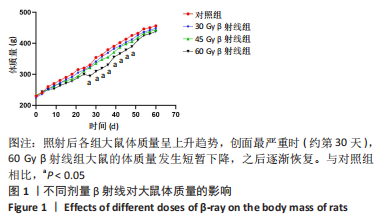
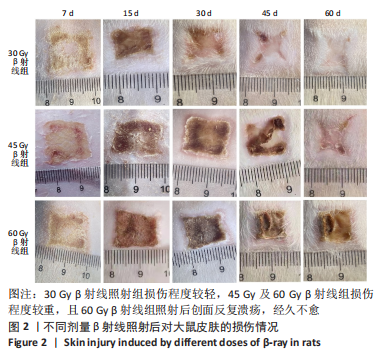
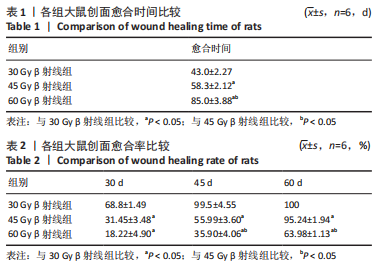
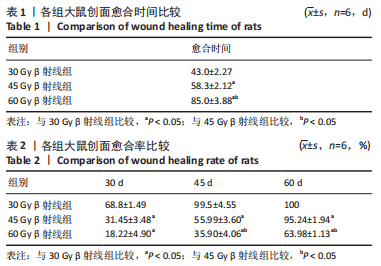
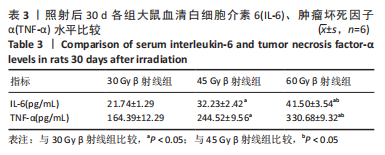
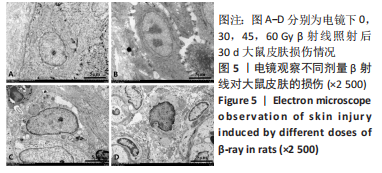
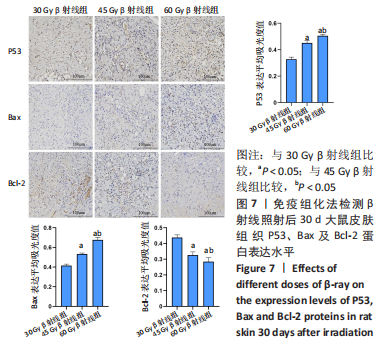
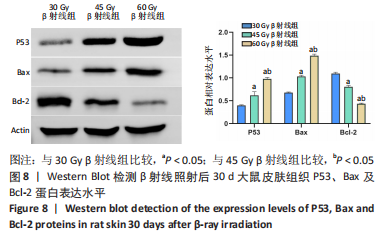
[1] DOCTROW SR, LOPEZ A, SCHOCK AM, et al. A synthetic superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetic EUK-207 mitigates radiation dermatitis and promotes wound healing in irradiated rat skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133(4):1088-1096.
[2] 刘玉龙,王优优,郭凯琳,等.南京“5.7”192Ir源放射事故患者的临床救治[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2016,36(5):324-330.
[3] TUIENG RJ, CARTMELL SH, KIRWAN CC, et al. The Effects of Ionising and Non-Ionising Electromagnetic Radiation on Extracellular Matrix Proteins. Cells. 2021; 10(11):3041.
[4] KUMAR A, KUMARCHANDRA R, RAI R, et al. Radiation mitigating activities of Psidium guajava L. against whole-body X-ray-induced damages in albino Wistar rat model.3 Biotech. 2020;10(12):507.
[5] DA SILVA SANTIN M, KOEHLER J, ROCHA DM, et al. Initial damage produced by a single 15-Gy x-ray irradiation to the rat calvaria skin. Eur Radiol Exp. 2020;4(1):32.
[6] BORRELLI MR, PATEL RA, SOKOL J, et al. Fat Chance: The Rejuvenation of Irradiated Skin. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7(2):e2092.
[7] WAN Y, TU W, Tang Y, et al. Prevention and treatment for radiation-induced skin injury during radiotherapy. Radiat Med Prot. 2020;1(2):60-68.
[8] TENORIO C, DE LA MATA D, LEYVA JAF, et al. Mexican radiationdermatitis management consensus. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022;27(5):914-926.
[9] CHU CN, HU KC, WU RS, et al. Radiation-irritated skin and hyperpigmentation may impact the quality of life of breast cancer patients after whole breast radiotherapy.BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):330.
[10] 蔡卫超,曹卫红.活性氧与放射性皮肤损伤的研究进展[J].辐射防护,2022, 42(3):111-118.
[11] JAKUBCZYK K, DEC K, KALDUNSKA J, et al. Reactivr oxygen species-sources,functions,oxidative damage. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2020;48(284):124-127.
[12] SHI M, HUANG J, SUN X et al. Effect of rivaroxaban on the injury during endotoxin-induced damage to human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019;31(4):468-473.
[13] WANG C, LI TK, ZENG CH, et al.Iodine-125 seed radiation induces ROS-mediated apoptosis, autophagy and paraptosis in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2020;43(6):2028-2044.
[14] HAO Q, CHEN J, LIAO J, et al.p53 induces ARTS to promote mitochondrial apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(2):204-209.
[15] OKAZAKI R. Role of p53 in Regulating Radiation Responses. Life (Basel). 2022; 12(7):1099.
[16] KIANG JG, CANNON G, OLSON MG, et al.Female Mice are More Resistant to the Mixed-Field (67% Neutron+33% Gamma) Radiation-Induced Injury in Bone Marrow and Small Intestine than Male Mice due to Sustained Increases in G-CSF and the Bcl-2/Bax Ratio and Lower miR-34a and MAPK Activation. Radiat Res. 2022;198(2):120-133.
[17] GANS I, ABIAD JE, JAMES AW, et al.Administration of TGF-ß Inhibitor Mitigates Radiation-induced Fibrosis in a Mouse Model.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021;479(3): 468-474.
[18] CHANG HP, CHO JH, LEE WJ, et al. Development of an easy-to-handle murine model for the characterization of radiation-induced gross and molecular changes in skin. Arch Plast Surg. 2018;45(5):403-410.
[19] 陈宇彤,李晨晨,刘阳,等.急性放射性皮肤损伤 Wistar大鼠模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(2):237-241.
[20] 沈国良,陆兴安,唐俊,等.大鼠急性β射线皮肤损伤动物模型的建立与应用[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2006,26(6):577-579.
[21] YANG X, REN H, GUO X, et al. Radiation-induced skin injury: pathogenesis, treatment, and management. Aging(AlbanyNY). 2020;12(22):23379-23393.
[22] HYMES SR, STROM EA, FIFE C, et al. Radiation dermatitis: clinical presentation, pathophysiology, and treatment 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(1):28-46.
[23] MARTIN MT, VULIN A, Hendry JH, et al. Human epidermal stem cells: role in adverse skin reactions and carcinogenesis from radiation. Mutat Res. 2016;770(Pt B):349-368.
[24] XIAO Y, MO W, JIA H, et al.Ionizing radiation induces cutaneous lipid remolding and skin adipocytes confer protection against radiation-induced skin injury. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;97(2):152-160.
[25] SHERMAN DW, WALSH SM. Promoting Comfort: A Clinician Guide and Evidence-Based Skin Care Plan in the Prevention and Management of Radiation Dermatitis for Patients with Breast Cancer. Healthcare (Basel). 2022;10(8):1496.
[26] YEE C, LAM E, GALLANT F, et al. A Feasibility Study of Mepitel Film for the Prevention of Breast Radiation Dermatitis in a Canadian Center. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2021;11(1):e36-e45.
[27] KIM JW, LEE DW, CHOI WH, et al. Development of a porcine skin injury model and characterization of the dose-dependent response to high-dose radiation. J Radiat Res. 2013;54(5):823-831.
[28] FALLAH M, SHEN Y, BRODEN J, et al. Plasminogen activation is required for the development of radiation-induced dermatitis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(11):1051.
[29] HOLLER V, BUARDV, GAUGLER MH, et al. Pravastatin limits radiationinduced vascular dysfunction in the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129(5):1280-1291.
[30] MEI K, ZHAO S, QIAN L, et al. Hydrogen protects rats from dermatitis caused by local radiation. J Dermatolog Treat. 2014;25(2):182-188.
[31] BERNHARDT T, KRIESENS, MANDA K, et al. Induction of Radiodermatitis in Nude Mouse Model Using Gamma Irradiator IBL 637. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2022;35(4):224-234.
[32] NIELSEN S, BASSLER N, GRZANKA L, et al. Proton scanning and X-ray beam irradiation induce distinct regulation of inflammatory cytokines in a preclinical mouse model. Int J Radiat Biol. 2020;96(10):1238-1244.
[33] CHEN Y, ZHANG Q, WU Y, et al. Short-term influences of radiation on musculofascial healing in a laparotomy rat model. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):11896.
[34] KESANIEMI J, JERNFORS T, LAVRINIENKO A, et al. Exposure to environmental radionuclides is associated with altered metabolic and immunity pathways in a wild rodent. Mol Ecol. 2019;28(20):4620-4635.
[35] KOIKE M, SUGASAWA J, KOIKE A, et al. p53 phosphorylation in mouse skin and in vitro human skin model by high-dose-radiation exposure.J Radiat Res. 2005;46(4):461-468.
[36] BERNHARDT T, KRIESEN S, MANDA K, et al. Induction of Radiodermatitis in Nude Mouse Model Using Gamma Irradiator IBL 637. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2022;35(4):224-234.
[37] YAO C, ZHOU Y, WANG H, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells alleviate radiation-induced dermatitis by suppressing apoptosis and downregulating cathepsin F expression. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):447.
[38] CUI YF, XIA GW, FU XB, et al.Relationship between expression of Bax and Bcl-2 proteins and apoptosis in radiation compound wound healing of rats.Chin J Traumatol. 2003;6(3):135-138.
[39] 赵小瑜,何罕亮,祁强,等.急性β射线皮肤损伤创面愈合过程中相关凋亡基因的表达[J].苏州大学学报(医学版),2012,32(6):853-857+878. |