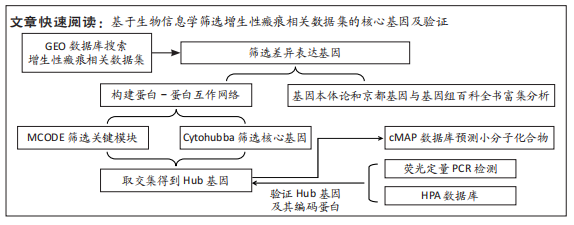
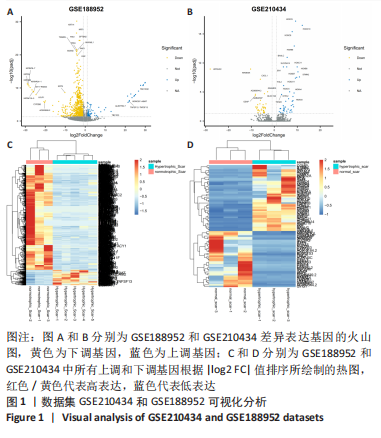
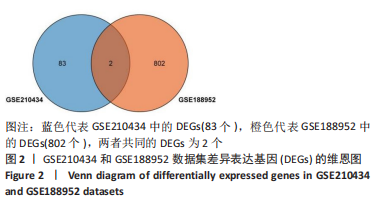
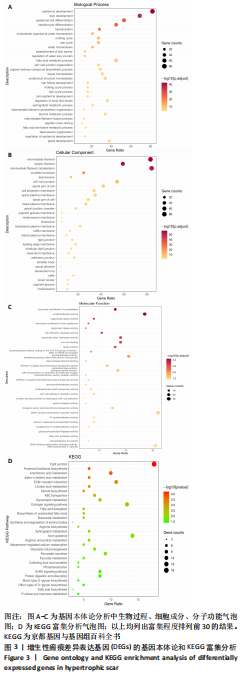
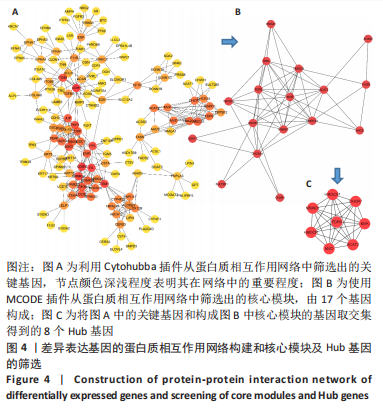
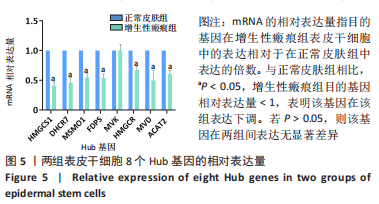
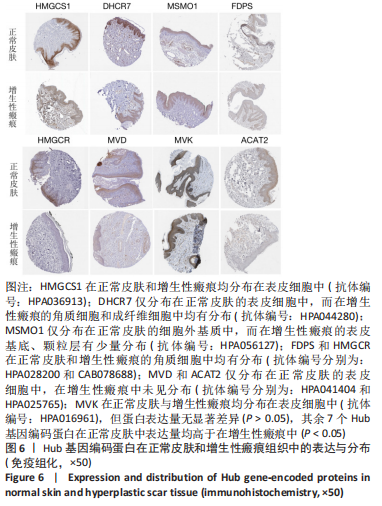
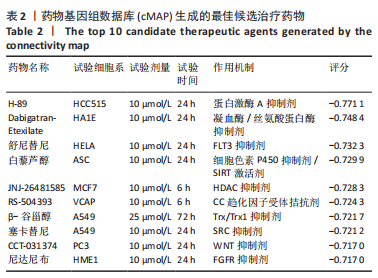
[1] WEI J, WANG Z, ZHONG C, et al. LncRNA MIR503HG promotes hypertrophic scar progression via miR-143-3p-mediated Smad3 expression. Wound Repair Regen. 2021;29(5):792-800.
[2] ZHANG H, WANG HY, WANG DL, et al. Effect of pressure therapy for treatment of hypertrophic scar. Med. Baltim. 2019;98(26):e16263.
[3] TAN J, ZHOU J, HUANG L, et al. Hypertrophic Scar Improvement by Early Intervention With Ablative Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser Treatment. Lasers Surg Med. 2021;53(4):450-457.
[4] TUNCA M, GAMSIZKAN M, YÜREKLI A, et al. Cryosurgery to remove perichondrium for the rabbit ear hypertrophic scar model: a simplified method. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2019;28(2):57-59.
[5] BI M, SUN P, LI D, et al. Intralesional Injection of Botulinum Toxin Type A Compared with Intralesional Injection of Corticosteroid for the Treatment of Hypertrophic Scar and Keloid: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:2950-2958.
[6] ELSAIE ML. Update on management of keloid and hypertrophic scars: A systemic review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20(9):2729-2738.
[7] OGAWA R. The Most Current Algorithms for the Treatment and Prevention of Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids: A 2020 Update of the Algorithms Published 10 Years Ago. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022;149(1):79e-94e.
[8] MCGINTY S, SIDDIQUI WJ. Keloid. London: BTI-StatPearls: StatPearls Publishing, 2021.
[9] KLIFTO KM, ASIF M, HULTMAN CS. Laser management of hypertrophic burn scars: a comprehensive review. Burns Trauma. 2020;8:tkz002.
[10] ANDERSON JB, FOGLIO A, HARRANT AB, et al. Scoping Review of Therapeutic Strategies for Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021;9(3):e3469.
[11] 贠张君,王慧静,俞仪萱,等. 基于生物信息学技术筛选结直肠癌的差异基因和中药预测研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2022,47(6):1666-1676.
[12] EGAWA G, KABASHIMA K. Barrier dysfunction in the skin allergy. Allergol Int. 2018;67(1):3-11.
[13] XIAO Y, ZHANG B, CLOYD JM, et al. Gene signature and connectivity mapping to assist with drug prediction for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Surg Oncol. 2022;44:101849.
[14] LEE HJ, JANG YJ. Recent Understandings of Biology, Prophylaxis and Treatment Strategies for Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):711.
[15] LESZCZYNSKI R, DA SILVA CA, PINTO ACPN, et al. Laser therapy for treating hypertrophic and keloid scars. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;9(9):CD011642.
[16] DENG X, ZHAO F, ZHAO D, et al. Oxymatrine promotes hypertrophic scar repair through reduced human scar fibroblast viability, collagen and induced apoptosis via autophagy inhibition. Int Wound J. 2022;19(5):1221-1231.
[17] BUTZELAAR L, ULRICH MM, MINK VAN DER MOLEN AB, et al. Currently known risk factors for hypertrophic skin scarring: A review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69(2):163-169.
[18] MOUSAVIZADEH SM, TORBATI PM, DARYANI A. The effects of kiwifruit dressing on hypertrophic scars in a rabbit ear model. J Wound Care. 2021;30(Sup9a):XVi-XVvii.
[19] LI W, WANG D, LI M, et al. Emodin inhibits the proliferation of papillary thyroid carcinoma by activating AMPK. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(4):1075.
[20] JIANG N, LI Z, LUO Y, et al. Emodin ameliorates acute pancreatitis-induced lung injury by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neutrophil recruitment. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(2):857.
[21] RU Z, HU Y, HUANG S, et al.Bioflavonoid GalanginSuppresses Hypertrophic Scar Formation by the TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:2444839.
[22] CHEN D, LI Q, ZHANG H, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine for hypertrophic scars-A review of the therapeutic methods and potential effects. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1025602.
[23] BÄSLER K, BERGMANN S, HEISIG M, et al. The role of tight junctions in skin barrier function and dermal absorption. J Control Release. 2016;242:105-118.
[24] 席榕,朱慧婷,李伯华,等. 皮肤屏障紧密连接在特应性皮炎发病机制中的作用[J]. 中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志,2022,16(2):172-177.
[25] FERNÁNDEZ-MAYOLA M, BETANCOURT L, MOLINA-KAUTZMAN A, et al. Growth hormone-releasing peptide 6 prevents cutaneous hypertrophic scarring: early mechanistic data from a proteome study. Int Wound J. 2018;15(4):538-546.
[26] HUANG C, OGAWA R. Roles of lipid metabolism in keloid development. Lipids Health Dis. 2013;12:60.
[27] 郑宇锟,王光忠,吴骁伟,等. 基于甲羟戊酸途径的盐酸小檗碱体外抗肺癌细胞药效及机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(13):92-101.
[28] KWON J, BAKHOUM SF. The Cytosolic DNA-Sensing cGAS-STING Pathway in Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020;10(1):26-39.
[29] MARTINS ÁM, RAMOS CC, FREITAS D, et al. Glycosylation of Cancer Extracellular Vesicles: Capture Strategies, Functional Roles and Potential Clinical Applications. Cells. 2021;10(1):109.
[30] WANG IH, HUANG TT, CHEN JL, et al. Mevalonate Pathway Enzyme HMGCS1 Contributes to Gastric Cancer Progression. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(5):1088.
[31] 蔡硕,陈思敏,王媛媛,等. 基于高通量测序技术探讨补骨脂宁治疗肺癌的潜在机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(14):183 -192 .
[32] HASHEMI M, HOSHYAR R, ANDE SR, et al. Mevalonate Cascade and its Regulation in Cholesterol Metabolism in Different Tissues in Health and Disease. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2017;10(1):13-26.
[33] HA NT, LEE CH. Roles of Farnesyl-Diphosphate Farnesyltransferase 1 in Tumour and Tumour Microenvironments. Cells. 2020;9(11):2352.
[34] ERSHOV P, KALUZHSKIY L, MEZENTSEV Y, et al. Enzymes in the Cholesterol Synthesis Pathway: Interactomics in the Cancer Context. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(8):895.
[35] PRABHU AV, LUU W, LI D, et al. DHCR7: A vital enzyme switch between cholesterol and vitamin D production. Prog Lipid Res. 2016;64:138-151.
[36] 赵路,周洋,黄君富,等. DHCR7基因在膀胱癌中的表达及其与临床特征及预后关系的生物信息学分析[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2022,43(21):2649-2654.
[37] SU L, FU L, LI Y, et al. Disruption of the association between drug transporter and actin cytoskeleton abolishes drug resistance in hypertrophic scar. Oncotarget. 2017;8(2):2617-2627.
[38] SHAIKH G, CRONSTEIN B. Signaling pathways involving adenosine A2A and A2B receptors in wound healing and fibrosis. Purinergic Signal. 2016;12(2):191-197.
[39] VORSTANDLECHNER V, LAGGNER M, COPIC D, et al. The serine proteases dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 and urokinase are key molecules in human and mouse scar formation. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):6242.
[40] HU M, YANG T, YANG L, et al. Preclinical studies of Flonoltinib Maleate, a novel JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor, in treatment of JAK2V617F-induced myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood Cancer J. 2022;12(3):37.
[41] BAI XZ, LIU JQ, YANG LL, et al. Identification of sirtuin 1 as a promising therapeutic target for hypertrophic scars. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173(10):1589-1601.
[42] DEVARAJ E, ROY A, ROYAPURAM VEERARAGAVAN G, et al. β-Sitosterol attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative stress and chronic liver injury in rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020;393(6):1067-1075.
[43] PARK YJ, BANG IJ, JEONG MH, et al. Effects of β-Sitosterol from Corn Silk on TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Lung Alveolar Epithelial Cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(35):9789-9795.
[44] 郭京龄,马晨. 白藜芦醇调节脂质代谢研究进展[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(6): 390-402.
[45] CUI H, ZHANG M, YANG Q, et al. The Prediction of Drug-Disease Correlation Based on Gene Expression Data. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:4028473. |