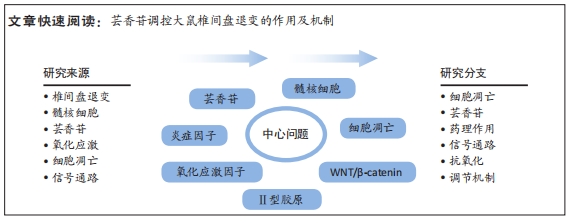
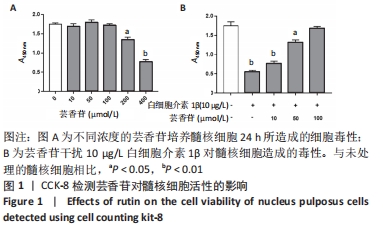
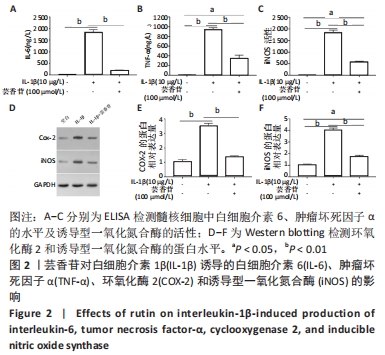
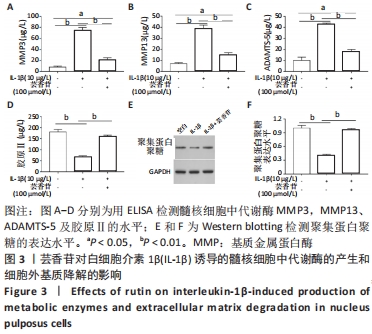
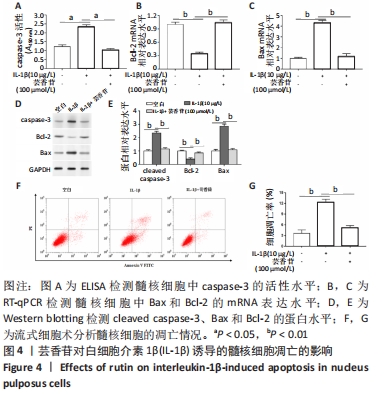
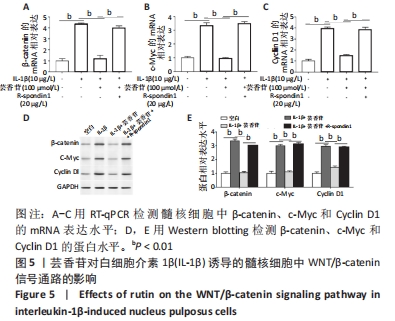
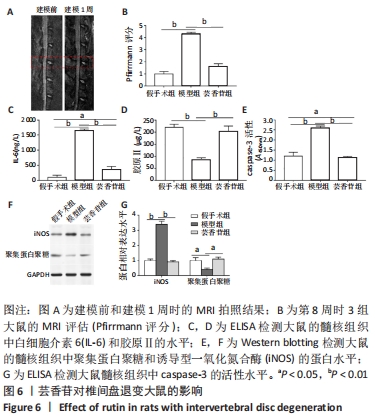
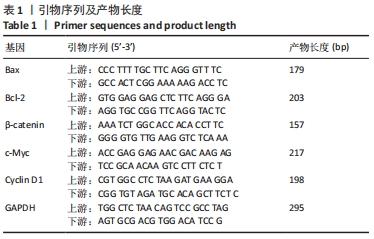
[1] RIDER SM, MIZUNO S, KANG JD. Molecular Mechanisms of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2018;3(1):1-11.
[2] JENSEN CE, RIIS A, PETERSEN KD, et al. Economic evaluation of an implementation strategy for the management of low back pain in general practice. Pain. 2017;158(5):891-899.
[3] FENG C, LIU H, YANG M, et al. Disc cell senescence in intervertebral disc degeneration: Causes and molecular pathways. Cell Cycle. 2016; 15(13):1674-1684.
[4] SAMPARA P, BANALA RR, VEMURI SK, et al. Understanding the molecular biology of intervertebral disc degeneration and potential gene therapy strategies for regeneration: a review. Gene Therapy. 2018;25(2):67-82.
[5] ZHANG XB, HU YC, CHENG P, et al. Targeted therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration: inhibiting apoptosis is a promising treatment strategy. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18(13):2799-2813.
[6] BASSO M, CAVAGNARO L, ZANIRATO A, et al. What is the clinical evidence on regenerative medicine in intervertebral disc degeneration?. Musculoskelet Surg. 2017;101(2):93-104.
[7] VAN UDEN S, SILVA-CORREIA J, OLIVEIRA JM, et al. Current strategies for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: substitution and regeneration possibilities. Biomater Res. 2017;21:22.
[8] DENT M, MATOBA N. Cancer biologics made in plants. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2020;61:82-88.
[9] GANESHPURKAR A, SALUJA AK. The Pharmacological Potential of Rutin. Saudi Pharm J. 2017;25(2):149-164.
[10] ENOGIERU AB, HAYLETT W, HISS DC, et al. Rutin as a Potent Antioxidant: Implications for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:6241017.
[11] CHUA LS. A review on plant-based rutin extraction methods and its pharmacological activities. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;150(3):805-817.
[12] CHE YJ, GUO JB, LIANG T, et al. Assessment of changes in the micro-nano environment of intervertebral disc degeneration based on Pfirrmann grade. Spine J. 2019;19(7):1242-1253.
[13] NAVONE SE, MARFIA G, GIANNONI A, et al. Inflammatory mediators and signalling pathways controlling intervertebral disc degeneration. Histol Histopathol. 2017;32(6):523-542.
[14] 赵赫, 俞兴, 唐向盛, 等. 炎性因子IL-1β、TNF-α与椎间盘退变关系的研究进展[J]. 中国骨伤,2017,30(9):866-871.
[15] JIN H, WANG Q, WU J, et al. Baicalein Inhibits the IL-1beta-Induced Inflammatory Response in Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Attenuates Disc Degeneration In vivo. Inflammation. 2019;42(3):1032-1044.
[16] SUN K, SUN X, SUN J, et al. Tissue Renin-Angiotensin System (tRAS) Induce Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Activating Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Reaction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021: 3225439.
[17] WANG K, CHEN T, YING X, et al. Ligustilide alleviated IL-1beta induced apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;69:398-407.
[18] ZHANG Y, HE F, CHEN Z, et al. Melatonin modulates IL-1β-induced extracellular matrix remodeling in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(22):10499-10512.
[19] YANG M, PENG Y, LIU W, et al. Sirtuin 2 expression suppresses oxidative stress and senescence of nucleus pulposus cells through inhibition of the p53/p21 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;513(3): 616-622.
[20] CHE H, LI J, LI Y, et al. p16 deficiency attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration by adjusting oxidative stress and nucleus pulposus cell cycle. Elife. 2020;9:e52570.
[21] WANG B, KE W, WANG K, et al. Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Piezo1 Activated by Matrix Stiffness Regulates Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence and Apoptosis in Human Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8884922.
[22] CAGLAYAN C, KANDEMIR FM, YILDIRIM S, et al. Rutin protects mercuric chloride-induced nephrotoxicity via targeting of aquaporin 1 level, oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation in rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2019;54:69-78.
[23] QU S, DAI C, GUO H, et al. Rutin attenuates vancomycin-induced renal tubular cell apoptosis via suppression of apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative stress. Phytother Res. 2019;33(8):2056-2063.
[24] ZHAN S, WANG K, SONG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates intervertebral disc degenerative changes via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):201.
[25] WANG JJ, LIU XY, DU W, et al. RBMS3 delays disc degeneration by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(2):499-507.
[26] KALITA B, RANJAN R, GUPTA ML. Combination treatment of podophyllotoxin and rutin promotes mouse Lgr5(+ ve) intestinal stem cells survival against lethal radiation injury through Wnt signaling. Apoptosis. 2019;24(3-4):326-340.
|