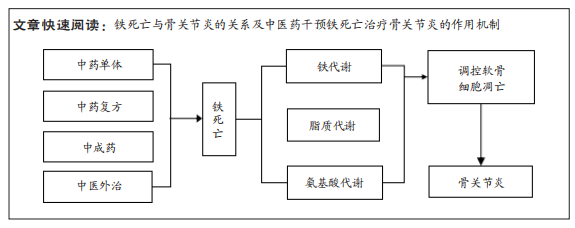
[1] RUBIO JE, SCANZELLO C, FELSON DT, et al. Correlation between senescence-associated secretory phenotypes factors in synovial fluid and serum and structural changes in osteoarthritis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2020;7(1):44-45.
[2] PIVA SR, SUSKO AM, KHOJA SS, et al. Links between osteoarthritis and diabetes:implications for management from a physical activity perspective. Clin Geriatr Med. 2015;31(1):67-87.
[3] 廖德发.我国骨性关节炎流行病学调查现状[J].微创医学,2017,12(4):521-524.
[4] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020,104(2):293-311.
[5] 邢丹,林剑浩.《骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)》更新解读及方法学评价[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2019,13(4):391-395.
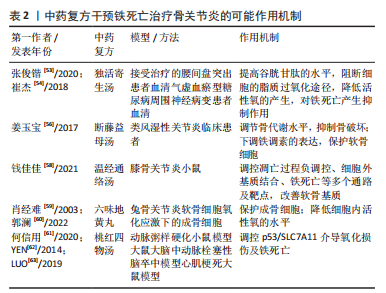
[6] 张俊锴.针刀松解术治疗膝骨关节炎的临床疗效观察[J].深圳中西医结合杂志, 2019,29(22):57-58.
[7] 庾明,张廷玖,张东.中药离子导入联合膝关节镜清理术治疗膝骨性关节炎的临床疗效及机制[J].西部医学,2018,30(8):1138-1142.
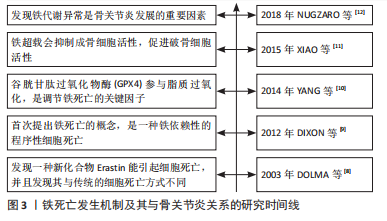
[8] DOLMA S, LESSNICK SL, HAHN WC, et al. Identification of genotype-selective antitumor agents using synthetic lethal chemical screening in engineered human tumor cells. Cancer Cell. 2003;3(3):285-296.
[9] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072.
[10] YANG WS, SRIRAMARATNAM R, WELSCH ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156(1-2):317-331.
[11] XIAO W, BEIBEI F, GUANGSI S, et al.Iron overload increases osteoclastogenesis and aggravates the effects of ovariectomy on bone mass. J Endocrinol. 2015;226(3):121-134.
[12] NUGZAR O, ZANDMAN-GODDARD G, OZ H, et al. The role of ferritin and adiponectin as predictors of cartilage damage assessed by arthroscopy in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32(5):662-668.
[13] ZHAO LR, XING RL, WANG PM, et al. NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes mediate LPS/ATP induced pyroptosis in knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(4): 5463-5469.
[14] XY A, KAI SA, SY B, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2021;27:33-43.
[15] KAZAN K, KALAIPANDIAN S. Ferroptosis: Yet Another Way to Die. Trends Plant Sci. 2019; 24(6):479-481.
[16] XIE Y, HOU W, SONG X, et al. Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016; 23(3):369-379.
[17] WOO JH, SHIMONI Y, YANG WS, et al. Elucidating Compound Mechanism of Action by Network Perturbation Analysis. Cell. 2015;162(2):441-451.
[18] STOCKWELL BR, FRIEDMANN AJ, BAYIR H, et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology,and Disease. Cell. 2017;171(2):273-285.
[19] TANG D, KANG R, BERGHE TV, et al.The molecular machinery of regulated cell death. Cell Res. 2019;29(5):347-364.
[20] MUCKENTHALER MU, RIVELLA S, HENTZE MW, et al. A red carpet for iron metabolism. Cell. 2017;168(3):344-361.
[21] HAO S, LIANG B, HUANG Q, et al. Metabolic networks in ferroptosis. Oncol Lett. 2018; 15(4):5405-5411.
[22] VERMA P, DALAL K. ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5: Key enzymes in osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(12):3507-3514.
[23] EL-SAYED ME, ASMAA KF, SAMAR E, et al. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: An updated review. Life Sci. 2019;234:116786.
[24] SALERNO A, BRADY K, RIKKERS M, et al. MMP13 and TIMP1 are functional markers for two different potential modes of action by mesenchymal stem/stromal cells when treating osteoarthritis. Stem Cells. 2020;38(11):1438-1453.
[25] SHIOMI T, LEMAÎTRE V, D’ARMIENTO J, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases, a disintegrin and metalloproteinases,and a disintegrin and metalloproteinases with thrombospondin motifs in non‐neoplastic diseases. Pathol Int. 2010;60(7):477-496.
[26] JING X, LIN J, DU T, et al. Iron overload is associated with accelerated progression of osteoarthritis: the role of DMT1 mediated iron homeostasis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021; 8:594509.
[27] SIMÃO M, GAVAIA PJ, CAMACHO A, et al. Intracellular iron uptake is favored in Hfe‐KO mouse primary chondrocytes mimicking an osteoarthritis‐related phenotype. Biofactors.2019;45(4):583-597.
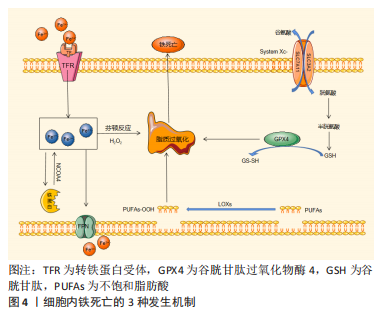
[28] GAO M, MONIAN P, QUADRI N, et al. Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol Cell. 2015;59(2):298-308.
[29] KAGAN VE, MAO G, QU F, et al. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;13(1):81-90.
[30] FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, SCHNEIDER M, PRONETH B, et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16(12):1180-1191.
[31] PIEPOLI T, MENNUNI L, ZERBI S, et al. Glutamate signaling in chondrocytes and the potential involvement of NMDA receptors in cell proliferation and inflammatory gene expression. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(8):1076-1083.
[32] KALEV-ZYLINSKA ML, HEARN JI, RONG J, et al. Altered N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subunit expression causes changes to the circadian clock and cell phenotype in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(11):1518-1530.
[33] STOYANOVSKY DA, TYURINA YY, SHRIVASTAVA I, et al. Iron catalysis of lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis:regulated enzymatic or random free radical reaction?. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133:153-161.
[34] YANG WS, KIM KJ, GASCHLER MM, et al. Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(34):E4966-E4975.
[35] BAKER KR, MATTHAN NR, LICHTENSTEIN AH, et al. Association of plasma n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids with synovitis in the knee:the MOST study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(5):382-387.
[36] LOEF M, SCHOONES JW, KLOPPENBURG M, et al. Fatty acids and osteoarthritis:different types, different effects. Joint Bone Spine. 2019;86(4):451-458.
[37] FREY N, HÜGLE T, JICK SS, et al. Hyperlipidaemia and incident osteoarthritis of the hand: a population-based case-control study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(7):1040-1045.
[38] ZHOU M, GUO Y, WANG D, et al. The cross-sectional and longitudinal effect of hyperlipidemia on knee osteoarthritis: Results from the Dongfeng-Tongji cohort in China. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):9739.
[39] BAUDART P, LOUATI K, MARCELLI C, et al. Association between osteoarthritis and dyslipidaemia:a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. RMD Open. 2017;3(2): e000442.
[40] FARNAGHI S, CRAWFORD R, XIAO Y, et al. Cholesterol metabolism in pathogenesis of osteoarthritis disease. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017;20(2):131-140.
[41] GKRETSI V, SIMOPOULOU T, TSEZOU A, et al. Lipid metabolism and osteoarthritis:lessons from atherosclerosis. Prog Lipid Res. 2011;50(2):133-140.
[42] IOAN-FACSINAY A, KLOPPENBURG M. Bioactive lipids in osteoarthritis: risk or benefit? Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018;30(1):108-113.
[43] MA TL, CHEN JX, ZHU P, et al. Focus on ferroptosis regulation: exploring novel mechanisms and applications of ferroptosis regulator. Life Sci. 2022;307:120868.
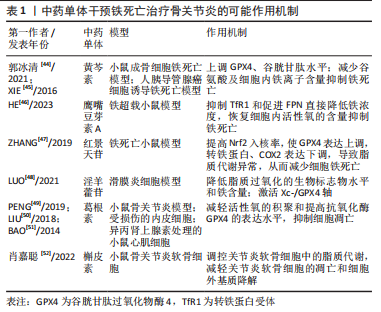
[44] 郭冰清.黄芩素对erastin诱导成骨细胞铁死亡的影响及潜在机制[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2021.
[45] XIE Y, SONG X, SUN X, et al. Identification of baicalein as a ferroptosis inhibitor by natural product library screening. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;473(4):775-780.
[46] HE Q, YANG J, PAN Z, et al. Biochanin A protects against iron overload associated knee osteoarthritis via regulating iron levels and NRF2/System xc-/GPX4 axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;157:113915.
[47] ZHANG W, HUAI Y, MIAO Z, et al. Systems pharmacology approach to investigate the molecular mechanisms of herb Rhodiola rosea L. radix. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019;45(3):456-464.
[48] LUO H, ZHANG R. Icariin enhances cell survival in lipopolysaccharide induced synoviocytes by suppressing ferroptosis via the Xc /GPX4 axis. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(1):1-1.
[49] PENG L, XIE Z, PEI J, et al. Puerarin alters the function of monocytes/macrophages and exhibits chondroprotection in mice. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(4):2876-2882.
[50] LIU B, ZHAO C, LI H, et al. Puerarin protects against heart failure induced by pressure overload through mitigation of ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497(1): 233-240..
[51] BAO M, ZHANG Y, LOU X, et al. Puerarin protects endothelial cells from oxidized low density lipoprotein induced injuries via the suppression of LOX-1 and induction of eNOS. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;92(4):299-306
[52] 肖嘉聪,麦嘉乐,张罡瑜,等.槲皮素调控关节炎软骨细胞胆固醇代谢的机制研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(9):1336-1341.
[53] 张俊锴,肖斌,许啸.独活寄生汤联合针刺治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床效果[J].世界中医药,2020,15(7):1067-1070.
[54] 崔杰,谈力欣,牛素贞,等.独活寄生汤口服或熏蒸对气虚血瘀型糖尿病周围神经病变患者MDA和GSH-Px水平的影响[J].江苏中医药,2018,50(12):27-30.
[55] LO SC, HANNINK M. PGAM5, a Bcl-XL-interacting protein, is a novel substrate for the redox-regulated Keap1-dependent ubiquitin ligase complex. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(49): 37893-37903.
[56] 姜玉宝.基于铁调素探讨断藤益母汤对类风湿关节炎骨代谢的影响及作用机制[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2017.
[57] WANG CY, BABITT JL. Liver iron sensing and body iron homeostasis. Blood. 2019;133(1): 18-29.
[58] 钱佳佳.基于蛋白组学研究温经通络汤调控血管新生治疗膝骨关节炎的作用机制[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2021.
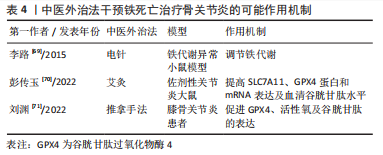
[59] 肖经难,谢丹,祁开泽.六味地黄丸对兔骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].长沙:湖南中医学院学报,2003(5):11-13.
[60] 郭澜.基于ERK/mTOR通路调控自噬探讨六味地黄丸减轻成骨细胞氧化应激损伤的分子机制[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2022.
[61] 何信用,王俊岩,宋囡,等.二陈汤合桃红四物汤调控p53/SLC7A11介导的氧化损伤及铁死亡抗动脉粥样硬化的作用及机制研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(5): 2344-2348.
[62] YEN TL, ONG ET, LIN KH, et al. Potential advantages of Chinese medicine Taohong Siwu Decoction (桃红四物汤) combined with tissue-plasminogen activator for alleviating middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced embolic stroke in rats. Chin J Integr Med. 2014 Sep 24. doi: 10.1007/s11655-014-1847-x.
[63] LUO ZR, LI H, XIAO X, et al. Taohong Siwu Decoction Exerts a Beneficial Effect on Cardiac Function by Possibly Improving the Microenvironment and Decreasing Mitochondrial Fission after Myocardial Infarction. Cardiol Res Pract. 2019;2019:5198278.
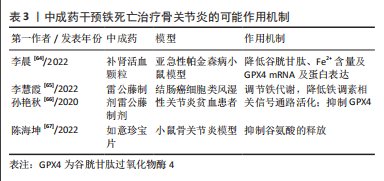
[64] 李晨,王鹏,王亮,等.补肾活血颗粒对亚急性帕金森病模型小鼠脑黑质多巴胺神经元铁死亡的影响[J].中医杂志,2022,63(15):1463-1469.
[65] 李慧霞,尤伟波,陈丽,等.谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4在雷公藤内酯酮激活结肠癌细胞铁死亡中的作用[J].浙江医学,2022,44(10):1038-1041.
[66] 孙艳秋,刘健,黄旦,等.不同雷公藤制剂对类风湿关节炎贫血患者的疗效及其机制[J].中国免疫学杂志,2020,36(3):360-364.
[67] 陈海坤,柏虎虎,李宇哲,等.如意珍宝片对骨关节炎性痛的抑制作用[J].中国药理学通报,2022,28(10):1579-1585.
[68] 白晓东,李顺月,宋晓晶,等.针灸治疗仪作用原理及其临床应用[J].中华中医药杂志,2015,30(2):488-491.
[69] 李路,张立德.电针双侧足三里、三阴交穴治疗脾气虚证大鼠和对机体铁代谢影响实验研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2015,17(7):81-85.
[70] 彭传玉,胡玲,吴子建,等.艾灸对佐剂性关节炎大鼠脊髓中N-甲基-D天冬氨酸受体-一氧化氮-环鸟苷酸通路的影响[J].针刺研究,2022,47(3):250-255.
[71] 刘渊,邓健,孙雪莲,等.足阳明经筋手法治疗对膝关节骨性关节炎患者股四头肌力学性能及软骨细胞铁死亡的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(9):5504-5507. |