中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (32): 5154-5158.doi: 10.12307/2024.497
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
白藜芦醇对膝骨关节炎模型大鼠关节液中氧化应激和炎症因子的调控作用
任伟亮,焦永伟,张 健,杨立英,杨 琦
- 河北中医学院第一附属医院(河北省中医院)骨伤三科,河北省石家庄市 050000
Modulatory effect of resveratrol on oxidative stress and inflammatory factors in the joint fluid of rats with knee osteoarthritis
Ren Weiliang, Jiao Yongwei, Zhang Jian, Yang Liying, Yang Qi
- Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University of Chinese Medicine (Hebei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
沉默信息调节因子1:简称SIRT1,是SIRT家族中的一员,是一个烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸(NAD+)依赖的组蛋白/非组蛋白去乙酰化酶,其在延长寿命、细胞周期调控、细胞凋亡调节、物质代谢调节和炎症过程中起着重要作用。氧化应激:是指体内氧化与抗氧化作用失衡的一种状态,倾向于氧化,导致中性粒细胞炎性浸润,蛋白酶分泌增加,产生大量氧化中间产物。氧化应激是由自由基在体内产生的一种负面作用。
背景:膝骨关节炎是临床常见退行性关节疾病,主要表现为慢性炎症和氧化应激反应。白藜芦醇具有抗炎和抗氧化应激的生物作用,因此可对症进行治疗,有望为膝骨关节炎治疗提供新的策略。
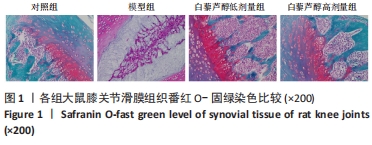
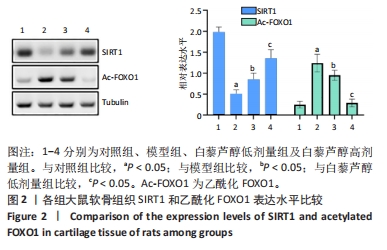
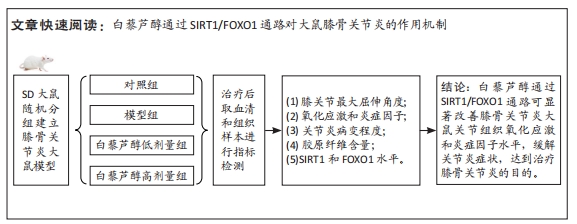
目的:探讨白藜芦醇通过沉默信息调节因子 1(silence information regulator 1,SIRT1)/叉头框转录因子O1(forkhead transcription factor O1,FOXO1)通路对大鼠膝骨关节炎的作用机制。方法:40只SD大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组、白藜芦醇低剂量组和白藜芦醇高剂量组,每组10只,除对照组外均建立膝骨关节炎模型,分别在造模的第1,4,7天注射4%木瓜蛋白酶溶液与0.3 mol/L半胱氨酸溶液(1∶1 混置0.5 h) 的混合液20 μL。造模成功后1 d开始给药,白藜芦醇低剂量组和白藜芦醇高剂量组大鼠经关节腔注射白藜芦醇25 mg/kg或100 mg/kg,对照组和模型组经关节腔注射等体积生理盐水。治疗28 d后,测定4组大鼠膝关节最大活动度;应用放射免疫法和ELISA法检测膝关节液中氧化应激指标和炎症因子水平;番红O-固绿染色分析膝关节中胶原纤维含量;采用Mankin组织学评分分析关节炎病变程度;蛋白质免疫印迹法检测膝关节SIRT1和FOXO1水平。
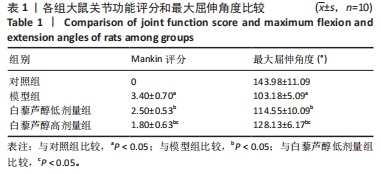
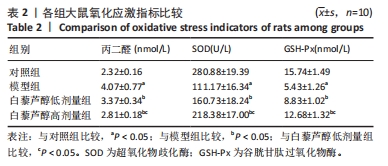
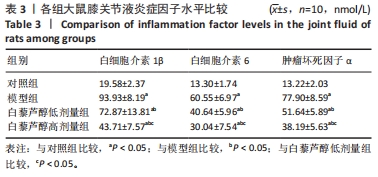
结果与结论:①与模型组比较,白藜芦醇低剂量组和高剂量组大鼠膝关节最大屈伸角度明显增加,且高剂量组明显高于低剂量组(P < 0.05);②与模型组比较,白藜芦醇低剂量组和高剂量组大鼠膝关节液中超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶水平显著增加;而丙二醛水平显著下降,且高剂量组明显优于低剂量组(P < 0.05);③与模型组比较,白藜芦醇低剂量组和高剂量组大鼠膝关节液炎症因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α水平明显下降,且高剂量组明显低于低剂量组(P < 0.05);④与模型组比较,白藜芦醇低剂量组和高剂量组大鼠膝关节胶原纤维含量增加,且高剂量组明显高于低剂量组(P < 0.05);⑤与模型组比较,白藜芦醇低剂量组和高剂量组大鼠膝关节SIRT1表达水平显著增加,乙酰化FOXO1水平显著下调,且高剂量组变化幅度明显优于低剂量组(P < 0.05);⑥提示白藜芦醇可显著改善膝骨关节炎大鼠关节液中的氧化应激和炎症因子水平,缓解关节炎症状,且呈剂量依赖性,可能是通过SIRT1/FOXO1通路实现的。
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-7502-7066(任伟亮)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: