中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (32): 5120-5125.doi: 10.12307/2023.539
• 皮肤粘膜组织构建 skin and mucosal tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
铁死亡诱导剂抑制增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞的增殖
贺 茜1,2,3,万 瑀1,2,3,唐玉婷1,2,3,杨安宁2,4,吴 凯4,焦 运5,白志刚6,姜怡邓2,4,沈江涌3
- 宁夏医科大学,1临床医学院,2国家卫生健康委代谢性心血管疾病研究重点实验室,4基础医学院,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004;宁夏医科大学总医院,3烧伤整形外科,5感染科,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004;6宁夏回族自治区人民医院骨科,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004
Erastin inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts
He Xi1, 2, 3, Wan Yu1, 2, 3, Tang Yuting1, 2, 3, Yang Anning2, 4, Wu Kai4, Jiao Yun5, Bai Zhigang6, Jiang Yideng2,4, Shen Jiangyong3
- 1School of Clinical Medicine, 2State Key Laboratory of Metabolic Cardiovascular Disease, National Health Commission of China, 4School of Basic Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Burn Plastic Surgery, 5Department of Infection, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 6Department of Orthopedics, People’s Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
铁死亡:是一种依赖铁离子参与、脂质过氧化物累积而导致的细胞死亡。
Erastin:是一种铁死亡诱导剂,可以诱导包括成纤维细胞在内的许多种类细胞发生铁死亡。
背景:增生性瘢痕是各种原因导致的皮肤创伤后愈合过程中出现的一种病理性瘢痕,目前缺乏特效治疗方法。
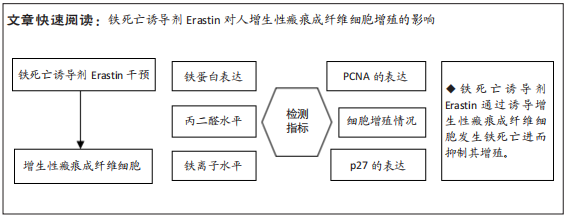
目的:探讨铁死亡诱导剂Erastin对人增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖的影响。
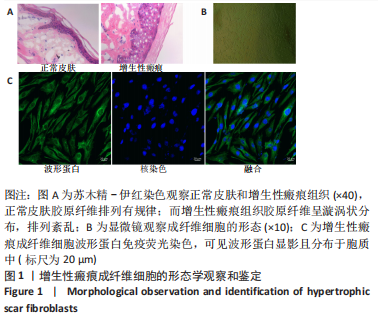
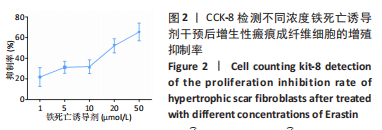
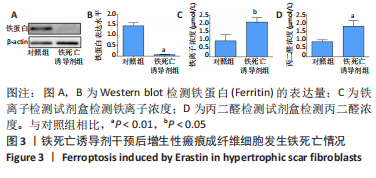
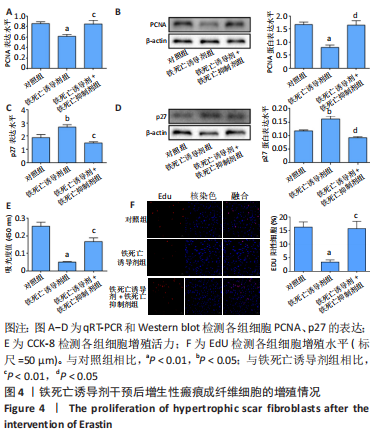
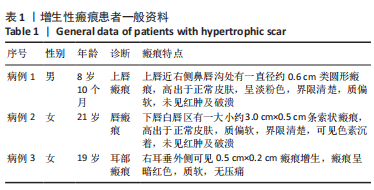
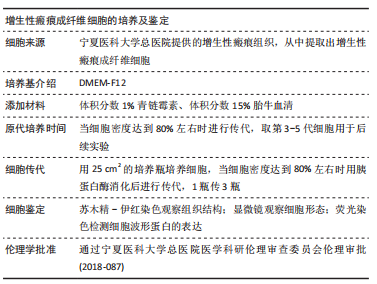
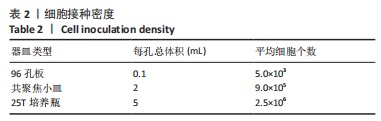
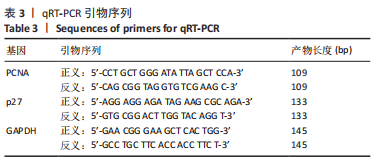
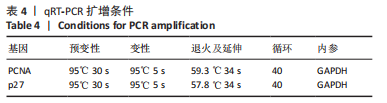
方法:收集宁夏医科大学总医院烧伤整形外科提供的增生性瘢痕组织和同一个体正常皮肤,提取人增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞进行后续实验。将细胞分为对照组(不做处理)和铁死亡诱导剂组(用20 μmol/L的Erastin干预细胞24 h),Western blot检测铁蛋白(Ferritin)的表达,铁离子检测试剂盒测定细胞铁离子浓度,丙二醛检测试剂盒检测细胞丙二醛水平;将细胞分为对照组(不做处理)、铁死亡诱导剂组(用20 μmol/L的Erastin干预细胞24 h)和铁死亡诱导剂+铁死亡抑制剂组(用20 μmol/L的Erastin和20 μmol/L的Ferrostatin-1同时干预细胞24 h),qRT-PCR检测PCNA及p27的mRNA表达,Western blot检测PCNA及p27的蛋白表达,CCK-8、EdU检测细胞增殖活力和增殖水平。
结果与结论:①与对照组相比,铁死亡诱导剂组铁蛋白减少(P < 0.01),铁离子增多(P < 0.05),丙二醛增多(P < 0.01);②与对照组相比,铁死亡诱导剂组PCNA的表达降低(P < 0.01),p27的表达增加(P < 0.05),细胞增殖能力减弱(P < 0.01),EdU阳性细胞数减少(P < 0.01);③与铁死亡诱导剂组相比,铁死亡诱导剂+铁死亡抑制剂组PCNA的表达增加(P < 0.05),p27的表达降低(P < 0.05),细胞增殖能力增强(P < 0.01),EdU阳性细胞数增多(P < 0.05);④结果表明,铁死亡诱导剂Erastin通过诱导增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞发生铁死亡进而抑制其增殖。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7859-0221(贺茜)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: