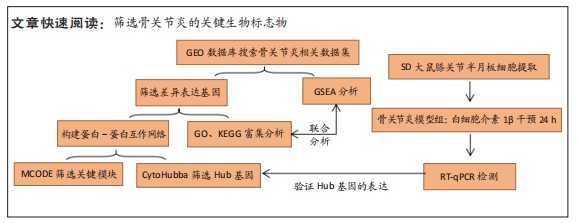
[1] BOYAN BD, TOSI L, COUTTS R, et al. Sex differences in osteoarthritis of the knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(10):668-669.
[2] LESPASIO MJ, PIUZZI NS, HUSNI ME, et al. Knee Osteoarthritis: A Primer. Perm J. 2017;21:16-183.
[3] 韩明睿,刘倩倩,孙洋.骨关节炎发病机制及药物调控新进展[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(6):807-812.
[4] RIM YA, JU JH. The Role of Fibrosis in Osteoarthritis Progression. Life (Basel). 2020;11(1):3.
[5] RIM YA, NAM Y, JU JH. The Role of Chondrocyte Hypertrophy and Senescence in Osteoarthritis Initiation and Progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2358.
[6] ENGLUND M, GUERMAZI A, LOHMANDER SL. The role of the meniscus in knee osteoarthritis: a cause or consequence? Radiol Clin North Am. 2009;47(4):703-712.
[7] BROPHY RH, SANDELL LJ, CHEVERUD JM, et al. Gene expression in human meniscal tears has limited association with early degenerative changes in knee articular cartilage. Connect Tissue Res. 2017;58(3-4):295-304.
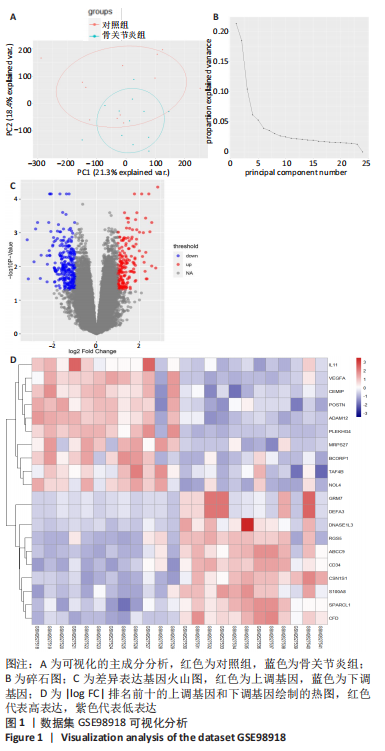
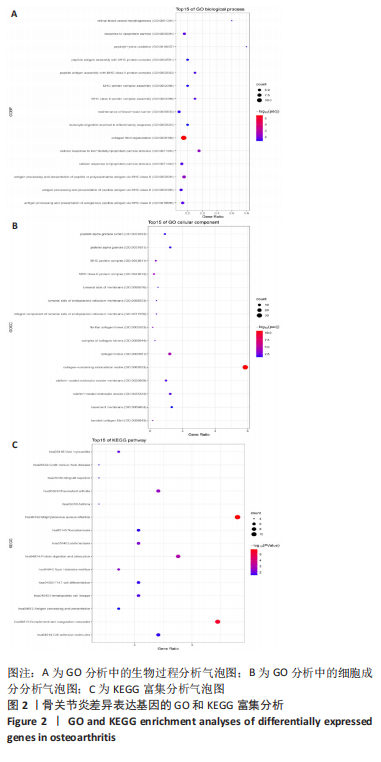
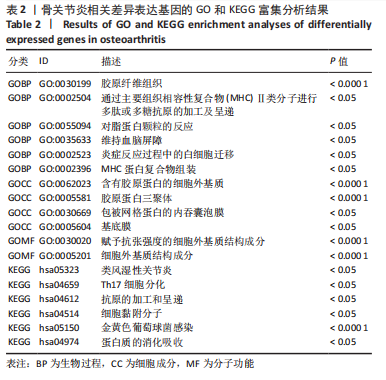
[8] 姚佳炜,徐雄峰,易鹏,等.骨关节炎滑膜组织差异表达基因筛选及关键基因的验证结果[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(18):2881-2887.
[9] 朱义芳,郭莉,陈露,等.骨关节炎的潜在生物标志物筛选及关键基因验证[J].四川医学,2021,42(10):969-975.
[10] 李升扬.基于生物信息学方法筛选骨关节炎相关关键分子靶点[D].长春:吉林大学,2021.
[11] 王海明,张驰,魏向阳,等.膝骨关节炎软骨细胞中差异基因表达的生物信息学分析[J].华西医学,2021,36(5):623-631.
[12] 杨威,袁普卫,韩清民.基于生物信息学筛选骨关节炎诊疗相关的关键基因[J].中华实验外科杂志,2022,39(1):44-44.
[13] BROPHY RH, ZHANG B, CAI L, et al. Transcriptome comparison of meniscus from patients with and without osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3): 422-432.
[14] 李明秀,王轩,杨杰,等.骨关节炎体外模型特点及设计新思路[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(2):300-306.
[15] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311.
[16] PEAT G, THOMAS MJ. Osteoarthritis year in review 2020: epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(2):180-189.
[17] DELPLACE V, BOUTET MA, LE VISAGE C, et al. Osteoarthritis: From upcoming treatments to treatments yet to come. Joint Bone Spine. 2021; 88(5):105206.
[18] ZHAO J, LU Q, LIU Y, et al. Th17 Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Cytokines, Plasticity, and Therapies. J Immunol Res. 2021;2021:8816041.
[19] SCANZELLO CR, GOLDRING SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2012;51(2):249-257.
[20] WOODELL-MAY JE, SOMMERFELD SD. Role of Inflammation and the Immune System in the Progression of Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):253-257.
[21] PARK J, LEE HS, GO EB, et al. Proteomic Analysis of the Meniscus Cartilage in Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8181.
[22] PENG Z, SUN H, BUNPETCH V, et al. The regulation of cartilage extracellular matrix homeostasis in joint cartilage degeneration and regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120555.
[23] SHI Y, HU X, CHENG J, et al. A small molecule promotes cartilage extracellular matrix generation and inhibits osteoarthritis development. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1914.
[24] Semenza GL.Hypoxia-inducible factors in physiology and medicine. Cell. 2012;148(3):399-408.
[25] YUDOH K, NAKAMURA H, MASUKO-HONGO K, et al. Catabolic stress induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha in articular chondrocytes: involvement of HIF-1 alpha in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(4):R904-R914.
[26] BOHENSKY J, SHAPIRO IM, LESHINSKY S, et al. HIF-1 regulation of chondrocyte apoptosis: induction of the autophagic pathway. Autophagy. 2007;3(3):207-214.
[27] ZHANG FJ, LUO W, LEI GH. Role of HIF-1αand HIF-2αin osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2015;82(3):144-147.
[28] ECKE A, LUTTER AH, SCHOLKA J, et al. Tissue Specific Differentiation of Human Chondrocytes Depends on Cell Microenvironment and Serum Selection. Cells. 2019;8(8):934.
[29] LI S, WANG H, ZHANG Y, et al. COL3A1 and MMP9 Serve as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Osteoarthritis and Are Associated With Immune Cell Infiltration. Front Genet. 2021;12:721258.
[30] BAYRAM B, THALER R, BETTENCOURT JW, et al. Human outgrowth knee fibroblasts from patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty exhibit a unique gene expression profile and undergo myofibroblastogenesis upon TGFβ1 stimulation. J Cell Biochem. 2022;123(5):878-892.
[31] KE H, MOU X, XIA Q. Remifentanil repairs cartilage damage and reduces the degradation of cartilage matrix in post-traumatic osteoarthritis, and inhibits IL-1β-induced apoptosis of articular chondrocytes via inhibition of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB phosphorylation. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(22):1487.
[32] REMST DF, BLOM AB, VITTERS EL, et al. Gene expression analysis of murine and human osteoarthritis synovium reveals elevation of transforming growth factor β-responsive genes in osteoarthritis-related fibrosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(3):647-656.
[33] JANG I, BENINGO KA. Integrins, CAFs and Mechanical Forces in the Progression of Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(5):721.
[34] PICKUP MW, MOUW JK, WEAVER VM. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014;15(12):1243-1253.
[35] PRIETO TG, MACHADO-RUGOLO J, BALDAVIRA CM, et al. The Fibrosis-Targeted Collagen/Integrins Gene Profile Predicts Risk of Metastasis in Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Front Oncol. 2021;11:706141.
[36] WU Y, XU Y. Integrated bioinformatics analysis of expression and gene regulation network of COL12A1 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2020; 9(13):4743-4755.
[37] FLOOD HM, BOLTE C, DASGUPTA N, et al. The Forkhead box F1 transcription factor inhibits collagen deposition and accumulation of myofibroblasts during liver fibrosis. Biol Open. 2019;8(2):bio039800.
[38] LI C, LUO J, XU X, et al. Single cell sequencing revealed the underlying pathogenesis of the development of osteoarthritis. Gene. 2020;757:144939.
[39] CHEN W, YANG A, JIA J, et al. Lysyl Oxidase (LOX) Family Members: Rationale and Their Potential as Therapeutic Targets for Liver Fibrosis. Hepatology. 2020;72(2):729-741.
[40] 刘荣清,孙伯坚,林佳静,等.类风湿关节炎和骨关节炎活动期赖氨酰氧化酶的比较[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2013,17(2): 95-97,插1.
[41] 吴嘉钦,杨力,许康,等.赖氨酰氧化酶LOX在OA疾病发生发展中的调控作用及其干预机制研究[J].医用生物力学,2021,36(S1):21.
[42] 许春明.赖氨酰氧化酶LOX在骨关节炎软骨中的调控作用及机制研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2020.
[43] YANG A, YAN X, FAN X, et al. Hepatic stellate cells-specific LOXL1 deficiency abrogates hepatic inflammation, fibrosis, and corrects lipid metabolic abnormalities in non-obese NASH mice. Hepatol Int. 2021;15(5):1122-1135.
[44] TASHKANDI MM, ALSAQER SF, ALHOUSAMI T, et al. LOXL2 promotes aggrecan and gender-specific anabolic differences to TMJ cartilage. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):20179.
[45] 周鑫,邢露,贺春霞,等.骨膜蛋白—一种有潜力的疾病早期诊断分子标志物[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(5):650-654.
[46] KKUDO A. The Structure of the Periostin Gene, Its Transcriptional Control and Alternative Splicing, and Protein Expression. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019; 1132:7-20.
[47] 曾峰,黄建芬,余新林,等.骨膜蛋白的研究新进展[J].中国医学创新,2021,18(7):171-176.
[48] BROPHY RH, TYCKSEN ED, SANDELL LJ, et al. Changes in Transcriptome-Wide Gene Expression of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears Based on Time From Injury. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(8):2064-2075.
[49] BROPHY RH, ZHANG B, CAI L, et al. Transcriptome comparison of meniscus from patients with and without osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3):422-432.
[50] CHOU CH, WU CC, SONG IW, et al. Genome-wide expression profiles of subchondral bone in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6):R190.
[51] TAJIKA Y, MOUE T, ISHIKAWA S, et al. Influence of Periostin on Synoviocytes in Knee Osteoarthritis. In Vivo. 2017;31(1):69-77.
[52] 王安琪,刘云鹏,卢文卿,等.PLOD家族在肿瘤中的研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2019,16(24): 29-31+39.
[53] WANG H, LUO W, DAI L. Expression and Prognostic Role of PLOD1 in Malignant Glioma. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:13285-13297.
[54] KOENIG SN, CAVUS O, WILLIAMS J, et al. New mechanistic insights to PLOD1-mediated human vascular disease. Transl Res. 2022;239:1-17.
[55] AYDıN N, KARAISMAILOĞLU B, ALAYLıOĞLU M, et al. Gene expression profiling of primary fibrochondrocyte cultures in traumatic and degenerative meniscus lesions. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2021;29(1): 23094990211000168. |