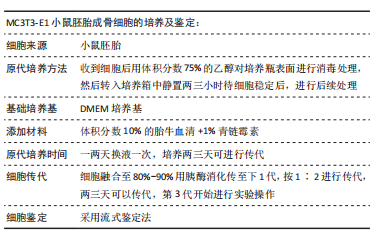
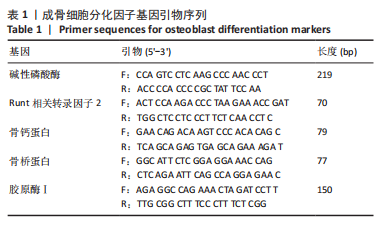
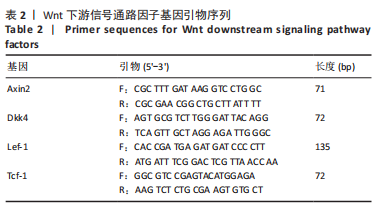
[1] LEWIECKI EM, BINKLEY N, CLARK P, et al. Core principles for fracture prevention: North American Consensus from the National Osteoporosis Foundation, Osteoporosis Canada, and Academia Nacional de Medicina de Mexico. Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(11):2073-2076.
[2] CONG E, WALKER MD. The Chinese skeleton: insights into microstructure that help to explain the epidemiology of fracture. Bone Res. 2014;2:14009.
[3] ZHANG T, HAN W, ZHAO K, et al. Psoralen accelerates bone fracture healing by activating both osteoclasts and osteoblasts. FASEB J. 2019;33(4):5399-5410.
[4] 张帆,梁清洋,韩超,等.Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调控成骨细胞、破骨细胞在骨质疏松中的作用探讨[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(10):1540-1544.
[5] YIN N, ZHU L, DING L, et al. MiR-135-5p promotes osteoblast differentiation by targeting HIF1AN in MC3T3-E1 cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019;24:51.
[6] GUO C, YANG RJ, JANG K, et al. Protective Effects of Pretreatment with Quercetin Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Apoptosis and the Inhibition of Osteoblast Differentiation via the MAPK and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathways in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(4):1547-1561.
[7] 聂鹤云,徐玲霞,李耿,等.中成药现代剂型发展现状及探讨[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(11):6347-6351.
[8] 柳海峰.三花接骨散论述[J].北京医学,1995(1):57.
[9] KIMURA A, TODA Y, MATSUMOTO Y, et al. Nuclear β-catenin translocation plays a key role in osteoblast differentiation of giant cell tumor of bone. Sci Rep. 2022; 12(1):13438.
[10] WANG N, GAN G, YANG J, et al. Barbaloin promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: involvement of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Curr Med Chem. 2022. doi: 10.2174/0929867329666220629150656.
[11] HAN J, WANG Y, ZHOU H, et al. CD137 Regulates Bone Loss via the p53 Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways in Aged Mice. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022; 13:922501.
[12] WANG B, KHAN S, WANG P, et al. A Highly Selective GSK-3β Inhibitor CHIR99021 Promotes Osteogenesis by Activating Canonical and Autophagy-Mediated Wnt Signaling. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:926622.
[13] LUO C, XU W, TANG X, et al. Canonical Wnt signaling works downstream of iron overload to prevent ferroptosis from damaging osteoblast differentiation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;188:337-350.
[14] TANG CY, WU M, ZHAO D, et al. Runx1 is a central regulator of osteogenesis for bone homeostasis by orchestrating BMP and WNT signaling pathways. PLoS Genet. 2021;17(1):e1009233.
[15] KIM JH, KIM M, HONG S, et al. Albiflorin Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation and Healing of Rat Femoral Fractures Through Enhancing BMP-2/Smad and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:690113.
[16] 万雷,黄宏兴,黄红,等.补肾健脾活血方含药血清提高过表达Sost转染成骨细胞增殖和碱性磷酸酶活性[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(16):2461-2466.
[17] LI Y, GE C, FRANCESCHI RT. Role of Runx2 in prostate development and stem cell function. Prostate. 2021;81(4):231-241.
[18] LIU XW, MA B, ZI Y, et al. Effects of rutin on osteoblast MC3T3-E1 differentiation, ALP activity and Runx2 protein expression. Eur J Histochem. 2021;65(1):3195.
[19] HOU Z, WANG Z, TAO Y, et al. KLF2 regulates osteoblast differentiation by targeting of Runx2. Lab Invest. 2019;99(2):271-280.
[20] LI W, ZHANG S, LIU J, et al. Vitamin K2 stimulates MC3T3‑E1 osteoblast differentiation and mineralization through autophagy induction. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(5):3676-3684.
[21] LIU Y, HUANG L, HAO B, et al. Use of an Osteoblast Overload Damage Model to Probe the Effect of Icariin on the Proliferation, Differentiation and Mineralization of MC3T3-E1 Cells through the Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(4):1605-1615.
[22] MOLAGODA IMN, KARUNARATHNE WAHM, CHOI YH, et al. Fermented Oyster Extract Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation by Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway, Leading to Bone Formation. Biomolecules. 2019;9(11):711.
[23] 郑苏阳. 基于内质网应激与Wnt/β-catenin信号通路研究蛇床子素对成骨细胞增殖与分化的影响及机制[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2017.
[24] DEL VALLE-PÉREZ B, ARQUÉS O, VINYOLES M, et al. Coordinated action of CK1 isoforms in canonical Wnt signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31(14):2877-2888.
[25] BHUKHAI K, SUKSEN K, BHUMMAPHAN N, et al. A phytoestrogen diarylheptanoid mediates estrogen receptor/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase 3β protein-dependent activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287(43):36168-36178.
[26] VAN ANDEL H, KOCEMBA KA, SPAARGAREN M, et al. Aberrant Wnt signaling in multiple myeloma: molecular mechanisms and targeting options. Leukemia. 2019;33(5):1063-1075.
[27] HIRAMITSU S, TERAUCHI M, KUBOTA T. The effects of Dickkopf-4 on the proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis of osteoblasts. Endocrinology. 2013; 154(12):4618-4626.
[28] HU L, SU P, YIN C, et al. Microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1 promotes osteoblast differentiation by promoting β-catenin/TCF1/Runx2 signaling axis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(2):1574-1584.
[29] 路鹏飞,田俊华,杨程.三花接骨散对股骨骨不连模型大鼠BMP-7/Runx2通路及骨愈合的影响[J].医学理论与实践,2021,34(14):2369-2373.
[30] 单红星,袁宏伟,王灿亚.三花接骨散配合手术治疗中青年股骨颈骨折临床研究[J].陕西中医,2018,39(10):1438-1440.
[31] 张洪范.探讨三花接骨散治疗糖尿病合并骨折的临床疗效[J].糖尿病新世界, 2015(4):61. |