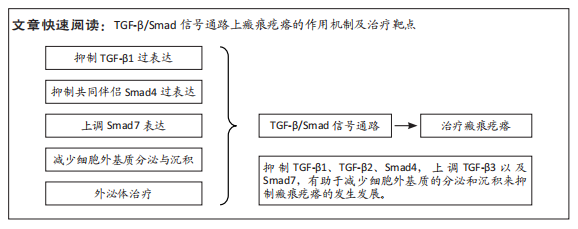
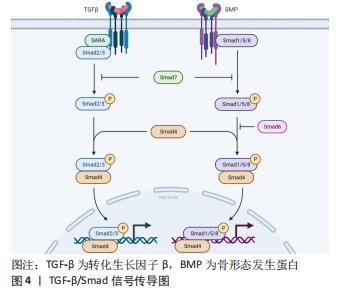
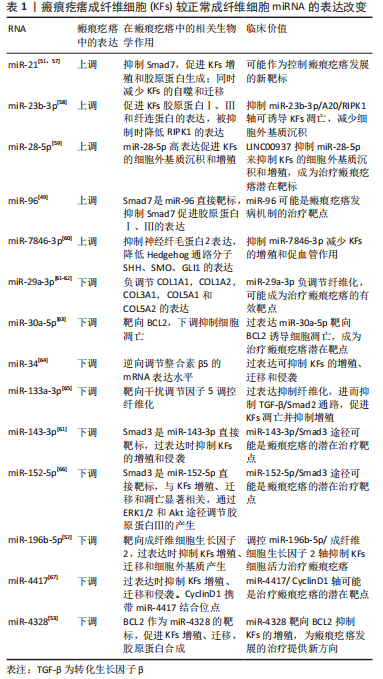
[1] OGAWA R. Keloid and Hypertrophic Scars Are the Result of Chronic Inflammation in the Reticular Dermis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):606.
[2] KIM SW. Management of keloid scars: noninvasive and invasive treatments. Arch Plast Surg. 2021;48(2):149-157.
[3] LEI R, LI J, LIU F, et al. HIF-1alpha promotes the keloid development through the activation of TGF-beta/Smad and TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathways. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(23):3239-3250.
[4] STONE RC, CHEN V, BURGESS J, et al. Genomics of Human Fibrotic Diseases: Disordered Wound Healing Response. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22): 8590.
[5] LIU R, XIAO H, WANG R, et al. Risk factors associated with the progression from keloids to severe keloids. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022;135(7):828-836.
[6] LU YY, TU HP, WU CH, et al. Risk of cancer development in patients with keloids. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):9390.
[7] HUGUIER V, GIOT JP, SIMONNEAU M, et al. Oncostatin M exerts a protective effect against excessive scarring by counteracting the inductive effect of TGFbeta1 on fibrosis markers. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):2113.
[8] LU YY, WU CH, HONG CH, et al. GLUT-1 Enhances Glycolysis, Oxidative Stress, and Fibroblast Proliferation in Keloid. Life (Basel). 2021;11(6):505.
[9] ZHANG T, WANG XF, WANG ZC, et al. Current potential therapeutic strategies targeting the TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway to attenuate keloid and hypertrophic scar formation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110287.
[10] MARTY P, CHATELAIN B, LIHOREAU T, et al. Halofuginone regulates keloid fibroblast fibrotic response to TGF-beta induction. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021; 135:111182.
[11] KIM J, KIM B, KIM SM, et al. Hypoxia-Induced Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition Mediates Fibroblast Abnormalities via ERK Activation in Cutaneous Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2546.
[12] ILIES RF, AIOANEI CS, CATANA A, et al. Involvement of COL5A2 and TGF-beta1 in pathological scarring. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(4):1067.
[13] WANG XM, LIU XM, WANG Y, et al. Activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) regulates cell growth, apoptosis, invasion and collagen synthesis in keloid fibroblast through transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)/SMAD signaling pathway. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):117-126.
[14] LIU X, CHEN W, ZENG Q, et al. Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Reveals Lineage-Specific Regulatory Changes of Fibroblasts and Vascular Endothelial Cells in Keloids. J Invest Dermatol. 2022;142(1):124-135 e11.
[15] ZHOU BY, WANG WB, WU XL, et al. Nintedanib inhibits keloid fibroblast functions by blocking the phosphorylation of multiple kinases and enhancing receptor internalization. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41(9):1234-1245.
[16] LI XY, WENG XJ, LI XJ, et al. TSG-6 Inhibits the Growth of Keloid Fibroblasts Via Mediating the TGF-beta1/Smad Signaling Pathway. J Invest Surg. 2021;34(9): 947-956.
[17] DOLIVO D, WEATHERS P, DOMINKO T. Artemisinin and artemisinin derivatives as anti-fibrotic therapeutics. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(2):322-339.
[18] CUI J, JIN S, JIN C, et al. Syndecan-1 regulates extracellular matrix expression in keloid fibroblasts via TGF-beta1/Smad and MAPK signaling pathways. Life Sci. 2020;254:117326.
[19] LI SN, WU JF. TGF-beta/SMAD signaling regulation of mesenchymal stem cells in adipocyte commitment. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):41.
[20] BETARBET U, BLALOCK TW. Keloids: A Review of Etiology, Prevention, and Treatment. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13(2):33-43.
[21] XU JH, XU SQ, DING SL, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviate the formation of pathological scars in rats. Regen Ther. 2022;20:86-94.
[22] 贾文斌,谭谦.病理性瘢痕的非手术治疗新进展[J].中国美容医学,2023, 32(1):183-189.
[23] KIM S, LEE SE, YI S, et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Decreases Keloid Formation by Reducing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress as Implicated in the Pathogenesis of Keloid. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(19):10765.
[24] LI X, ZHAI Y, XI B, et al. Pinocembrin Ameliorates Skin Fibrosis via Inhibiting TGF-beta1 Signaling Pathway. Biomolecules. 2021;11(8):1240.
[25] WANG X, GU C, SHANG F, et al. Inhibitory Effect of the LY2109761 on the Development of Human Keloid Fibroblasts. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2021;2021: 8883427.
[26] YANG S, LUO YJ, LUO C. Network Meta-Analysis of Different Clinical Commonly Used Drugs for the Treatment of Hypertrophic Scar and Keloid. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021; 8:691628.
[27] 尚念胜,牛燕英. A型肉毒毒素对瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞TGF-β/Smad通路和ERK通路表达的影响[J].中国美容医学,2020,29(5):104-109.
[28] 黄立军,王瑞肖,徐瑞,等. A型肉毒素治疗瘢痕疙瘩的疗效[J].安徽医学, 2023,44(2):162-165.
[29] NAGAR H, KIM S, LEE I, et al. Downregulation of CR6-interacting factor 1 suppresses keloid fibroblast growth via the TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):500.
[30] HE L, ZHU C, DOU H, et al. Keloid Core Factor CTRP3 Overexpression Significantly Controlled TGF-beta1-Induced Propagation and Migration in Keloid Fibroblasts. Dis Markers. 2023;2023:9638322.
[31] WANG M, CHEN L, HUANG W, et al. Improving the anti-keloid outcomes through liposomes loading paclitaxel-cholesterol complexes. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019; 14:1385-1400.
[32] MINGYUAN X, QIANQIAN P, SHENGQUAN X, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha activates transforming growth factor-beta1/Smad signaling and increases collagen deposition in dermal fibroblasts. Oncotarget. 2018;9(3):3188-3197.
[33] LIN X, WANG Y, JIANG Y, et al. Sumoylation enhances the activity of the TGF-beta/SMAD and HIF-1 signaling pathways in keloids. Life Sci. 2020;255:117859.
[34] ZHOU R, WANG C, WEN C, et al. miR-21 promotes collagen production in keloid via Smad7. Burns. 2017;43(3):555-561.
[35] STEVENSON AW, DENG Z, ALLAHHAM A, et al. The epigenetics of keloids. Exp Dermatol. 2021;30(8):1099-1114.
[36] LIU F, LI T, ZHAN X. Silencing circular RNAPTPN12 promoted the growth of keloid fibroblasts by activating Wnt signaling pathway via targeting microRNA-21-5p. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2):3503-3515.
[37] LI Z, GONG C, WEI H. Long non-coding RNA H19 aggravates keloid progression by upregulating SMAD family member 5 expression via miR-196b-5p. Bioengineered. 2022;13(1):1447-1458.
[38] XU L, SUN N, LI G, et al. LncRNA H19 promotes keloid formation through targeting the miR-769-5p/EIF3A pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(3):1477-1487.
[39] YUAN R, DAI X, LI Y, et al. Exosomes from miR-29a-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce excessive scar formation by inhibiting TGF-beta2/Smad3 signaling. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(5):758.
[40] MORETTI L, STALFORT J, BARKER TH, et al. The interplay of fibroblasts, the extracellular matrix, and inflammation in scar formation. J Biol Chem. 2022; 298(2):101530.
[41] 羊剑秋,高以红,朱红柳.重组人源Ⅲ型胶原蛋白功能凝胶对皮肤创口愈合的疗效及其机制[J].山东医药,2021,61(34):80-83.
[42] 杨帅,蒋小姣,马海燕.超脉冲点阵CO2激光联合窄谱强脉冲光治疗创伤后早期增生性瘢痕效果分析[J].中国美容医学,2022,31(2):58-61.
[43] OJEH N, BHARATHA A, GAUR U, et al. Keloids: Current and emerging therapies. Scars Burn Heal. 2020;6:2059513120940499.
[44] ZHENG W, WU H, LI Y, et al. Phenalen-1-one-mediated photodynamic therapy inhibits keloid graft progression by reducing vessel formation and promoting fibroblast apoptosis. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2021;30(4):431-439.
[45] 游传华,王一贺,陆雪飞.光动力对瘢痕疙瘩的抑制效果研究[J].中国医疗美容,2019,9(5):55-58.
[46] LI J, LI Z, WANG S, et al. Exosomes from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit production of extracellular matrix in keloid fibroblasts via downregulating transforming growth factor-beta2 and Notch-1 expression. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):8515-8525.
[47] BOJANIC C, TO K, HATOUM A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in hypertrophic and keloid scars. Cell Tissue Res. 2021;383(3):915-930.
[48] ZHOU C, ZHANG B, YANG Y, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):107.
[49] CHAO L, HUA-YU Z, WEN-DONG B, et al. miR-96 promotes collagen deposition in keloids by targeting Smad7. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(1):773-781.
[50] SHEN Z, SHAO J, SUN J, et al. Exosomes released by melanocytes modulate fibroblasts to promote keloid formation: a pilot study. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022;23(8):699-704.
[51] LI Q, FANG L, CHEN J, et al. Exosomal MicroRNA-21 Promotes Keloid Fibroblast Proliferation and Collagen Production by Inhibiting Smad7. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42(6):1266-1274.
[52] YANG J, DENG P, QI Y, et al. NEAT1 Knockdown Inhibits Keloid Fibroblast Progression by miR-196b-5p/FGF2 Axis. J Surg Res. 2021;259:261-270.
[53] TANG H, CHEN Q, YU W, et al. MiR-4328 inhibits proliferation, metastasis and induces apoptosis in keloid fibroblasts by targeting BCL2 expression. Open Life Sci. 2020;15(1):638-646.
[54] SHI J, YAO S, CHEN P, et al. The integrative regulatory network of circRNA and microRNA in keloid scarring. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(1):201-209.
[55] HU H, MAO G, ZHENG J, et al. Keloid Patient Plasma-Derived Exosomal hsa_circ_0020792 Promotes Normal Skin Fibroblasts Proliferation, Migration, and Fibrogenesis via Modulating miR-193a-5p and Activating TGF-beta1/Smad2/3 Signaling. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16:4223-4234.
[56] 陶瑞,谭植襄,李思成,等.外泌体在增生性瘢痕和瘢痕疙瘩治疗中的研究进展[J].临床外科杂志,2022,30(12):1196-1199.
[57] YAN L, WANG LZ, XIAO R, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-21-5p reduces keloid fibroblast autophagy and migration by targeting PTEN after electron beam irradiation. Lab Invest. 2020;100(3):387-399.
[58] KUAI Q, JIAN X. Inhibition of miR-23b-3p Ameliorates Scar-Like Phenotypes of Keloid Fibroblasts by Facilitating A20 Expression. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:1549-1559.
[59] WAN J, HE XL, JIAN QC, et al. LINC00937 suppresses keloid fibroblast proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting the miR-28-5p/MC1R axis. Histol Histopathol. 2021;36(9):995-1005.
[60] WU D, LIU X, JIN Z. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-sourced exosomal microRNA-7846-3p suppresses proliferation and pro-angiogenic role of keloid fibroblasts by suppressing neuropilin 2. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15721.
[61] HE Y, ZHANG Z, YIN B, et al. Identifying miRNAs Associated with the Progression of Keloid through mRNA-miRNA Network Analysis and Validating the Targets of miR-29a-3p in Keloid Fibroblasts. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:6487989.
[62] GALLANT-BEHM CL, PIPER J, LYNCH JM, et al. A MicroRNA-29 Mimic (Remlarsen) Represses Extracellular Matrix Expression and Fibroplasia in the Skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139(5):1073-1081.
[63] JIAN X, QU L, WANG Y, et al. Trichostatin A‑induced miR‑30a‑5p regulates apoptosis and proliferation of keloid fibroblasts via targeting BCL2. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(6):5251-5262.
[64] JIANG L, SHI X, WANG M, et al. Study on the Mechanism of miR-34a Affecting the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Human Keloid Fibroblasts by Regulating the Expression of SATB1. J Healthc Eng. 2021;2021:8741512.
[65] HUANG Y, WANG Y, LIN L, et al. Overexpression of miR-133a-3p inhibits fibrosis and proliferation of keloid fibroblasts by regulating IRF5 to inhibit the TGF-beta/Smad2 pathway. Mol Cell Probes. 2020;52:101563.
[66] PANG Q, WANG Y, XU M, et al. MicroRNA-152-5p inhibits proliferation and migration and promotes apoptosis by regulating expression of Smad3 in human keloid fibroblasts. BMB Rep. 2019;52(3):202-207.
[67] LIU P, HU Y, XIA L, et al. miR-4417 suppresses keloid fibrosis growth by inhibiting CyclinD1. J Biosci. 2020;45:47.
[68] 谭欢,张远理,唐原,等.瘢痕疙瘩患者128例生活质量评估及影响因素分析[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志,2021,35(2):200-204.
[69] LU W, CHU H, ZHENG X. Effects on quality of life and psychosocial wellbeing in Chinese patients with keloids. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(3):1636-1642.
[70] 王畅,陈炜,王宝家.阿魏酸钠对人皮肤增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖和凋亡的调控作用及其信号机制[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2022,38(5):471-480.
[71] 徐琦,刘伟.不良饮食习惯影响瘢痕疙瘩形成的研究进展[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2022,38(4):389.
[72] LOMBARDI F, AUGELLO FR, ARTONE S, et al. Efficacy of probiotic Streptococcus thermophilus in counteracting TGF-beta1-induced fibrotic response in normal human dermal fibroblasts. J Inflamm (Lond). 2022;19(1):27. |