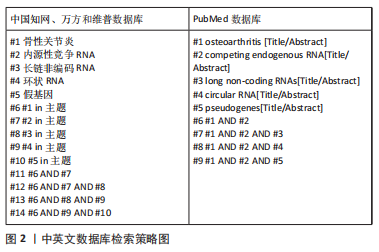
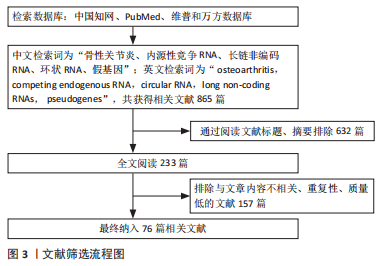
[1] SANCHEZ-LOPEZ E, CORAS R, TORRES A, et al. Guma M. Synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis progression. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(5):258-275.
[2] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072.
[3] MOBASHERI A, BAY-JENSEN AC, VAN SPIL WE, et al. Levesque MC. Osteoarthritis Year in Review 2016: biomarkers (biochemical markers). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(2):199-208.
[4] ALI SA, PEFFERS MJ, ORMSETH MJ, et al. The non-coding RNA interactome in joint health and disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(11):692-705.
[5] GHOURI A, QUICKE JG, CONAGHAN PG. New developments in osteoarthritis pharmacological therapies. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60(Suppl 6):vi1-vi11.
[6] BRUMAT P, KUNŠIČ O, NOVAK S, et al. The Surgical Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Life (Basel). 2022;12(7):982.
[7] ZHOU J, XIONG W, GOU P, et al. Clinical effect of intramuscular calcitonin compared with oral celecoxib in the treatment of knee bone marrow lesions: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):230.
[8] LIU D, LIANG YH, YANG YT, et al. Circular RNA in osteoarthritis: an updated insight into the pathophysiology and therapeutics. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(1):11-23.
[9] BOER CG, HATZIKOTOULAS K, SOUTHAM L, et al. Deciphering osteoarthritis genetics across 826,690 individuals from 9 populations. Cell. 2021;184(18):4784-4818.e17.
[10] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393 (10182): 1745-1759.
[11] LIU HY, CHANG CF, LU CC, et al. The Role of Mitochondrial Metabolism, AMPK-SIRT Mediated Pathway, LncRNA and MicroRNA in Osteoarthritis. Biomedicines. 2022;10(7):1477.
[12] MAO X, CAO Y, GUO Z, et al. Biological roles and therapeutic potential of circular RNAs in osteoarthritis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:856-867.
[13] YAN H, BU P. Non-coding RNA in cancer. Essays Biochem. 2021;65(4):625-639.
[14] SALMENA L, POLISENO L, TAY Y, et al. A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell. 2011;146(3):353-358.
[15] NIE D, FU J, CHEN H, et al. Roles of MicroRNA-34a in Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition, Competing Endogenous RNA Sponging and Its Therapeutic Potential. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):861.
[16] IZAURRALDE E. A role for eIF4AII in microRNA-mediated mRNA silencing. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013;20(5):543-545.
[17] YAO RW, WANG Y, CHEN LL. Cellular functions of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(5):542-551.
[18] RUAN X, LI P, CHEN Y, et al. In vivo functional analysis of non-conserved human lncRNAs associated with cardiometabolic traits. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):45.
[19] BRIDGES MC, DAULAGALA AC, KOURTIDIS A. LNCcation: lncRNA localization and function. J Cell Biol. 2021;220(2):e202009045.
[20] LI J, YANG T, TANG H, et al. Inhibition of lncRNA MAAT Controls Multiple Types of Muscle Atrophy by cis- and trans-Regulatory Actions. Mol Ther. 2021;29(3):1102-1119.
[21] NAPOLI M, LI X, ACKERMAN HD, et al. Pan-cancer analysis reveals TAp63-regulated oncogenic lncRNAs that promote cancer progression through AKT activation. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):5156.
[22] SHIGEYASU K, TODEN S, OZAWA T, et al. The PVT1 lncRNA is a novel epigenetic enhancer of MYC, and a promising risk-stratification biomarker in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):155.
[23] KONG H, SUN ML, ZHANG XA, et al. Crosstalk Among circRNA/lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:774370.
[24] GRAMMATIKAKIS I, LAL A. Significance of lncRNA abundance to function. Mamm Genome. 2022;33(2):271-280.
[25] NÚÑEZ-MARTÍNEZ HN, RECILLAS-TARGA F. Emerging Functions of lncRNA Loci beyond the Transcript Itself. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6258.
[26] ZHANG X, HONG R, CHEN W, et al. The role of long noncoding RNA in major human disease. Bioorg Chem. 2019;92:103214.
[27] WU W, CAO L, JIA Y, et al. Emerging Roles of miRNA, lncRNA, circRNA, and Their Cross-Talk in Pituitary Adenoma. Cells. 2022;11(18):2920.
[28] QIU Y, XU M, HUANG S. Long noncoding RNAs: emerging regulators of normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Blood. 2021;138(23):2327-2336.
[29] HARTFORD CCR, LAL A. When Long Noncoding Becomes Protein Coding. Mol Cell Biol. 2020;40(6):e00528-e00519.
[30] CHARLES RICHARD JL, EICHHORN PJA. Platforms for Investigating LncRNA Functions. SLAS Technol. 2018;23(6):493-506.
[31] ROBINSON EK, COVARRUBIAS S, CARPENTER S. The how and why of lncRNA function: An innate immune perspective. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020;1863(4):194419.
[32] REN S, LIN P, WANG J, et al. Circular RNAs: Promising Molecular Biomarkers of Human Aging-Related Diseases via Functioning as an miRNA Sponge. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020;18:215-229.
[33] CHEN I, CHEN CY, CHUANG TJ. Biogenesis, identification, and function of exonic circular RNAs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2015;6(5):563-579.
[34] SHANG Q, YANG Z, JIA R, et al. The novel roles of circRNAs in human cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):6.
[35] MENG S, ZHOU H, FENG Z, et al. CircRNA: functions and properties of a novel potential biomarker for cancer. Mol Cancer. 2017;16(1):94.
[36] MAO X, CAO Y, GUO Z, et al. Biological roles and therapeutic potential of circular RNAs in osteoarthritis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:856-867.
[37] LI B, LI Y, HU L, et al. Role of Circular RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2020;13(4):572-583.
[38] HOLDT LM, KOHLMAIER A, TEUPSER D. Molecular roles and function of circular RNAs in eukaryotic cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(6):1071-1098.
[39] TANG CM, ZHANG M, HUANG L, et al. CircRNA_000203 enhances the expression of fibrosis-associated genes by derepressing targets of miR-26b-5p, Col1a2 and CTGF, in cardiac fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40342.
[40] HAN B, CHAO J, YAO H. Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: From the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;187:31-44.
[41] GUO L, JIA L, LUO L, et al. Critical Roles of Circular RNA in Tumor Metastasis via Acting as a Sponge of miRNA/isomiR. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(13):7024.
[42] AKHBARI MH, ZAFARI Z, SHEYKHHASAN M. Competing Endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) in Colorectal Cancer: A Review. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2022;24:e27.
[43] CAO M, ZHANG L, WANG JH, et al. Identifying circRNA-associated-ceRNA networks in retinal neovascularization in mice. Int J Med Sci. 2019;16(10):1356-1365.
[44] LIU D, LIANG YH, YANG YT, et al. Circular RNA in osteoarthritis: an updated insight into the pathophysiology and therapeutics. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(1):11-23.
[45] ZANG J, LU D, XU A. The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: An important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J Neurosci Res. 2020;98(1): 87-97.
[46] KHAN FA, NSENGIMANA B, KHAN NH, et al. Chimeric Peptides/Proteins Encoded by circRNA: An Update on Mechanisms and Functions in Human Cancers. Front Oncol. 2022;12:781270.
[47] STASIAK M, KOLENDA T, KOZŁOWSKA-MASŁOŃ J, et al. The World of Pseudogenes: New Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets in Cancers or Still Mystery Molecules? Life (Basel). 2021;11(12):1354.
[48] JACQ C, MILLER JR, BROWNLEE GG. A pseudogene structure in 5S DNA of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1977;12(1):109-120.
[49] QI Y, WANG X, LI W, et al. Pseudogenes in Cardiovascular Disease. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;7:622540.
[50] LIU WH, TSAI ZT, TSAI HK. Comparative genomic analyses highlight the contribution of pseudogenized protein-coding genes to human lincRNAs. BMC Genomics. 2017;18(1):786.
[51] HEZRONI H, BEN-TOV PERRY R, MEIR Z, et al. A subset of conserved mammalian long non-coding RNAs are fossils of ancestral protein-coding genes. Genome Biol. 2017;18(1):162.
[52] MA Y, CHEN Z, YU J. Pseudogenes and their potential functions in hematopoiesis. Exp Hematol. 2021;103:24-29.
[53] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311.
[54] MAO L, WU W, WANG M, et al. Targeted treatment for osteoarthritis: drugs and delivery system. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1):1861-1876.
[55] ZHANG W, QI L, CHEN R, et al Circular RNAs in osteoarthritis: indispensable regulators and novel strategies in clinical implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021; 23(1):23.
[56] Tu J, Huang W, Zhang W, et al. The emerging role of lncRNAs in chondrocytes from osteoarthritis patients. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110642.
[57] OKUYAN HM, BEGEN MA. LncRNAs in Osteoarthritis. Clin Chim Acta. 2022;532: 145-163.
[58] XING D, LIANG JQ, LI Y, et al. Identification of long noncoding RNA associated with osteoarthritis in humans. Orthop Surg. 2014;6(4):288-293.
[59] LU X, YU Y, YIN F, et al. Knockdown of PVT1 inhibits IL-1β-induced injury in chondrocytes by regulating miR-27b-3p/TRAF3 axis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;79:106052.
[60] MAO G, KANG Y, LIN R, et al. Long Non-coding RNA HOTTIP Promotes CCL3 Expression and Induces Cartilage Degradation by Sponging miR-455-3p. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:161.
[61] HU J, WANG Z, SHAN Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes osteoarthritis progression via miR-17-5p/FUT2/β-catenin axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(7):711.
[62] ZHANG G, ZHANG Q, ZHU J, et al. LncRNA ARFRP1 knockdown inhibits LPS-induced the injury of chondrocytes by regulation of NF-κB pathway through modulating miR-15a-5p/TLR4 axis. Life Sci. 2020;261:118429.
[63] CHEN K, FANG H, XU N. LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 is transcriptionally activated by JUND and contributes to osteoarthritis progression via targeting the miR-423-5p/KDM5C axis. Life Sci. 2020;258:118095.
[64] LIU Y, LIU K, TANG C, et al. Long non-coding RNA XIST contributes to osteoarthritis progression via miR-149-5p/DNMT3A axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;128: 110349.
[65] CHEN C, YIN P, HU S, et al. Circular RNA-9119 protects IL-1β-treated chondrocytes from apoptosis in an osteoarthritis cell model by intercepting the microRNA-26a/PTEN axis. Life Sci. 2020;256:117924.
[66] LI BF, ZHANG Y, XIAO J, et al. Hsa_circ_0045714 regulates chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis and extracellular matrix synthesis by promoting the expression of miR-193b target gene IGF1R. Hum Cell. 2017;30(4):311-318.
[67] CHEN G, LIU T, YU B, et al. CircRNA-UBE2G1 regulates LPS-induced osteoarthritis through miR-373/HIF-1a axis. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(13):1696-1705.
[68] ZHANG J, CHENG F, RONG G, et al. Hsa_circ_0005567 Activates Autophagy and Suppresses IL-1β-Induced Chondrocyte Apoptosis by Regulating miR-495. Front Mol Biosci. 2020;7:216.
[69] WANG T, HAO Z, LIU C, et al. LEF1 mediates osteoarthritis progression through circRNF121/miR-665/MYD88 axis via NF-кB signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(7):598.
[70] SHEN P, YANG Y, LIU G, et al. CircCDK14 protects against Osteoarthritis by sponging miR-125a-5p and promoting the expression of Smad2. Theranostics. 2020;10(20):9113-9131.
[71] CHEN X, WAN L, WANG W, et al. Re-recognition of pseudogenes: From molecular to clinical applications. Theranostics. 2020;10(4):1479-1499.
[72] LIU Q, HU X, ZHANG X, et al. The TMSB4 Pseudogene LncRNA Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Promote Cartilage Degradation in Human Osteoarthritis. Mol Ther. 2016;24(10):1726-1733.
[73] YU H, HUANG T, LU WW, et al. Osteoarthritis Pain. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(9):4642.
[74] KONG H, SUN ML, ZHANG XA, et al. Crosstalk Among circRNA/lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:774370.
[75] WANG C, LI N, LIU Q, et al. The role of circRNA derived from RUNX2 in the serum of osteoarthritis and its clinical value. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021;35(7):e23858.
[76] YANG Z, TANG Y, LU H, et al. Long non-coding RNA reprogramming (lncRNA-ROR) regulates cell apoptosis and autophagy in chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(10):8432-8440. |
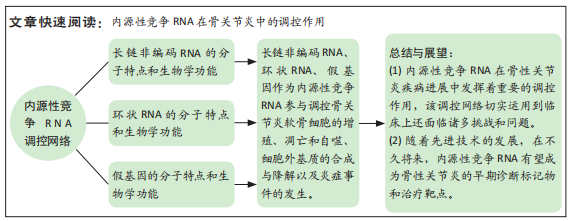

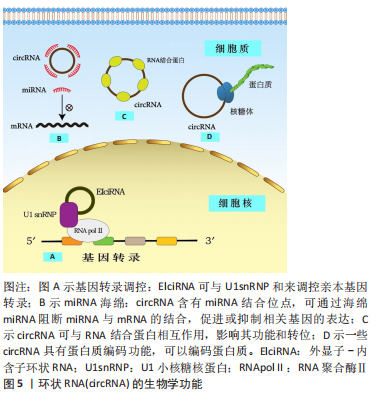
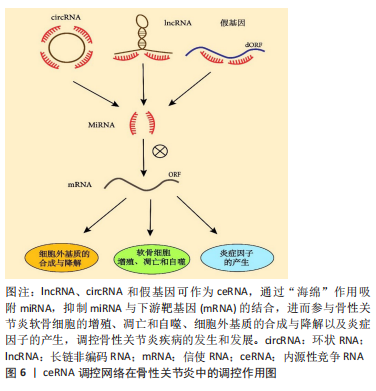

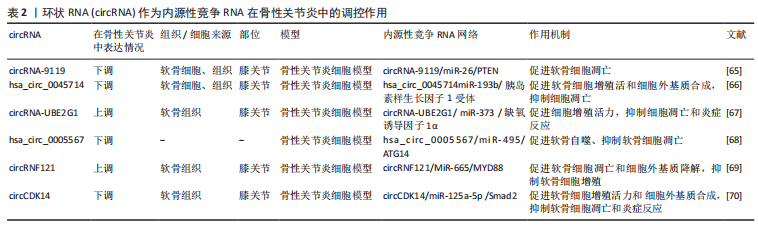

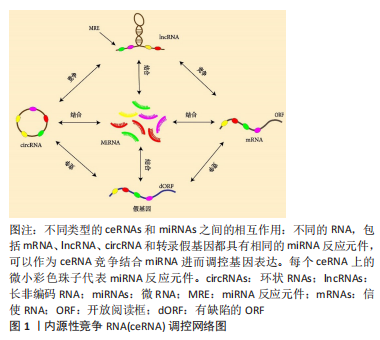 此综述着重阐述lncRNA、circRNA、假基因的重要生物学功能以及它们作为ceRNA在骨性关节炎发病中的调控作用,并且讨论了ceRNA目前存在的局限性以及其运用到骨性关节炎精确医疗中所面临的挑战以及未来前景。这将有助于准确定位骨性关节炎的特定生物标志物和有效的潜在治疗靶点,为骨性关节炎的早期诊断、治疗和疾病的检测管理提供新途径。
此综述着重阐述lncRNA、circRNA、假基因的重要生物学功能以及它们作为ceRNA在骨性关节炎发病中的调控作用,并且讨论了ceRNA目前存在的局限性以及其运用到骨性关节炎精确医疗中所面临的挑战以及未来前景。这将有助于准确定位骨性关节炎的特定生物标志物和有效的潜在治疗靶点,为骨性关节炎的早期诊断、治疗和疾病的检测管理提供新途径。