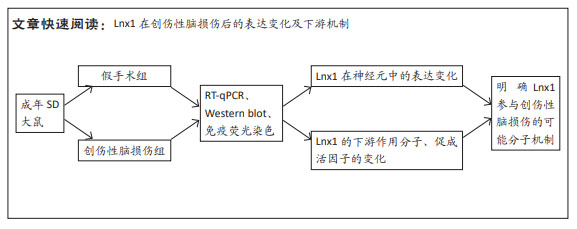
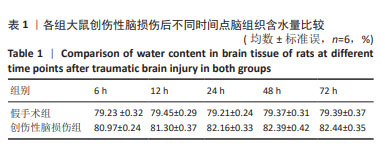
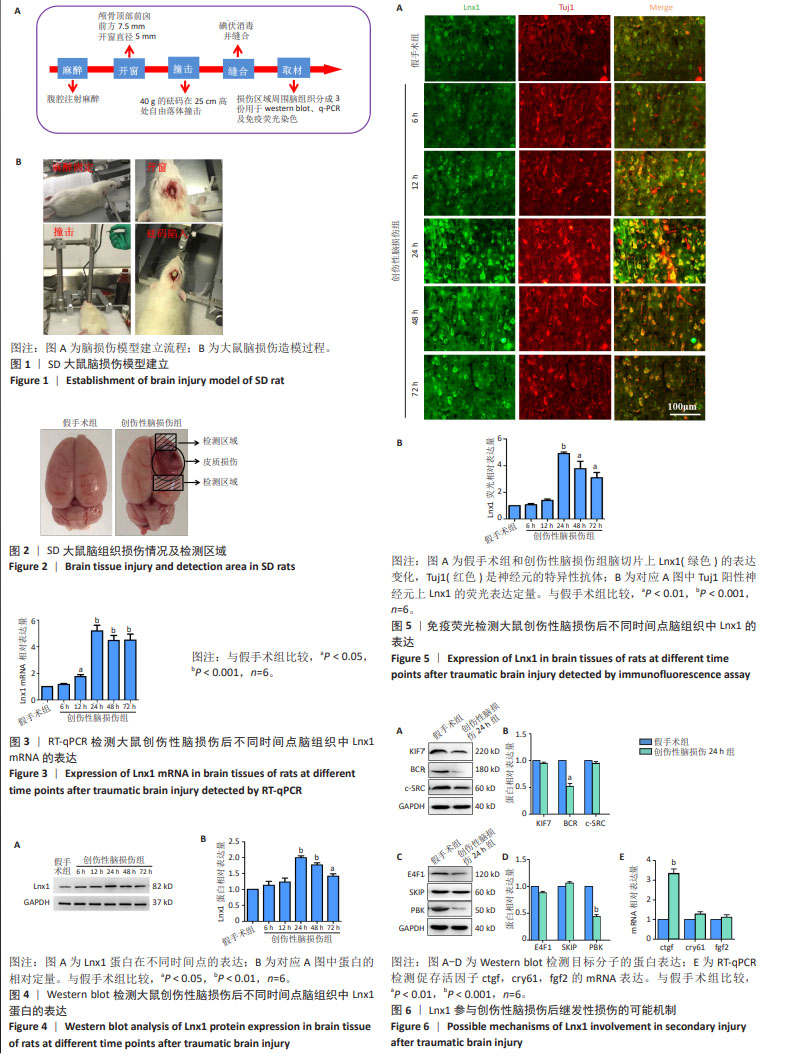
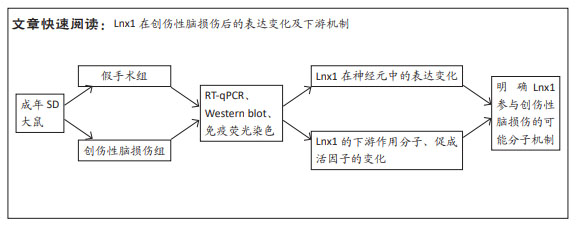
|
[1] GALGANO M, TOSHKEZI G, QIU X, et al. Traumattc Brain Injury:
Current Treatment Strategies and Future Endeavors. Cell Transplant.
2017;26(7):1118-1130.
[2] LORD K, ZIMMERMAN J, DUFF MC, et al. Memory for social media
images following traumattc brain injury. Brain Inj. 2023:1-11. doi:
10.1080/02699052.2023.2272902.
[3] KHELLAF A, KHAN DZ, HELMY A. Recent advances in traumattc brain
injury. J Neurol. 2019;266(11):2878-2889.
[4] SUDHAKARAN P. Traumattc Brain Injury: Acupuncture Treatment. Med
Acupunct. 2023;35(5):251-256.
[5] HACKENBERG K, UNTERBERG A. Traumattc brain injury. Nervenarzt.
2016;87(2):203-214.
[6] OLSEN A, BABIKIAN T, BIGLER ED, et al. Toward a global and
reproducible science for brain imaging in neurotrauma: the ENIGMA
adult moderate/severe traumattc brain injury working group. Brain
Imaging Behav. 2021;15(2):526-554.
[7] LINDSEY HM, WILDE EA, CAEYENBERGHS K, et al. Longitudinal
Neuroimaging in Pediatric Traumattc Brain Injury: Current State and
Consideratton of Factors That Inffuence Recovery. Front Neurol.
2019;10:1296.
[8] HOPP S, NOLTE MW, STETTER C, et al. Alleviatton of secondary brain
injury, posttraumattc inffammatton, and brain edema formatton by
inhibitton of factor XIIa. J Neuroinffammatton. 2017;14(1):39.
[9] KEANE RW, HADAD R, SCOTT XO, et al. Neural-Cardiac Inffammasome
Axis affer Traumattc Brain Injury. Pharmaceuttcals (Basel). 2023;16(10):
1382.
[10] TANG R, LIN YM, LIU HX, et al. Neuroprotecttve effect of
docosahexaenoic acid in rat traumattc brain injury model via regulatton
of TLR4/NF-Kappa B signaling pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;99:
64-71.
[11] YOUNG PW. LNX1/LNX2 proteins: functtons in neuronal signalling and
beyond. Neuronal Signal. 2018;2(2):NS20170191.
[12] DHO SE, JACOB S, WOLTING CD, et al. The mammalian numb
phosphotyrosine-binding domain. Characterizatton of binding
speciffcity and identtffcatton of a novel PDZ domain-containing numb
binding protein, LNX. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(15):9179-9187.
[13] LENIHAN JA, SAHA O, MANSFIELD LM, et al. Tight, cell type-speciffc
control of LNX expression in the nervous system, at the level of
transcriptton, translatton and protein stability. Gene. 2014;552(1):
39-50.
[14] BEKRI A, LIAO M, DRAPEAU P. Glycine Regulates Neural Stem Cell
Proliferatton During Development via Lnx1-Dependent Notch Signaling.
Front Mol Neurosci. 2019;12:44.
[15] LENIHAN JA, SAHA O, YOUNG PW. Proteomic analysis reveals novel
ligands and substrates for LNX1 E3 ubiquittn ligase. PLoS One. 2017;
12(11):e0187352.
[16] LIU XD, ZHU XN, HALFORD MM, et al. Retrograde regulatton of mossy
ffber axon targettng and terminal maturatton via postsynapttc Lnx1. J
Cell Biol. 2018; 217(11):4007-4024.
[17] LIU XD, AI PH, ZHU XN, et al. Hippocampal Lnx1-NMDAR multtprotein
complex mediates inittal social memory. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26(8):
3956-3969.
[18] DE LA ROCHA-MUÑOZ A, NÚÑEZ E, ARRIBAS-GONZÁLEZ E, et al. E3
ubiquittn ligases LNX1 and LNX2 are major regulators of the presynapttc
glycine transporter GlyT2. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):14944.
[19] CHEN J, XU J, ZHAO W, et al. Characterizatton of human LNX, a novel
ligand of Numb protein X that is downregulated in human gliomas. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37(11):2273-2283.
[20] CHEN W, GUO Y, YANG W, et al. Phosphorylatton of connexin 43 induced
by traumattc brain injury promotes exosome release. J Neurophysiol.
2018;119(1): 305-311.
[21] LI L, ACIOGLU C, HEARY RF, et al. Role of astroglial toll-like
receptors (TLRs) in central nervous system infecttons, injury and
neurodegenerattve diseases. Brain Behav Immun. 2021;91:740-755.
[22] XU XJ, GE QQ, YANG MS, et al. Neutrophil-derived interleukin-17A
parttcipates in neuroinffammatton induced by traumattc brain injury.
Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(5):1046-1051.
[23] NAJEM D, RENNIE K, RIBECCO-LUTKIEWICZ M, et al. Traumattc
brain injury: classiffcatton, models, and markers. Biochem Cell Biol.
2018;96(4):391-406.
[24] ESTRADA-ROJO F, MARTÍNEZ-TAPIA RJ, ESTRADA-BERNAL F, et al.
Models used in the study of traumattc brain injury. Rev Neurosci.
2018;29(2):139-149.
[25] JANG M, PARK R, PARK YI, et al. LNX1 Contributes to Cell Cycle
Progression and Cisplattn Resistance. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(16):
4066.
[26] NAYAK D, SIVARAMAN J. Structure of LNX1:Ubc13~Ubiquittn Complex
Reveals the Role of Addittonal Mottfs for the E3 Ligase Acttvity of LNX1.
J Mol Biol. 2018; 430(8):1173-1188.
[27] ZHENG D, SUN Y, GU S, et al. LNX (Ligand of Numb-protein X) interacts
with RhoC, both of which regulate AP-1-mediated transcripttonal
acttvatton. Mol Biol Rep. 2010;37(5):2431-2437.
[28] ZHENG D, GU S, LI Y, et al. A global genomic view on LNX siRNAmediated
cell cycle arrest. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38(4):2771-2783.
[29] NANDI AK, FORD T, FLEKSHER D, et al. Attenuatton of DNA damage
checkpoint by PBK, a novel mitottc kinase, involves protein-protein
interactton with tumor suppressor p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
2007;358(1):181-188.
[30] SHAHAB SW, ROGGEVEEN CM, SUN J, et al. The LIN28B-let-7-PBK
pathway is essenttal for group 3 medulloblastoma tumor growth and
survival. Mol Oncol. 2023;17(9):1784-1802.
[31] GUO Z, SONG E, MA S, et al. Proteomics strategy to identtfy substrates
of LNX, a PDZ domain-containing E3 ubiquittn ligase. J Proteome Res.
2012;11(10):4847-4862.
[32] FU B, XUE W, ZHANG H, et al. MicroRNA-325-3p Facilitates Immune
Escape of Mycobacterium tuberculosis through Targettng LNX1 via
NEK6 Accumulatton to Promote Antt-Apoptottc STAT3 Signaling. mBio.
2020;11(3):e00557-20.
|