Siqi1, Xu Jianxia1, Lu Tingting1, 2, Huang Hai1, 2, Wei Sixi1, 2
- 1Clinical Biochemistry Teaching and Research Department, School of Medical Laboratory, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Clinical Laboratory Center of Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
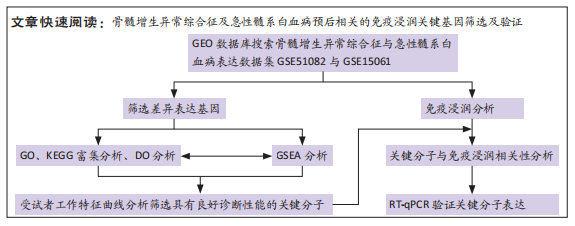
文题释义:
骨髓增生异常综合征:是一种源于造血干细胞的异质性髓系克隆性疾病,以髓系细胞分化及发育异常为特征,常表现为无效造血、难治性血细胞减少、造血功能衰竭及高风险向急性髓系白血病转化。免疫浸润:肿瘤的免疫浸润是指免疫细胞在肿瘤组织中发生浸润,从而影响肿瘤内免疫反应的过程。
背景:骨髓增生异常综合征具有较高的急性髓系白血病转化风险,有研究表明免疫浸润在二者之间发挥重要作用,但免疫细胞浸润与相关差异表达基因的调控关系仍需更多研究证实。
目的:通过生物信息学分析方法,寻找与骨髓增生异常综合征和急性髓系白血病具有预后意义的差异表达基因,探讨差异基因与免疫浸润细胞调控在疾病发生发展中的可能作用及机制。方法:利用GEO数据集筛选差异表达基因用于生物信息学分析,对差异表达基因进行DO、GO、KEGG和GSEA分析。利用TCGA预后数据库绘制差异表达基因的K-M曲线,并对预后相关的差异基因进行受试者工作特征曲线分析判断基因的临床诊断性能。最后,采用CIBERSORT分析预后相关关键基因与免疫浸润细胞分布之间的相关性,利用RT-qPCR检测健康对照、骨髓增生异常综合征及急性髓系白血病患者外周血样本对筛选出的关键基因进行初步验证。
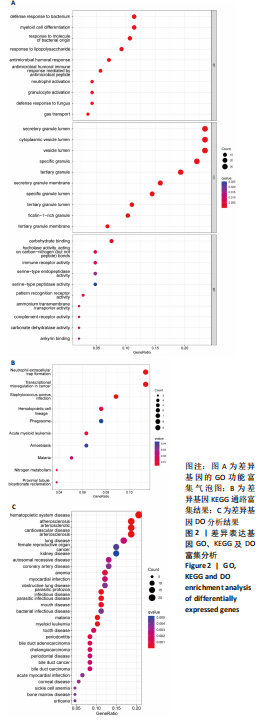
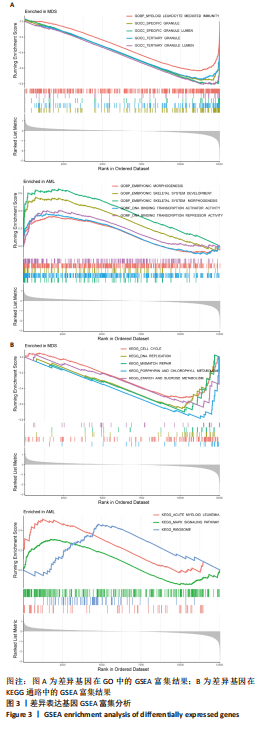
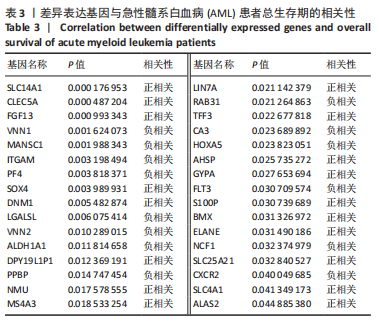
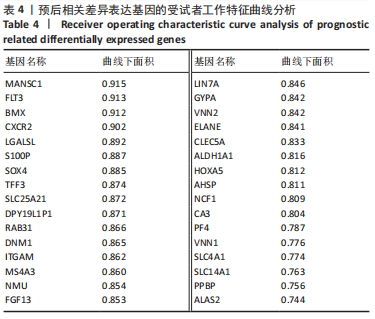
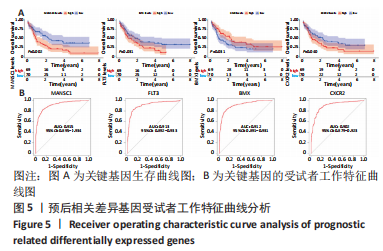
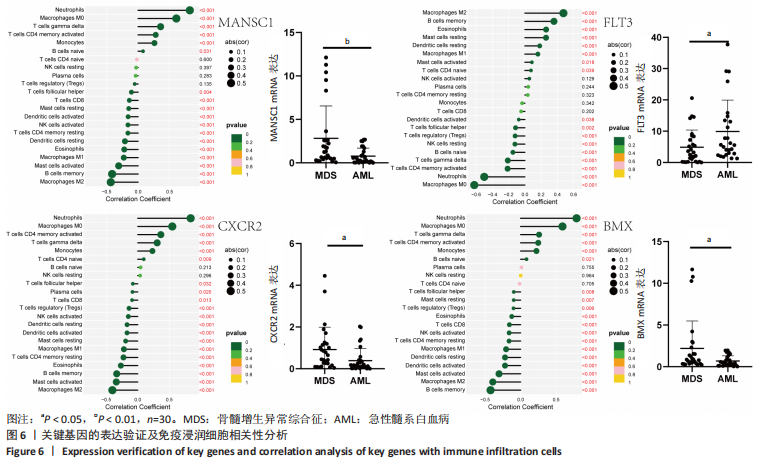
结果与结论:①在骨髓增生异常综合征和急性髓系白血病之间共获得150个差异表达基因,其中16个基因表达上调,134个基因表达下调;②DO、GO、KEGG及GSEA分析结果提示差异表达基因可能通过调节免疫应答促进骨髓增生异常综合征向急性髓系白血病发展,CIBERSORT分析显示骨髓增生异常综合征与急性髓系白血病之间存在免疫浸润差异,其中CD4+ T细胞、单核细胞、中性粒细胞、M1巨噬细胞在急性髓系白血病患者中分布降低,而炎症抑制细胞M2巨噬细胞在急性髓系白血病患者中分布增加,可能与急性髓系白血病免疫抑制有关;③利用K-M曲线及受试者工作特征曲线从150个差异基因中筛选出4个与免疫和预后相关且具有较好诊断性能的基因:MANSC1、FLT3、BMX及CXCR2;④RT-qPCR检测结果显示MANSC1、BMX及CXCR2在急性髓系白血病患者中低表达,而FLT3在急性髓系白血病患者中高表达。结果表明,MANSC1、FLT3、BMX及CXCR2在骨髓增生异常综合征与急性髓系白血病患者间差异表达,不仅与患者预后显著相关,还可能通过调节患者的免疫浸润影响骨髓增生异常综合征及急性髓系白血病的发生和进展,它们可作为骨髓增生异常综合征向急性髓系白血病转化的潜在生物标志物和治疗靶点,为骨髓增生异常综合征“转白”的临床诊疗研究提供新的方向。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0305-1746 (邓发滑)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: