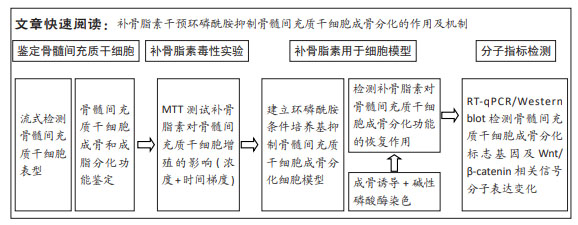
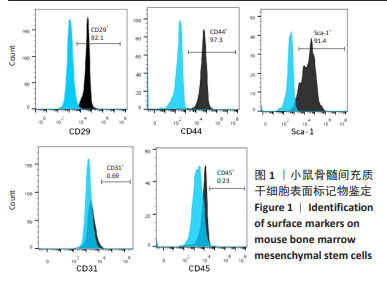
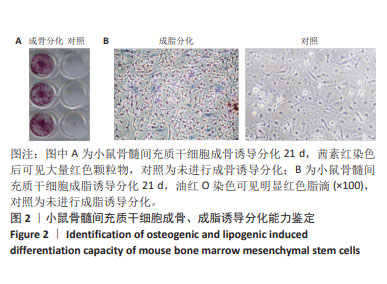
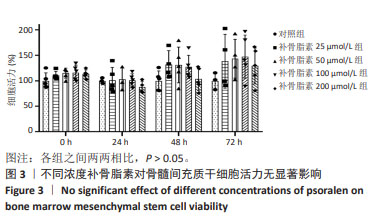
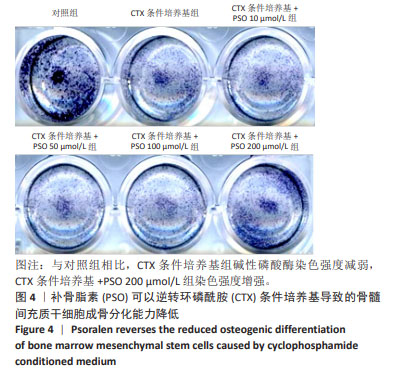
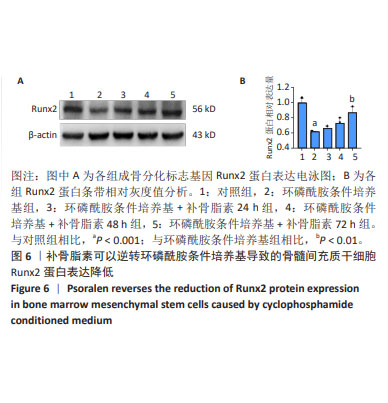
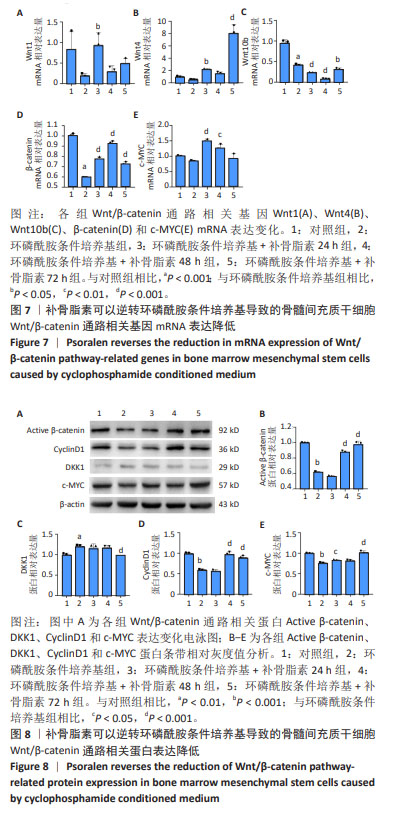
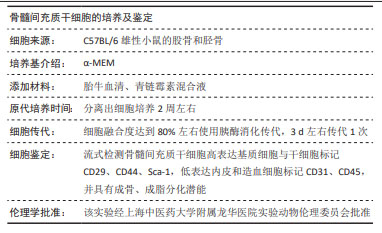
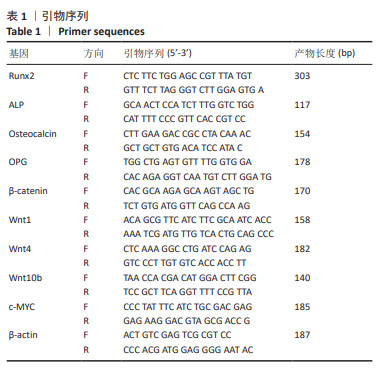
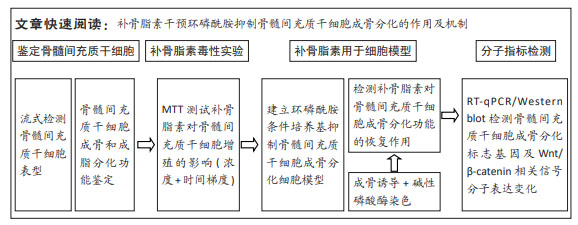
|
[1] ADLER RA. Cancer treatment-induced bone loss. Curr Opin Endocrinol
Diabetes Obes. 2007;14(6):442-445.
[2] PFEILSCHIFTER J, DIEL IJ. Osteoporosis due to cancer treatment:
pathogenesis and management. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(7):1570-1593.
[3] STAVA CJ, JIMENEZ C, HU MI, et al. Skeletal sequelae of cancer and
cancer treatment. J Cancer Surviv. 2009;3(2):75-88.
[4] COLEMAN RE, RATHBONE E, BROWN JE. Management of cancer
treatment-induced bone loss. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 20139(6):365-374.
[5] MICHAUD LB, GOODIN S. Cancer-treatment-induced bone loss, part 1.
Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006;63(5):419-430.
[6] DIANA A, CARLINO F, GIUNTA EF, et al. Cancer Treatment-Induced
Bone Loss (CTIBL): State of the Art and Proper Management in Breast
Cancer Pattents on Endocrine Therapy. Curr Treat Opttons Oncol.
2021;22(5):45.
[7] WANG TM, SHIH C. Study of histomorphometric changes of the
mandibular condyles in neonatal and juvenile rats affer administratton
of cyclophosphamide. Acta Anat (Basel). 1986;127(2):93-99.
[8] ZHAO D, WANG C, ZHAO Y, et al. Cyclophosphamide causes
osteoporosis in C57BL/6 male mice: suppressive effects of
cyclophosphamide on osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis.
Oncotarget. 2017;8(58):98163-98183.
[9] NAJI A, EITOKU M, FAVIER B, et al. Biological functtons of mesenchymal
stem cells and clinical implicattons. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(17):
3323-3348.
[10] 吴铭 , 张岩 . 调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的 Wnt/β-catenin 信
号通路及相关因素 [J]. 中国组织工程研究 ,2021,25(1):116-122.
[11] 李晋蒙 , 王新涛 .Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路在骨质疏松症和非骨质
疏松症环境下促进成骨的研究进展 [J]. 医学综述 ,2021,27(12):
2301-2305.
[12] 李智奎 , 孔俊博 , 赵王林 . 淫羊藿苷调控 Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路
干预大鼠 MSCs 成脂成骨双向分化实验研究 [J]. 中国免疫学杂志 ,
2019,35(24):2985-2990.
[13] 马忠平 , 杨云 , 张志峰 , 等 . 芝麻素通过 Wnt/β-catenin 通路调控大
鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨细胞分化预防骨质疏松的作用研究 [J].
中国骨质疏松杂志 , 2021,27(1):50-54+59.
[14] 王一凤 , 樊国峰 , 陈胜乐 . 西红花苷对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠 Wnt/
β-Catenin 信号通路的影响 [J]. 临床和实验医学杂志 ,2022,21(1):
8-13.
[15] REN Y, SONG X, TAN L, et al. A Review of the Pharmacological Properttes
of Psoralen. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:571535.
[16] 杨阔 , 高茸 , 马亚中 , 等 . 补骨脂素药理作用及肝毒性机制的研究
进展 [J]. 中草药 ,2021,52(1):289-298.
[17] 董熠 , 刘丽佳 , 韩潞雯 , 等 . 香豆素类化学成分的药理作用及毒性
机制研究进展 [J]. 中草药 ,2023,54(16):5462-5472.
[18] WANG X, XU C, HUA Y, et al. Psoralen induced cell cycle arrest by
modulattng Wnt/β-catenin pathway in breast cancer cells. Sci Rep.
2018;8(1):14001.
[19] LI S, TU H. Psoralen inhibits the proliferatton and promotes apoptosis
through endoplasmic rettculum stress in human osteosarcoma cells.
Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2022;60(1):101-109.
[20] WU Y, ZHANG YZ, LI MJ, et al. The In Vitro Effect of Psoralen on Glioma
Based on Network Pharmacology and Potenttal Target Research. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:1952891.
[21] ZHENG W, LIN P, MA Y, et al. Psoralen promotes the expression of cyclin
D1 in chondrocytes via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Mol
Med. 2017;40(5):1377-1384.
[22] HUANG Y, LIAO L, SU H, et al. Psoralen accelerates osteogenic
differenttatton of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by
acttvattng the TGF-β/Smad3 pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(3):940.
[23] 杨志烈 , 王成龙 , 赵东峰 , 等 . 淫羊藿苷对环磷酰胺化疗导致小鼠
骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化障碍的保护作用 [J]. 中国组织工程研
究 ,2016,20(6):777-784.
[24] OGINO MH, TADI P. Cyclophosphamide. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island
(FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2023.
[25] SUN S, GUO Z, XIAO X, et al. Isolatton of mouse marrow mesenchymal
progenitors by a novel and reliable method. Stem Cells. 2003;21(5):
527-535.
[26] LI F, LI Q, HUANG X, et al. Psoralen sttmulates osteoblast proliferatton
through the acttvatton of nuclear factor-κB-mitogen-acttvated protein
kinase signaling. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(3):2385-2391.
[27] HUANG Y, HOU Q, SU H, et al. miR-488 negattvely regulates osteogenic
differenttatton of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by
psoralen by targettng Runx2. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(4):3746-3754.
[28] YIN BF, LI ZL, YAN ZQ, et al. Psoralen alleviates radiatton-induced
bone injury by rescuing skeletal stem cell stemness through AKTmediated
upregulatton of GSK-3β and NRF2. Stem Cell Res Ther.
2022;13(1):241.
[29] ZHANG Q, PAN Y, JI J, et al. Roles and actton mechanisms of WNT4 in
cell differenttatton and human diseases: a review. Cell Death Discov.
2021;7(1):287.
[30] ZHOU P, LI Y, DI R, et al. H19 and Foxc2 synergisttcally promotes
osteogenic differenttatton of BMSCs via Wnt-β-catenin pathway. J Cell
Physiol. 2019;234(8): 13799-13806.
[31] LI X, LI Z, WANG J, et al. Wnt4 signaling mediates protecttve effects of
melatonin on new bone formatton in an inffammatory environment.
FASEB J. 2019;33(9):10126-10139.
[32] CHANG J, SONOYAMA W, WANG Z, et al. Noncanonical Wnt-4
signaling enhances bone regeneratton of mesenchymal stem cells
in craniofacial defects through acttvatton of p38 MAPK. J Biol Chem.
2007;282(42):30938-30948.
[33] YU B, CHANG J, LIU Y, et al. Wnt4 signaling prevents skeletal aging and
inffammatton by inhibittng nuclear factor-κB. Nat Med. 2014;20(9):
1009-1017.
[34] CHAI L, ZHOU K, WANG S, et al. Psoralen and Bakuchiol Ameliorate
M-CSF Plus RANKL-Induced Osteoclast Differenttatton and Bone
Resorptton Via Inhibitton of AKT and AP-1 Pathways in Vitro. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 2018;48(5):2123-2133.
|