[1] JEONG J, KIM HS, LEE D, et al. Association between Four Dietary Patterns and the Risk of Periodontal Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2022;14(20):4362.
[2] MA Q, LIANG M, WU Y, et al. Osteoclast-derived apoptotic bodies couple bone resorption and formation in bone remodeling. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):5.
[3] 刘艳,格根塔娜.细胞因子在慢性牙周炎骨吸收中的作用[J].医学信息,2021,34(21):36-38.
[4] 王东红,王春爱,薛建军.葛根素的研究进展[J].西部中医药,2017, 30(1):139-142.
[5] 闫波.葛根素抑制PMMA颗粒诱导破骨细胞形成及骨溶解的机制研究[D].郑州:郑州大学,2020.
[6] 杨一秋,李兰,解继胜,等.葛根素介导PTEN-PI3K-AKT信号通路抑制绝经后骨质疏松症的机制研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022, 28(3):347-351.
[7] 詹乐,马瑞堉,万妮,等.葛根素对牙周炎大鼠Th17/Treg细胞免疫平衡及相关转录因子表达的影响[J].昆明医科大学学报,2022, 43(11):36-43.
[8] ZHAO B, GRIMES SN, LI S, et al. TNF-induced osteoclastogenesis and inflammatory bone resorption are inhibited by transcription factor RBP-J. J Exp Med. 2012;209(2):319-334.
[9] FUJIWARA T, ZHOU J, YE S, et al. RNA-binding protein Musashi2 induced by RANKL is critical for osteoclast survival. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(7): e2300.
[10] CANALIS E, PARKER K, FENG JQ, et al. Osteoblast lineage-specific effects of notch activation in the skeleton. Endocrinology. 2013;154(2):623-634.
[11] 乔松,许琦,叶子青,等.骨保护素对高龄骨质疏松症患者骨代谢的影响[J].解放军医学杂志,2015,40(6):472-474.
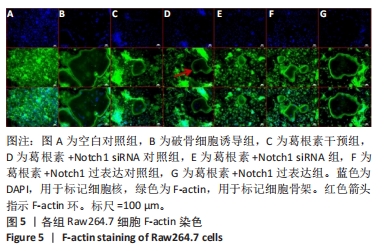
[12] 刘春丽,闫雨娟,莫礼文,等.葛根素对Raw264.7细胞破骨分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(32):5114-5119.
[13] LI X, LI B, SHI Y, et al. Targeing reactive oxygen species in stem cells for bone therapy. Drug Discov Today. 2021;26(5):1226-1244.
[14] LUNDBERG M, SUN S, EBETINO FH, et al. Osteoclasts recycle via osteomorphs during RANKL-stimulated bone resorption. Cell. 2021; 184(5):1330-1347.
[15] ABDELMAGID SM, SONDAG GR, MOUSSA FM, et al. Mutation in Osteoactivin Promotes Receptor Activator of NFκB Ligand (RANKL)-mediated Osteoclast Differentiation and Survival but Inhibits Osteoclast Function. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(33):20128-20146.
[16] KIM H, LEE K, KIM JM, et al. Selenoprotein W ensures physiological bone remodeling by preventing hyperactivity of osteoclasts. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2258.
[17] VAN DEN MOLEN E. Penicilline en streptomycine bij periodontitis en paradentitis [Penicillin and streptomycin in the treatment of periodontitis and paradentitis]. Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 1950;57(5):376-379.
[18] 路瑞芳,徐莉,冯向辉,等.侵袭性牙周炎基础治疗中不同时机口服抗生素的短期疗效观察[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2012,47(11): 666-670.
[19] 梁向阳,李春年.雷尼酸锶对实验性牙周炎大鼠牙槽骨改建的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2021,37(4):310-313.
[20] KULCZYŃSKI B, GRAMZA-MICHAŁOWSKA A, SULIBURSKA J, et al. Puerarin-an isoflavone with beneficial effects on bone health. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021;26(12):1653-1667.
[21] ZHOU YX, ZHANG H, PENG C. Puerarin: a review of pharmacological effects. Phytother Res. 2014;28(7):961-975.
[22] 朱庆磊,吕欣然,何爱霞.葛根素对氧自由基的清除和抗氧化性损伤作用[J].解放军药学学报,2001,17(1):1-3,13.
[23] MIZUKAMI J, TAKAESU G, AKATSUKA H, et al. Receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) activates TAK1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase through a signaling complex containing RANK, TAB2, and TRAF6. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(4):992-1000.
[24] XIE BP, SHI LY, LI JP, et al. Oleanolic acid inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via ER alpha/miR-503/RANK signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;117:109045.
[25] SANO T, AKEDA K, YAMADA J, et al. Expression of the RANK/RANKL/OPG system in the human intervertebral disc: implication for the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):225.
[26] ARTAVANIS-TSAKONAS S, RAND MD, LAKE RJ. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999; 284(5415):770-776.
[27] HAYMAN AR. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) and the osteoclast/immune cell dichotomy. Autoimmunity. 2008;41(3): 218-223.
[28] 刘官娟,宋娜,霍花,等.唑来膦酸调控NLRP3信号通路抑制脂多糖诱导的破骨细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(29): 4677-4683.
[29] MATSUNO K. Notch signaling. Dev Growth Differ. 2020;62(1):3.
[30] PENTON AL, LEONARD LD, SPINNER NB. Notch signaling in human development and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012;23(4):450-457.
[31] EHEBAUER M, HAYWARD P, MARTINEZ-ARIAS A. Notch signaling pathway. Sci STKE. 2006;2006(364):cm7.
[32] FANG ZQ, RUAN B, LIU JJ, et al. Notch-triggered maladaptation of liver sinusoidal endothelium aggravates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Hepatology. 2022;76(3): 742-758.
[33] YOSHIDA G, KAWABATA T, TAKAMATSU H, et al. Degradation of the NOTCH intracellular domain by elevated autophagy in osteoblasts promotes osteoblast differentiation and alleviates osteoporosis. Autophagy. 2022;18(10):2323-2332.
[34] 胡超,李适廷,张纲,等.NICD过表达对人牙髓干细胞细胞增殖及细胞迁移的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2014,24(4):196-201.
[35] 龙晏,邱申彩,李淑慧,等.转化生长因子-β1对人牙周膜干细胞生物学行为的影响[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2018,32(11): 1044-1046.
[36] FILIPOVIĆ M, FLEGAR D, ŠUĆUR A, et al. Inhibition of Notch Signaling Stimulates Osteoclastogenesis From the Common Trilineage Progenitor Under Inflammatory Conditions. Front Immunol. 2022;13:902947.
[37] BALLHAUSE TM, JIANG S, BARANOWSKY A, et al. Relevance of Notch Signaling for Bone Metabolism and Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(3):1325.
[38] 康鑫.葛根素促进成骨细胞增殖及信号调控机制的实验研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2015.
[39] 冯燕陵. FoxO1介导白藜芦醇、葛根素抑制破骨细胞生成和活性的机制研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2018.
[40] 曾芳馨,熊中云.抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶与骨代谢[J].华西医学,2005, 20(3):545.
[41] JULES J, CHEN W, FENG X, et al. C/EBPα transcription factor is regulated by the RANK cytoplasmic 535IVVY538 motif and stimulates osteoclastogenesis more strongly than c-Fos. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(4): 1480-1492.
[42] ARMSTRONG AP, TOMETSKO ME, GLACCUM M, et al. A RANK/TRAF6-dependent signal transduction pathway is essential for osteoclast cytoskeletal organization and resorptive function. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277(46):44347-44356.
|