[1] MOSKOWITZ MA, LO EH, IADECOLA C. The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron. 2010;67(2):181-198.
[2] NITZSCHE A, POITTEVIN M, BENARAB A, et al. Endothelial S1P(1) Signaling Counteracts Infarct Expansion in Ischemic Stroke. Circ Res. 2021;128(3):363-382.
[3] NUSSE R, CLEVERS H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell. 2017;69(6):985-999.
[4] 樊飞燕, 张运克. 益气活血中药联合骨髓间充质干细胞促进缺血性脑卒中血管新生的作用与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(13): 2060-2069.
[5] SHI Y, XU X, LUAN P, et al. miR‑124‑3p regulates angiogenesis in peripheral arterial disease by targeting STAT3. Mol Med Rep. 2020; 22(6):4890-4898.
[6] CUI Y, YIN Y, XIAO Z, et al. LncRNA Neat1 mediates miR-124-induced activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in spinal cord neural progenitor cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;(1):400.
[7] SONG S, HUANG H, GUAN X, et al. Activation of endothelial Wnt/β-catenin signaling by protective astrocytes repairs BBB damage in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2021;199:101963.
[8] XU SY, JIANG XL, LIU Q, et al. Role of rno-miR-124-3p in regulating MCT1 expression in rat brain after permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Genes Dis. 2019;(4):398-406.
[9] 杨程, 张婕, 李花, 等. 中医药治疗脑梗死的临床研究进展[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2018,29(8):1963-1965.
[10] 秦微. 彭氏眼针的理论研究[D]. 沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2011.
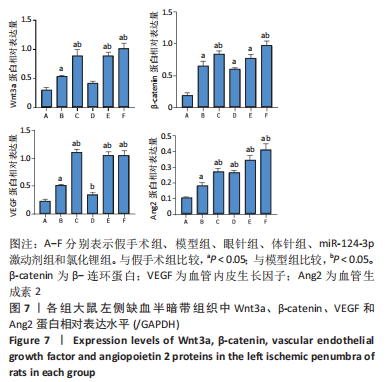
[11] LONGA EZ, WEINSTEIN PR, CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle
cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;(1): 84-91.
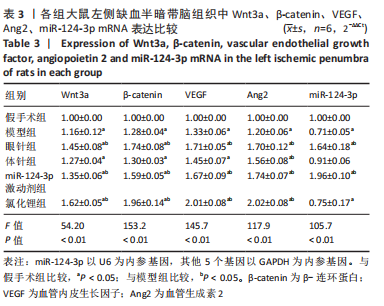
[12] 王艳杰, 柴纪严, 任平, 等. 大鼠眼针八区十三穴分区定位和刺法标准化研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2013,28(6):1695-1698.
[13] 范鸣玥. 氯化锂对血管性认知功能障碍小鼠认知功能的影响及机制研究[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学,2015.
[14] 辽宁中医药大学附属医院. 针灸技术操作规范. 第15部分:眼针[S]. 国家市场监督管理总局;国家标准化管理委员会,2021: 16.
[15] HU JZ, HUANG JH, ZENG L, et al. Anti-apoptotic effect of microRNA-21 after contusion spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurotrauma. 2013;(15): 1349-1360.
[16] ASHWAL S, TONE B, TIAN HR, et al. Core and penumbral nitric oxide synthase activity during cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in the rat pup. Pediatr Res. 1999;6(4):390-400.
[17] SU X, WU ZQ, MAI FY, et al. Governor vessel-unblocking and mind-regulating acupuncture therapy ameliorates cognitive dysfunction in a rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. Int J Mol Med. 2019; 43(1):221-232.
[18] WU Y H, HU R, ZHONG XY, et al. Electric acupuncture treatment promotes angiogenesis in rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion through EphB4/EphrinB2 mediated src/PI3K signal pathway. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021;30(3):105165.
[19] LIU L, CAO Q, GAO W, et al. Melatonin ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic mice by enhancing autophagy via the SIRT1-BMAL1 pathway. FASEB J. 2021;35(12):e22040.
[20] 浦延鹏,王鹏琴.眼针对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠脑组织自噬的影响[J].针刺研究,2021,46(2):100-105.
[21] 徐畅,邰东梅,马贤德,等.眼针和体针对24 h脑缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠脑血流和脑源性神经营养因子表达的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(9):2178-2181.
[22] 张勇.针刺治疗脑缺血再灌注损伤相关信号通路的机制研究进展[J].上海针灸杂志,2021,40(2):234-242.
[23] 高蕙兰(Treesukol Waranan). 基于少突胶质细胞参与髓鞘再生作用探讨眼针疗法对CI/RI大鼠脑保护作用机制[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2021.
[24] 喻腾云, 吴艳华, 孙寒静, 等. 缺血性脑卒中中医病因病机的层次关系[J]. 吉林中医药,2016,36(4):328-331.
[25] WEI ZZ, ZHANG JY, TAYLOR TM, et al. Neuroprotective and regenerative roles of intranasal Wnt-3a administration after focal ischemic stroke in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018;8(3):404-421.
[26] LIU J, XIAO Q, XIAO J, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):3.
[27] OBERMEIER B, DANEMAN R, RANSOHOFF RM. Development, maintenance and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Nat Med. 2013; 19(12):1584-1596.
[28] LI R, BEEBE T, JEN N, et al. Shear stress-activated Wnt-angiopoietin-2 signaling recapitulates vascular repair in zebrafish embryos. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(10):2268-2275.
[29] LI Z, SONG Y, HE T, et al. M2 microglial small extracellular vesicles reduce glial scar formation via the miR-124/STAT3 pathway after ischemic stroke in mice. Theranostics. 2021;11(3):1232-1248.
[30] XU SY, JIANG XL, LIU Q, et al. Role of rno-miR-124-3p in regulating MCT1 expression in rat brain after permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Genes Dis. 2019;(4):398-406.
[31] DE-PAULA VJ, DOS SANTOS CCC, LUQUE MCA, et al. Acute and chronic lithium treatment increases Wnt/β-catenin transcripts in cortical and hippocampal tissue at therapeutic concentrations in mice. Metab Brain Dis. 2021;36(1):193-197.
[32] ZHENG H, JIA L, LIU CC, et al. TREM2 Promotes Microglial Survival by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. J Neurosci. 2017;37(7):1772-1784.
[33] SONG P, FENG L, LI J, et al. β-catenin represses miR455-3p to stimulate m6A modification of HSF1 mRNA and promote its translation in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):129.
[34] ZHOU Q, CHEN S, LU M, et al. EFEMP2 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human bladder cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(10):2139-2155.
[35] WEICH A, ROGOLL D, GAWLAS S, et al. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates CXCR4 Expression and [68Ga] Pentixafor Internalization in Neuroendocrine Tumor Cells. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11(2):367.
[36] LAKSITORINI MD, YATHINDRANATH V, XIONG W, et al. Impact of Wnt/β-catenin signaling on ethanol-induced changes in brain endothelial cell permeability. J Neurochem. 2021;157(4):1118-1137.
[37] YU H, LIU Y, YANG X, et al. Strontium ranelate promotes chondrogenesis through inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):296.
[38] CONG J, CHENG B, LIU J, et al. TEF-1 Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Calcification through Regulating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021;109(2):203-214.
[39] HAO HP, WEN LB, LI JR, et al. LiCl inhibits PRRSV infection by enhancing Wnt/β-catenin pathway and suppressing inflammatory responses. Antiviral Res. 2015;117:99-109.
|