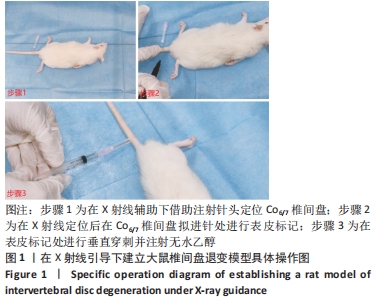
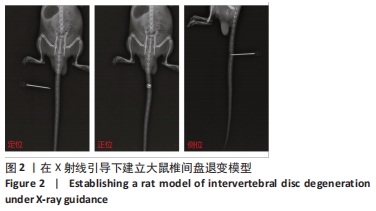
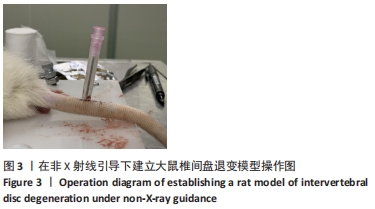
[1] ADAMS MA, ROUGHLEY PJ. What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine. 2006;31(18):2151-2161.
[2] ZHENG C, CHEN J. Disc degeneration implies low back pain. Theor Biol Med Model. 2015;12:24.
[3] 海宝,祝斌,刘晓光.椎间盘退变动物模型的研究进展[J].中国实验动物学报,2019,27(3):374-379.
[4] WU X, LIU Y, GUO X, et al. Prolactin inhibits the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration through inactivation of the NF-κB pathway in rats. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):98.
[5] JI M, JIANG H, ZHANG X, et al. Preclinical development of a microRNA-based therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):5051.
[6] GRUNERT P, BORDE BH, HUDSON KD, et al. Annular repair using high-density collagen gel: a rat-tail in vivo model. Spine. 2014;39(3):198-206.
[7] BORDE B, GTUNERT P, HARTL R, et al. Injectable, high-density collagen gels for annulus fibrosus repair: An in vitro rat tail model. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(8):2571-2581.
[8] QIAN J, GE J, YAN Q, et al. Selection of the Optimal Puncture Needle for Induction of a Rat Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Model. Pain Physician. 2019;22(4):353-360.
[9] YUAN W, CHE W, JIANG Y, et al. Establishment of intervertebral disc degeneration model induced by ischemic sub-endplate in rat tail. Spine J. 2015;15(5):1050-1059.
[10] Ge J, Yan Q, Wang Y, et al. IL-10 delays the degeneration of intervertebral discs by suppressing the p38 MAPK signaling pathway-10 protects intervertebral disc via p38 MAPK pathway. Free Radical Bio Med. 2019;147:262-270.
[11] THOMPSON JP, PEARCE RH, SCHECHETER MT, et al. Preliminary evaluation of a scheme for grading the gross morphology of the human intervertebral disc. Spine. 1990;15(5):411-415.
[12] ZHANG H, LA MF, HOLLISTER SJ, et al. Developing consistently reproducible intervertebral disc degeneration at rat caudal spine by using needle puncture. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;10(6):522-530.
[13] ROUSSEAU MA, ULRICH JA, BASS EC, et al. Stab incision for inducing intervertebral disc degeneration in the rat. Spine. 2007;32(1):17-24.
[14] NAKASHIMA D, FUJITA N, HATA J, et al. Quantitative analysis of intervertebral disc degeneration using Q-space imaging in a rat model. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(10):2220-2229.
[15] 黄帆,吴存书,张水冰,等.腰椎间盘退变动物模型研究进展及其“筋骨并重”复合因素实验动物模型构建思路[J].广州中医药大学学报,2021,38(3):607-612.
[16] 梁倩倩,侯炜,王拥军,等.1月龄双前肢去势大鼠腰椎间盘退变动物模型的建立[A].中国中西医结合学会.第三届世界中西医结合大会论文摘要集[C].中国中西医结合学会,2007:2.
[17] WANG X, SUN J, TAN J, et al. Effect of sIL-13Rα2-Fc on the progression of rat tail intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019; 14(1):386.
[18] CHEN CH, CHIANG CJ, WU LC, et al. Time course investigation of intervertebral disc degeneration in a rat-tail puncture model. Life Sci. 2016;156:15-20.
[19] VINCENT K, MOHANTY S, PINELLI R, et al. Aging of mouse intervertebral disc and association with back pain. Bone. 2019;123:246-259.
[20] KAISER J, ALLAIRE B, FEIN PM, et al. Correspondence between bone mineral density and intervertebral disc degeneration across age and sex. Arch Osteoporos. 2018;13(1):123.
[21] 徐浩伟,王善金,易宇阳,等.大鼠尾椎间盘退变造模器械的研发与应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(5):447-453.
[22] ZHANG B, ZHAO Q, LI Y, et al. Moxibustion alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration activation of the HIF-1α/VEGF pathway in a rat model. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(9):6221-6231.
[23] RESTALL BS, HAVEN NJM, KEDARISETTI P, et al. Virtual hematoxylin and eosin histopathology using simultaneous photoacoustic remote sensing and scattering microscopy. Opt Express. 2021;29(9):13864-13875.
[24] BORUCKI R, PERRY DM, LOPEZ DR, et al. Fluorescence microscopy for the evaluation of elastic tissue patterns within fibrous proliferations of the skin on hematoxylin-eosin-stained slides. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85(2):419-422.
[25] YANG RZ, XU WN, ZHENG HL, et al. Involvement of oxidative stress-induced annulus fibrosus cell and nucleus pulposus cell ferroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2021; 236(4):2725-2739.
[26] SHAO Z, WANG B, SHI Y, et al. Senolytic agent Quercetin ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via the Nrf2/NF-κB axis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(3):413-422.
[27] 白荣飞,张震,林一峰,等.三种方法建立大鼠腰椎间盘退变模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(16):2514-2519.
[28] HAN B, ZZHU K, LI FC, et al. A simple disc degeneration model induced by percutaneous needle puncture in the rat tail. Spine. 2008;33(18): 1925-1934.
[29] LI Y, CAO L, LI J, et al. Influence of microgravity-induced intervertebral disc degeneration of rats on expression levels of p53/p16 and proinflammatory factors. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(2):1367-1373.
[30] GRUNERT P, HUDSON KD, MACIELAK MR, et al. Assessment of intervertebral disc degeneration based on quantitative magnetic resonance imaging analysis: an in vivo study. Spine. 2014;39(6):E369-E378.
[31] LUO TD, MARQUEZ A, ZZBARSKY ZK, et al. A percutaneous, minimally invasive annulus fibrosus needle puncture model of intervertebral disc degeneration in rabbits. J Orthop Surg. 2018;26(3):2309499018792715.
[32] XI Y, KONG J, LIU Y, et al. Minimally invasive induction of an early lumbar disc degeneration model in rhesus monkeys. Spine. 2013;38(10): E579-E586.
[33] LI D, YANG H, HUANG Y, et al. Lumbar intervertebral disc puncture under C-arm fluoroscopy: a new rat model of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Anim. 2014;63(2):227-234.
[34] MASUDA K, AOTA Y, MMEHLEMAN C, et al. A novel rabbit model of mild, reproducible disc degeneration by an anulus needle puncture: correlation between the degree of disc injury and radiological and histological appearances of disc degeneration. Spine. 2005;30(1):5-14.
[35] SOBAJIMA S, KOMPEL JF, KIM JS, et al. A slowly progressive and reproducible animal model of intervertebral disc degeneration characterized by MRI, X-ray, and histology. Spine. 2005;30(1):15-24.
[36] FERNÁNDEZ-SUSAVILA H, PARDO-SECO JP, IGLESIAS-REY R, et al. Model of Disc Degeneration in Rat Tail Induced Through a Vascular Isolation of Vertebral Endplates. J Invest Surg. 2018;31(4):265-274.
[37] JI Y, ZHU P, ZHANG L, et al. A novel rat tail disc degeneration model induced by static bending and compression. Animal Model Exp Med. 2021;4(3):261-267.
[38] XIA W, ZHANG LL, MO J, et al. Effect of Static Compression Loads on Intervertebral Disc: An in Vivo Bent Rat Tail Model. Orthop Surg. 2018; 10(2):134-143.
[39] 毛强,何帮剑,张圣扬,等.异常力学负荷导致椎间盘退变的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020,28(12):1-6.
[40] FILARDI V, SIMONA P, CACCIOLA G, et al. Finite element analysis of sagittal balance in different morphotype: Forces and resulting strain in pelvis and spine. J Orthop. 2017;14(2):268-275.
[41] 黄帆,赵思怡,邸安琪,等.基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的推拿干预腰椎间盘退变作用机制探讨[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(5): 2991-2994.
[42] BAYNE K, RAMACHANDRA GS, RIVERA EA, et al. The evolution of animal welfare and the 3Rs in Brazil, China, and India. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2015;54(2):181-91.
[43] NORTON JN, REYNOLDS RP, CHAN C, et al. Assessing the satisfaction and burden within an academic animal care and use program. FASEB J. 2017;31(9):3913-3921.
[44] KILKENNY C, BROWNE W, CUTHILL IC, et al. NC3Rs Reporting Guidelines Working Group. Animal research: reporting in vivo experiments: the ARRIVE guidelines. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;160(7):1577-1579.
[45] XIAO LY, LI Z, DU YZ, et al. Acupuncture for Hypertension in Animal Models: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:8171636.
[46] FESTING MF, NEVALAINEN T. The design and statistical analysis of animal experiments: introduction to this issue. ILAR J. 2014;55(3):379-382.
[47] VRIES RD, HOOIJMANS CR, LANGENDAM MW, et al. A protocol format for the preparation, registration and publication of systematic reviews of animal intervention studies. Evidence-based Preclinical Medicine. 2015;2(1):1-9.
[48] HOOIJMANS C, VRIES RD, LEENAARS M, et al. The Gold Standard Publication Checklist (GSPC) for improved design, reporting and scientific quality of animal studies GSPC versus ARRIVE guidelines. Lab Anim. 2011;45(1):61.
[49] PERCIE DU SERT N, AHLUWALIA A, ALAM S, et al. Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol. 2020;18(7):e3000411.
|