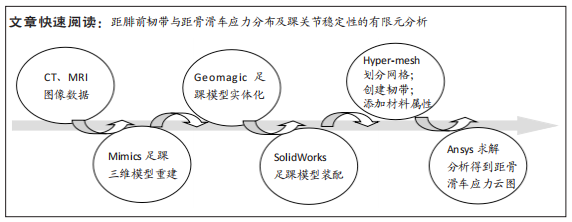
[1] HALABCHI F, HASSABI M. Acute ankle sprain in athletes: Clinical aspects and algorithmic approach. World J Orthop. 2020;11(12):534-558.
[2] SZARO P, GHALI GATAA K, POLACZEK M, et al. The double fascicular variations of the anterior talofibular ligament and the calcaneofibular ligament correlate with interconnections between lateral ankle structures revealed on magnetic resonance imaging. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):20801.
[3] TAKAO M, LOWE D, OZEKI S, et al. Strain patterns in normal anterior talofibular and calcaneofibular ligaments and after anatomical reconstruction using gracilis tendon grafts: A cadaver study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):558.
[4] DE ASLA RJ, KOZÁNEK M, WAN L, et al. Function of anterior talofibular and calcaneofibular ligaments during in-vivo motion of the ankle joint complex. J Orthop Surg Res. 2009;4:7.
[5] ZENG GL, CAI LM, XIE QX, et al. Anterior Talofibular Ligament All-Inside Arthroscopic Reconstruction with InternalBrace™ for Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability. Med Sci Monit. 2022;28:e937699.
[6] 史长安,刘丽,王建伟.早期负重对距骨骨软骨病损关节镜下修复术后关节功能恢复影响的前瞻性研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(9):703-707.
[7] NEHRER S, VANNINI F.Ankle Cartilage Repair. Cartilage. 2017;8(1):11.
[8] LEE C, BRODKE D, PERDUE PW JR, et al. Talus fractures: evaluation and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(20):e878-e887.
[9] POWERS RT, DOWD TC, GIZA E. Surgical treatment for osteochondral lesions of the talus. Arthroscopy. 2021;37(12):3393-3396.
[10] 张高伟,张浩,张宇飞,等.成人距骨骨软骨损伤的个性化治疗研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2022,11(8):625-630
[11] MERCER NP, AZAM MT, DAVALOS N, et al. Anterior talofibular ligament augmentation with internal brace in the office setting.Arthrosc Tech. 2022; 11(4):e545-e550.
[12] GEFEN A.Plantar soft tissue loading under the medial metatarsals in the standing diabetic foot. Med Eng Phys. 2003;25(6):491-499.
[13] 夏煜博,唐晓霞,罗文,等.有限元建模分析牵开成形治疗踝关节骨性关节炎的生物力学响应[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(22):3469-3475.
[14] 梁继勇,林元问.腓骨、外踝韧带与踝关节稳定性的生物力学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,1993,11(1):68-70.
[15] MKANDAWIRE C, LEDOUX WR, SANGEORZAN BJ, et al. Foot and ankle ligament morphometry.J Rehabil Res Dev. 2005;42(6):809-820.
[16] 贺李平,龙凯,肖介平. ANSYS 13.0与HyperMesh 11.0联合仿真有限元分析[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2012:269.
[17] FRIGG A, FRIGG R, HINTERMANN B, et al. The biomechanical influence of tibio-talar containment on stability of the ankle joint. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15(11):1355-1362.
[18] BOTTLANG M, MARSH JL, BROWN TD. Articulated external fixation of the ankle: minimizing motion resistance by accurate axis alignment. J Biomech. 1999;32(1):63-70.
[19] 白子兴,曹旭含,孙承颐,等.步态周期中踝关节有限元模型的构建及生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(9):1362-1366.
[20] GIDDINGS VL, BEAUPRE GS, WHALEN RT, et al. Calcaneal loading during walking and running.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000;32(3):627-634.
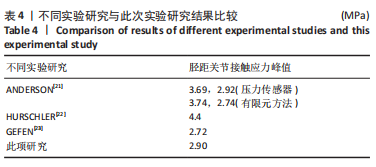
[21] ANDERSON DD, GOLDSWORTHY JK, LI W, et al. Physical validation of a patient-specific contact finite element model of the ankle. J Biomech. 2007; 40(8):1662-1669.
[22] HURSCHLER C, EMMERICH J, WÜLKER N. In vitro simulation of stance phase gait part I: Model verification. Foot Ankle Int. 2003;24(8):614-622.
[23] GEFEN A, MEGIDO-RAVID M, ITZCHAK Y, et al. Biomechanical analysis of the three-dimensional foot structure during gait: a basic tool for clinical applications. J Biomech Eng. 2000;122(6):630-639.
[24] 卢昌怀,余斌,陈辉强,等.正常步态下距骨三维有限元模型的建立及应力分析[J].南方医科大学学报,2010,30(10):2273-2276.
[25] BRUNS J, HABERMANN C, WERNER M. Osteochondral lesions of the talus: a review on talus osteochondral injuries, including osteochondritis dissecans.Cartilage. 2021;13(1_suppl):1380S-1401S.
[26] TAO H, HU Y, LU R, et al. Impact of chronic lateral ankle instability with lateral collateral ligament injuries on biochemical alterations in the cartilage of the subtalar and midtarsal joints based on MRI T2 mapping.Korean J Radiol. 2021;22(3):384-394.
[27] LAN R, PIATT ET, BOLIA IK, et al. Suture tape augmentation in lateral ankle ligament surgery: current concepts review. Foot Ankle Orthop. 2021;6(4): 24730114211045978.
[28] LI D, TANG Q, LIU Q, et al. Arthroscopic anterior talofibular ligament repair with Internal Brace and lasso-loop technique for chronic ankle lateral instability.Int Orthop. 2022;46(12):2821-2828.
[29] 刘立峰,蔡锦方.不同步态位相跟、距骨应力分布的三维有限元分析[J].第二军医大学学报,2003,24(9):1006-1009.
[30] 郭鹏超,王成伟.踝关节三维有限元生物力学研究的临床转化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(31):5056-5061.
|