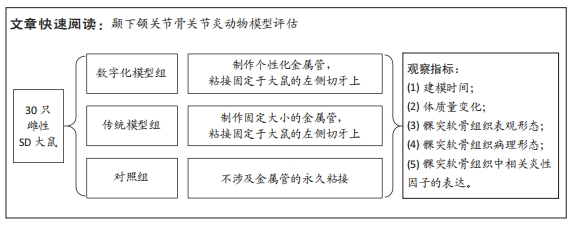
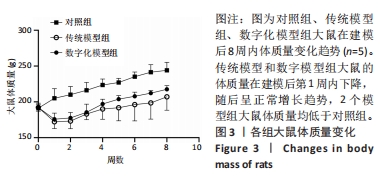
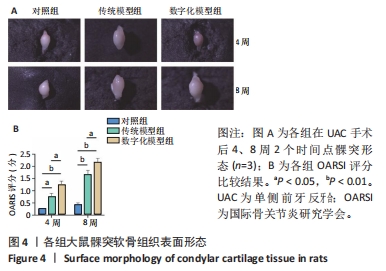
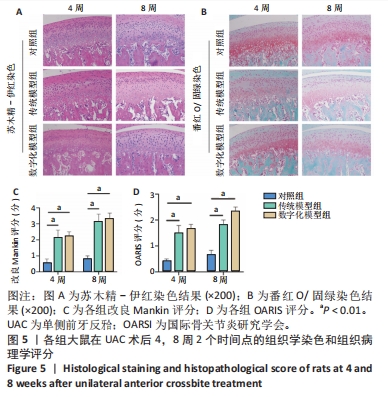
[1] WANG XD, ZHANG JN, GAN YH, et al. Current understanding of pathogenesis and treatment of TMJ osteoarthritis. J Dent Res. 2015;94(5):666-673.
[2] 孟娟红,甘业华,马绪臣.颞下颌关节骨关节炎发病的分子机制及相关治疗的实验研究[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2013,45(1):4.
[3] HE D, AN Y, LI Y, et al. RNA sequencing reveals target genes of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis in rats after the treatment of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound. Gene. 2018;672:126-136.
[4] ZHANG M, YANG H, LU L, et al. Matrix replenishing by BMSCs is beneficial for osteoarthritic temporomandibular joint cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(9):1551-1562.
[5] LONG HQ, TIAN PF, GUAN YX, et al. Expression of Ihh signaling pathway in condylar cartilage after bite-raising in adult rats. J Mol Histol. 2019; 50(5):459-470.
[6] ZHANG M, WANG H, ZHANG J, et al. Unilateral anterior crossbite induces aberrant mineral deposition in degenerative temporomandibular cartilage in rats. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016; 24(5):921-931.
[7] ZHANG HY, XIE MJ, YANG HX, et al. Catabolic changes of rat temporomandibular joint discs induced by unilateral anterior crossbite. J Oral Rehabil. 2019;46(4):340-348.
[8] WANG D, YANG H, ZHANG M, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 engaged in the mandibular condylar cartilage degeneration induced by experimental unilateral anterior crossbite. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;98: 17-25.
[9] LIU J, YANG H, ZHANG H, et al. Biomechanically reduced expression of Derlin-3 is linked to the apoptosis of chondrocytes in the mandibular condylar cartilage via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Arch Oral Biol. 2020;118:104843.
[10] ROBINSON NB, KRIEGER K, KHAN FM, et al. The current state of animal models in research: a review. Int J Surg. 2019;72:9-13.
[11] NESIC D, SCHAEFER BM, SUN Y, et al. 3D printing approach in dentistry: the future for personalized oral soft tissue regeneration. J Clin Med. 2020;9(7):2238.
[12] ZHENG J, CHEN X, JIANG W, et al. An innovative total temporomandibular joint prosthesis with customized design and 3D printing additive fabrication: a prospective clinical study. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):4.
[13] LIU YD, LIAO LF, ZHANG HY, et al. Reducing dietary loading decreases mouse temporomandibular joint degradation induced by anterior crossbite prosthesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(2):302-312.
[14] ZHANG J, LIAO L, ZHU J, et al. Osteochondral interface stiffening in mandibular condylar osteoarthritis. J Dent Res. 2018;97(5):563-570.
[15] WANG Y L, ZHANG J, ZHANG M, et al. Cartilage degradation in temporomandibular joint induced by unilateral anterior crossbite prosthesis. Oral Dis. 2014;20(3):301-306.
[16] PRITZKER KP, GAY S, JIMENEZ SA, et al. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: grading and staging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14(1):13-29.
[17] VAN DER SLUIJS JA, GEESINK RG, VAN DER LINDEN AJ, et al. The reliability of the Mankin score for osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 1992; 10(1):58-61.
[18] YUAN W, WU Y, ZHOU X, et al. Comparison and applicability of three induction methods of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis in murine models. J Oral Rehabil. 2022;49(4):430-441.
[19] 叶程心月,汤颖,刘超,等.SD大鼠牙列的显微CT观测 [J].实用口腔医学杂志,2019,35(6):794-799.
[20] LIU X, CAI HX, CAO PY, et al. TLR4 contributes to the damage of cartilage and subchondral bone in discectomy-induced TMJOA mice. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(19):11489-11499.
[21] BI R, CHEN K, WANG Y, et al. Regulating fibrocartilage stem cells via TNF-alpha/Nf-kappaB in TMJ osteoarthritis. J Dent Res. 2022;101(3):312-322.
[22] JIANG H, XU L, LIU W, et al. Chronic pain causes peripheral and central responses in MIA-induced TMJOA rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022;42(5):1441-1451.
[23] ZHANG C, ZHU M, WANG H, et al. LOXL2 attenuates osteoarthritis through inactivating Integrin/FAK signaling. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):17020.
[24] LIANG C, YANG T, WU G, et al. Therapeutic effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on temporomandibular joint injury induced by chronic sleep deprivation in rats. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(6):3328-3340.
[25] CHEN G, ZHAO H, MA S, et al. Circadian rhythm protein bmal1 modulates cartilage gene expression in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis via the MAPK/ERK pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11: 527744.
[26] DU J, JIANG Q, MEI L, et al. Effect of high fat diet and excessive compressive mechanical force on pathologic changes of temporomandibular joint. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):17457.
[27] ROGERS-DECOTES AW, PORTO SC, DUPUIS LE, et al. ADAMTS5 is required for normal trabeculated bone development in the mandibular condyle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(4):547-557.
[28] ZHANG J, ZHANG S, QI WJ, et al. Mechanism and potential contributing factors to temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Oral Dis. 2023;29(3): 1060-1069.
[29] ZHANG Y, XU X, ZHOU P, et al. Elder mice exhibit more severe degeneration and milder regeneration in temporomandibular joints subjected to bilateral anterior crossbite. Front Physiol. 2021;12:750468.
[30] ZHANG Y, LIU Q, XU X, et al. Long-term effect of bilateral anterior elevation of occlusion on the temporomandibular joints. Oral Dis. 2022;28(7):1911-1920.
[31] MA S, ZHANG A, LI X, et al. MiR-21-5p regulates extracellular matrix degradation and angiogenesis in TMJOA by targeting Spry1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020;22(1):99.
[32] SPERRY MM, KARTHA S, WINKELSTEIN BA, et al. Experimental methods to inform diagnostic approaches for painful TMJ osteoarthritis. J Dent Res. 2019;98(4):388-397. |