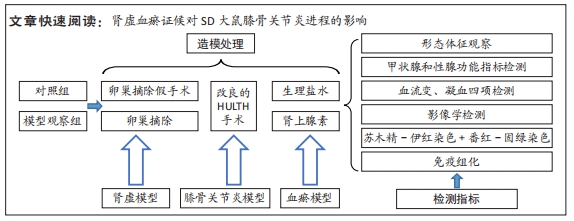
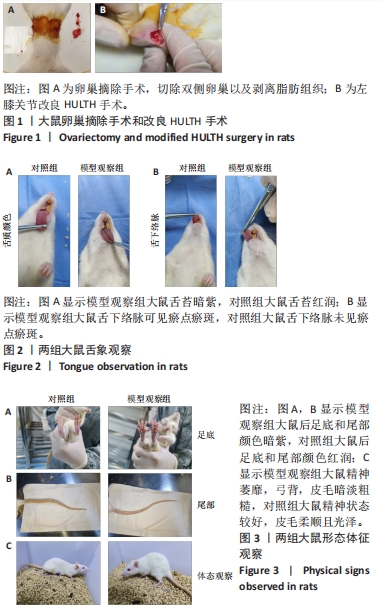
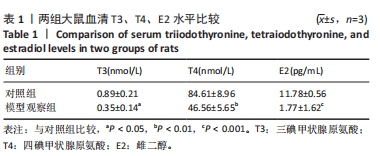
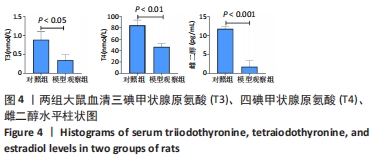
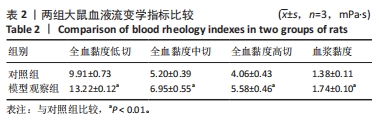
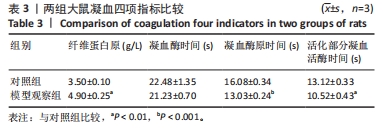
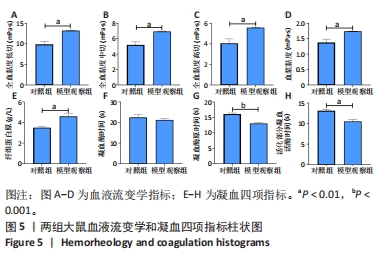
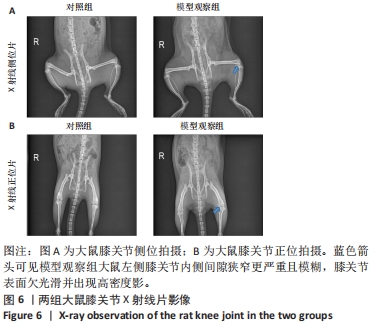
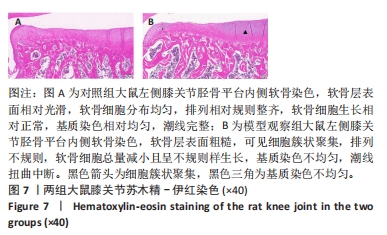
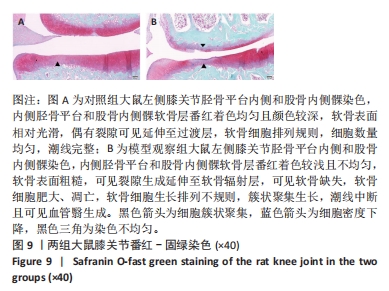
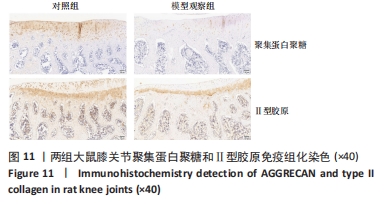
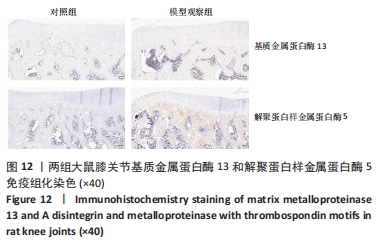
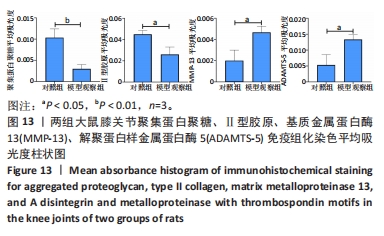
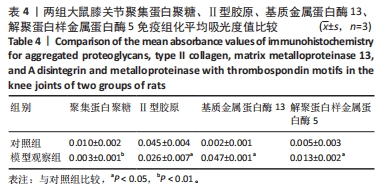
[1] VITALONI M, BOTTO-VAN BEMDEN A, SCIORTINO R, et al. A patients’ view of OA: the Global Osteoarthritis Patient Perception Survey (GOAPPS), a pilot study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):727.
[2] CROSS M, SMITH E, HOY D, et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1323-1330.
[3] 李盛华,周明旺.规范膝骨关节炎的分期分型,倡导膝骨关节炎的中医疗法 ——《膝骨关节炎中医诊疗指南(2020年版)》解读[J].中医正骨,2021,33(7):1-3.
[4] 徐传毅,樊粤光,宁显明.肾虚血瘀与膝骨性关节炎关系初探[J].新中医,2002,34(3):7-9.
[5] 陈宇,胡小钰,罗泽红,等.基于肾虚血瘀理论探讨膝骨关节炎的发病机制[J].微量元素与健康研究,2023,40(2):85-86+89.
[6] 梁健忠,黄韵,李廉行.补肾活血汤治疗肾虚血瘀型膝骨性关节炎的疗效及对血清炎症因子的影响[J].四川中医,2023,41(4):140-144.
[7] 刘振峰,方锐,艾力江•阿斯拉,等.肾虚血瘀型膝骨性关节炎大鼠模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(2):270-274.
[8] 叶劲松,梁子聪.3种不同膝骨关节炎造模方法比较[J].中国老年学杂志,2023,43(16):3948-3954.
[9] 杨会珍,胡广,苗兰,等.肾上腺素致慢性血瘀证大鼠模型的血浆代谢组学研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2022,28(2): 205-209.
[10] MANKIN HJ, DORFMAN H, LIPPIELLO L, et al. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. II. Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971;53(3):523-537.
[11] 宋威江,周丽,杜梦梦,等.肾阳虚对骨关节炎大鼠软骨退变的影响[J].风湿病与关节炎,2020,9(11):1-4+13.
[12] PRITZKER KP, GAY S, JIMENEZ SA, et al. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: grading and staging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14(1):13-29.
[13] ALLEN KD, THOMA LM, GOLIGHTLY YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):184-195.
[14] 余伟杰,刘爱峰,陈继鑫,等.中医药治疗肾虚血瘀型膝骨关节炎研究进展[J].天津中医药,2022,39(2):266-272.
[15] 黄文庭,黄枫,崔邦胜,等.肾虚血瘀证与膝骨性关节炎的关系研究[J].中国实用医药,2020,15(29):175-177.
[16] DYREK N, WIKAREK A, NIEMIEC M, et al. Selected musculoskeletal disorders in patients with thyroid dysfunction, diabetes, and obesity. Reumatologia. 2023;61(4):305-317.
[17] BASSETT JH, WILLIAMS AJ, MURPHY E, et al. A lack of thyroid hormones rather than excess thyrotropin causes abnormal skeletal development in hypothyroidism. Mol Endocrinol. 2008;22(2):501-512.
[18] 张薇薇,华芳,梁超帅,等.促甲状腺激素通过抗炎蛋白CTRP3促进软骨细胞分化[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2022,60(10):1-8+26.
[19] LI L, PANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Triiodothyronine potentiates angiogenesis-related factor expression through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in human osteoarthritic osteoblasts. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020;23(6):819-825.
[20] 牟利民,张文豪,张思平,等.绝经后女性退变性膝骨关节炎疼痛与性激素水平及关节液炎性因子的相关性研究[J].中国全科医学, 2022,25(29):3652-3657.
[21] KAROLCZAK K, WATALA C. Estradiol as the Trigger of Sirtuin-1-Dependent Cell Signaling with a Potential Utility in Anti-Aging Therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(18):13753.
[22] WU J, LI Y, ZHANG X, et al. Assessment of blood flow around the knee joint in patients with knee osteoarthritis by color Doppler ultrasound. Eur J Radiol. 2023;166:111005.
[23] 唐利,曾鹏,胡再吉.针刺加隔姜灸治疗膝骨关节炎疗效及对血清炎症因子和血液流变学影响[J].实用医院临床杂志,2022,19(5):69-73.
[24] 谢宏哲,彭伟军,易荣宾.补肾祛寒治尪汤治疗膝骨性关节炎(肾虚血瘀证)大鼠的作用及机制探讨[J].中药药理与临床,2023, 39(3):19-25.
[25] 张哲,赵雯雯,孙秀蕊,等.肉桂对肾阳虚大鼠下丘脑-垂体-靶腺轴相关mRNA表达及组织病理变化的影响[J].中华中医药学刊, 2023,41(4):59-63+264.
[26] 许兵,刘慧,金红婷,等.经典骨质疏松症模型大鼠的肾虚证研究[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(9):766-770.
[27] 王建红,伍庆华,刘海云,等.肾阳虚大鼠垂体-甲状腺轴功能动态分析[J].辽宁中医杂志,2006,33(6):751-752.
[28] 赵蓉,陈大蓉.更年期妇女中医辨证分型与雌二醇、卵泡刺激素及黄体生成激素相关性研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2008(2):171-173.
[29] 胡智星,杨超,方罗昌婷,等.基于“病-证-症”结合探索激素性股骨头坏死大鼠血瘀证的表征变化[J].中国中药杂志,2023, 48(22):6128-6141.
[30] 郭文鹤,黄娜娜,张晓亮,等.动脉粥样硬化(气滞血瘀证)病证结合大鼠模型的研究[J].中国比较医学杂志,2019,29(9):32-41.
[31] 史晓敏,齐瑶.种子汤加减方对气滞血瘀型输卵管炎性不孕大鼠血流变学及纤维化的影响[J].甘肃医药,2020,39(11):966-968+972.
[32] JYOTHI VGS, VEERABOMMA H, KUMAR R, et al. Meloxicam emulgel potently suppressed cartilage degradation in knee osteoarthritis: Optimization, formulation, industrial scalability and pharmacodynamic analysis. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2023;228:113399.
[33] SHI H, LI B, GAO H, et al. Intrauterine programming of cartilaginous 11β-HSD2 induced by corticosterone and caffeine mediated susceptibility to adult osteoarthritis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022; 239:113624.
[34] HATTORI Y, HASEGAWA M, IINO T,et al. Role of Syndecan-4 in the Inhibition of Articular Cartilage Degeneration in Osteoarthritis. Biomedicines. 2023;11(8):2257. |