中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (16): 2616-2624.doi: 10.12307/2023.107
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇
医用金属材料促血管生成的分子机制
周岚曦,邵 路,董士武,喻正文
- 遵义医科大学口腔医学院,贵州省遵义市 563099
-
收稿日期:2022-03-11接受日期:2022-04-28出版日期:2023-06-08发布日期:2022-11-11 -
通讯作者:喻正文,副教授,硕士生导师,遵义医科大学口腔医学院,贵州省遵义市 563099 -
作者简介:周岚曦,女,1998年生,湖南省岳阳市人,汉族,遵义医科大学在读硕士,主要从事口腔材料方面的研究。 -
基金资助:贵州省科技计划项目(黔科合平台人才[2017]5733-057),项目负责人:喻正文;贵州省医用生物材料研发人才基地(黔人领发 [2018]3号),项目参与人:喻正文
Molecular mechanism of angiogenesis promoted by medical metal materials
Zhou Lanxi, Shao Lu, Dong Shiwu, Yu Zhengwen
- School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-11Accepted:2022-04-28Online:2023-06-08Published:2022-11-11 -
Contact:Yu Zhengwen, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zhou Lanxi, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Planning Project of Guizhou province, No. QKHPTRC[2017]5733-057 (to YZW); Talent Base of Medical Biomaterials Research of Guizhou Province, No. QRLF[2018]3 (to YZW)
摘要:
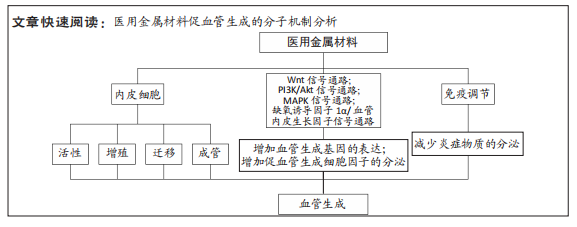
文题释义:
医用金属材料:是一类具有良好生物相容性、优秀的力学性能以及方便加工制作的植入机体的生物金属材料,此类材料通常以支架、种植体、赝复体及外科辅助材料的形式广泛应用于骨科、牙科、整形及介入治疗中。血管生成:血液供应是骨再生的先决条件,植入材料与病损组织相互作用,刺激内皮细胞向病损区迁移增殖,诱导血管生成相关基因的表达,促进血管生成,加快骨再生进程,改善骨再生效果。
背景:血管生成对于组织修复与再生是必不可少的,提高医用金属材料促血管生成的能力是近年来的研究热点。
目的:整理讨论了医用金属材料促内皮细胞血管化的可能分子机制,为后续研发各种促血管生成的医用金属材料奠定基础。
方法:检索PubMed、ScienceDirect、中国知网和万方数据库收录的相关文献。英文检索词为“medical metal materials OR alloy”“stent OR scaffold”“vascularization OR angiogenesis”“molecular mechanism OR signaling pathway”“endothelial cells”,中文检索词为“医用金属材料、金属”“支架”“血管化、血管生成”“分子机制、信号通路”“内皮细胞”,最终纳入76篇文献进行分析总结。
结果与结论:①医用金属材料植入机体后在降解过程中所释放的金属离子,可以通过促进内皮细胞的增殖、迁移、黏附和提高成管能力来影响血管生成。②镁、锌、铜、锶及钴等金属离子可以激活Wnt、PI3K/Akt、MAPK、缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子等信号通路,上调血管内皮生长因子、血小板衍生生长因子及缺氧诱导因子1α等血管生成因子的表达,促进血管生成相关细胞因子的分泌,从而诱导血管生成。③金属植入体内引起的免疫反应不仅影响植入材料的稳定性,还会影响血管化及成骨效果。④金属离子的浓度会影响血管生成的过程,金属材料降解过快,金属离子爆发积累会导致细胞毒性。确定金属离子最佳促血管化及成骨分化的浓度,是开发多功能金属材料的关键。⑤通过合金化、表面修饰改性等手段提高金属材料的耐腐蚀性,调控金属离子释放速率,有利于营造良好的成骨和血管生成微环境,加速组织的修复与再生。⑥金属促血管生成的机制丰富,但具体分子机制尚未彻底明晰,未来仍需进一步的研究。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0176-7540 (周岚曦);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9392-6042 (喻正文)
中图分类号:
引用本文
周岚曦, 邵 路, 董士武, 喻正文. 医用金属材料促血管生成的分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(16): 2616-2624.
Zhou Lanxi, Shao Lu, Dong Shiwu, Yu Zhengwen. Molecular mechanism of angiogenesis promoted by medical metal materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2616-2624.
2.1.1 镁(Mg)对内皮细胞的影响 镁作为人体必需的元素之一,是机体代谢过程中重要的辅助因子,对于神经冲动的传导、肌肉收缩、调节血管张力至关重要,镁可维持血管内皮细胞结构和功能的稳定,保持心血管健康,促进内皮损伤的修复。研究表明,Mg2+浓度的变化对内皮细胞增殖和细胞毒性产生不同的影响,当Mg2+浓度在1-5 mmol/L时,内皮细胞增殖随着Mg2+浓度的增加而增加,然而过高浓度的Mg2+(20 mmol/L)对内皮细胞活性造成负面影响,细胞的凋亡率显著增加[7]。适当提高细胞外Mg2+浓度可以提高内皮细胞活性,促进细胞迁移、增殖、血管新生,而高镁环境则会对内皮细胞产生增殖抑制,可能是由于细胞活力下降所导致的[8]。
ZHANG等[9]通过3D打印设计了制造一种含硅、镁和钙的生物陶瓷空心管状支架,通过体外Transwell和Western Blot实验检测支架释放的离子对内皮细胞的调控功能,发现支架释放的Mg2+可以直接调控内皮细胞向缺损区迁移,促进新生血管的形成。将支架植入兔桡骨节段性缺损中,4周后病损处实现了显著的血管化骨再生,并在12周内骨缺损修复完全,表现出良好的生物相容性和出色的促血管化骨再生性能。植入支架结构可以影响种植体稳定性,并在一定程度上影响成骨和血管生成。有研究报道,不规则结构弯曲程度更大,具有更大的3D空间,从而使更多的骨组织向内生长,生成的血管更粗[10],因此文章推测ZHANG等[9]设计的空心管状结构可为细胞附着与生长提供更广阔的接触面积,更利于组织向内生长进而加速骨修复过程。3D打印可以任意设计支架的结构与形状,从而适应各种缺损,尤其在修复大面积骨缺损中颇具前景,空心管状结构在植入体设计方面提供了一种新的思路。
2.1.2 锌(Zn)对内皮细胞的影响 锌是体内多种酶的重要组成成分,这些酶催化的反应影响多种生理功能,包括糖代谢、蛋白质代谢、脂类氧化和核酸合成等。Zn2+和Mg2+一样对内皮细胞的活性、增殖和迁移具有双相反应,且呈浓度依赖性。研究表明,低浓度的Zn2+(≤80 μmol/L)能促进内皮细胞的存活、增殖和迁移,而高浓度的Zn2+(≥200 μmol/L)能抑制内皮细胞的细胞功能[11]。此外,低浓度的Zn2+还能导致细胞骨架重组,促进F-肌动蛋白和纽蛋白表达[12]。锌对内皮细胞的作用可用于钛及其合金的表面改性,研究人员通过阳极氧化在钛表面负载Zn2+,以提高钛的生物相容性,钛表面负载Zn2+后可明显促进内皮细胞黏附、增殖和提高细胞内一氧化氮酶的活性[13]。除此之外,锌还可以影响内皮细胞成管,ZHANG等[14]发现含锌的生物活性玻璃可诱导内皮细胞使其形态发生显著变化,导致细胞结构重排,内皮细胞中形成毛细血管样网络状结构。因此,控制锌基植入物的降解速率有助于骨缺损处维持适宜的Zn2+浓度,对内皮细胞产生正面影响,从而促进血管生成,加快骨再生。合金化、加工方式和表面改性是提高锌基合金力学性能及耐腐蚀性的常用手段[15]。
2.1.3 铜(Cu)对内皮细胞的影响 Cu2+是人体内不可或缺的一种微量元素,具有成骨作用和出色的抗菌性,同时铜也是赖氨酰氧化酶的重要组成部分,在维持血管壁完整性方面发挥了重要作用,正常的Cu2+浓度有利于保护血管内皮细胞[16-17]。LI
等[18]研究发现Cu2+浓度在100 μmol/L以下对内皮细胞的生长有促进作用,然而,200 μmol/L以上的Cu2+对内皮细胞具有细胞毒性,抑制细胞的生长与增殖。因此,高浓度的铜具有细胞毒性,并为细胞生长提供不利条件,但是将Cu2+的浓度合理控制也可以改善细胞迁移。ALIZADEH等[19]首次证明了浓度为1 μmol/L
的80 nm铜纳米颗粒可促进内皮细胞的迁移和血管生成,加速了大鼠皮肤伤口愈合过程,并且在大鼠肝脏中未显示任何积累,无任何不良反应,表现出良好的生物相容性和生物安全性。另外相关研究也证明Cu2+在低浓度(0-1 μmol/L)时,内皮细胞迁移与Cu2+浓度呈正相关[20]。合金化是改善金属支架机械力学性能及生物学性能的常用方法,操作简单易实现,研究人员通常将铜通过合金化添加进其他金属材料中,以期在成骨和血管生成的同时拥有抗菌性。Mg-Cu合金比纯Mg更好地促进细胞附着和内皮细胞的活性,然而随着Mg-Cu合金中Cu浓度的增加,Mg-Cu合金的对内皮细胞活力产生负性影响[21]。因此,在设计金属植入材料时,由于不同的材料降解速率不一,释放离子的能力不同,导致其产生的生物效应也不同,要充分考虑金属离子的添加剂量和形式、基底材料的形式以及材料的降解速率,使金属离子释放量限制在合理范围内。综上所述,探索铜与其产生的生物效应之间的剂量-反应关系,便可实现抗菌、成骨与血管生成最优化。
2.1.4 锶(Sr)对内皮细胞的影响 在人体中,锶大多数集中于骨骼和牙齿中,对骨骼和牙齿的钙化必不可少,许多研究已经阐明了锶在成骨方面所产生的作用,然而有研究发现,锶可能通过某些机制促进血管生成。最近相关实验研究表明,锶可促进内皮细胞增殖、黏附和迁移[22],促进内皮细胞生成更广泛的网络状结构,管的长度更长,形成的分支点更多[23]。WU等[24]试图在骨水泥中掺入锶来诱导体内血管生成,通过一系列实验发现Sr2+的持续释放改善了内皮细胞的黏附和增殖,促进内皮细胞成管。另外,在研究人员构建的动物模型中也发现,掺锶骨水泥在体内生物相容性好,降解少,骨水泥周围出现的血管数量增加,与对照组比较表现出更优秀的血管生成能力,对新骨生成也有显著的改善。聚磷酸钙具有良好的生物相容性、理想的力学性能,已被广泛用作骨修复材料,因其缺乏促血管生成的能力,骨修复效果受限,研究人员通常在聚磷酸钙支架中添加锶以改善血管生成。GU等[25]通过MTT法及显微镜观察评估掺锶聚磷酸钙支架在体外诱导血管生成的能力,他们的研究结果同样显示掺锶组中内皮细胞显示出更高的增殖率,形成的管状结构更长。除此之外,锶的掺入还改变了支架表面形貌,使支架表面变得更光滑并且具有更致密的体积,这可能会上调血管内皮生长因子的表达。由此可见,在生物材料中添加锶元素是一种改善植入体生物学效应的有效手段,与将昂贵脆弱的生长因子整合入支架中相比,掺锶支架操作更简单,价格更低廉,且能持续较长时间促血管生成作用。锶作为促血管化骨生成的微量元素广泛用于骨组织再生,前景广阔。
2.2 医用金属材料促血管化的相关信号通路
2.2.1 Wnt信号通路 有证据表明Wnt信号通路在血管细胞群中表达,促进血管细胞迁移增殖和分化,调节血管生成过程[26]。金属离子在血管修复与重建中的促进作用是否由Wnt信号通路介导,具体机制如何,一些学者对此进行了研究。PAN等[27]将人脐静脉内皮细胞与不同浓度的MgCl2和ZnCl2进行孵育,研究MgCl2和ZnCl2对内皮细胞的特异性影响及其相关机制。他们的研究首次证明了MgCl2和ZnCl2通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路增强内皮细胞的迁移和侵袭能力,刺激细胞骨架重组,揭示了镁、锌诱导血管生成过程受Wnt/β-catenin信号调控的潜在机制。
有研究发现锂可以用于激素相关性骨坏死的治疗,用大鼠股骨头建立的激素相关性骨坏死模型,在经锂离子处理后血管明显增多,血管内皮生长因子的表达显著增高,并且实验数据显示锂抑制了糖原合成酶激酶3β的活性并促进了β-catenin的表达[28],见图3。

然而既往研究发现血管内皮生长因子是血管生成过程中β-catenin信号转导的靶基因[29],由此可以推测锂可通过激活β-catenin通路促进血管生成,在后来的研究中也证实了这一点。大量的实验结果表明,锂可以激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,促进内皮细胞的增殖、迁移及成管,并使血管生成相关因子的表达增加[30-32],这为锂在血管化组织的再生和修复中的应用奠定了理论基础。通过微弧氧化在镁合金表面制造含锂纳米涂层对镁合金进行表面改性,锂的加入既可以提高镁合金的耐腐蚀性能,还能改善血管生成和骨整合效果,并且植入体在体内未对重要组织器官产生影响,具有良好的生物相容性[33],这是镁合金材料表面改性的成功实践,为将来镁锂材料的临床应用奠定基础。
血管化是修复骨缺损的关键环节之一,不仅对骨组织再生意义重大,在牙科领域中也是当今的研究热点,血管生成是牙髓再生的研究重点。ZHANG等[14]将磷酸钙骨水泥与生物活性玻璃结合,同时掺入Zn2+,制成一种促进牙本质牙髓再生的材料,并评估了该材料血管生成效应及可能的分子机制。Wnt1,
Wnt3a,Wnt5a和β-catenin蛋白在经该材料处理后显著增加,血管内皮生长因子基因表达上调并在体外促进管形成,表明Zn2+可激活Wnt/β-catenin通路来促进血管生成。值得注意的是,除了Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,整合素和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)等信号通路也被激活,这些通路在血管生成过程中是否为协同作用,彼此之间是否相互交联,哪条通路发挥主导作用这些问题尚未可知,仍需更深一步的研究。
综上所述,金属离子可介导Wnt通路,促进内皮细胞增殖、迁移和成管,增强血管生成相关基因的表达,调控血管生成。然而,激活的Wnt通路在血管生成过程中的调控作用是否占据主体地位尚未得到研究证明,具体机制仍待研究。
2.2.2 磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶 (phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase,PI3K)信号通路 PI3K/Akt信号通路在细胞增殖、黏附、迁移、代谢和存活中发挥重要作用[34]。血管内皮生长因子是一种有效的血管生成因子,其促进内皮细胞生长作用可以由PI3K通路介导,Akt1可磷酸化内皮型一氧化氮合酶,诱导血管内皮生成一氧化氮,从而参与血管生成[35]。PI3K/Akt通路对胚胎发育过程中的正常血管发育至关重要,PI3K的信号传导受到干扰将导致异常血管生成,如血管畸形及肿瘤血管生成[36]。
镁的弹性模量与人体骨骼最为接近,因具有在体内外增强成骨、生物可降解性等特性,医用镁合金材料在医学领域炙手可热,镁促成骨分化作用和机制是当今研究热点。ZHANG等[37]在研究Mg2+调节骨再生机制的过程中发现,Mg2+通过瞬时受体电位离子通道7/PI3K信号通路不仅上调了碱性磷酸酶等成骨基因的表达,还使成血管内皮生长因子等血管生成基因表达水平增加,见图4。同时,拮抗PI3K的活性可显著减少成骨及成血管基因的表达,揭示了镁经PI3K通路促骨和血管生成的分子机制。LI等[38]发现6.25% Mg-Zn-Mn合金提取物可显著促进内皮细胞的DNA合成,增加内皮细胞活力和诱导内皮细胞成管。实验中p-PI3K/PI3K和p-Akt/Akt的比值明显升高,表明了6.25%的Mg-Zn-Mn对PI3K/Akt信号通路的激活具有正向调控作用。
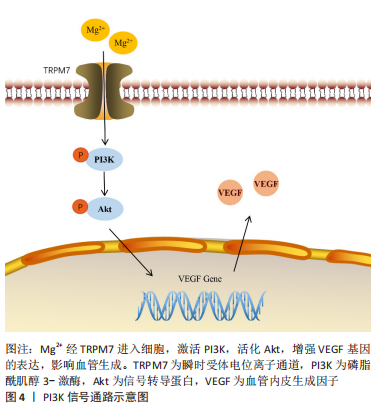
然而,镁合金的副反应也不可忽视,纯镁和镁合金的降解产生氢气,并伴随着pH值急剧的升高,造成细胞毒性。对此,Wu等[39]设计制造了掺杂不同质量分数的MgO的生物陶瓷,MgO与体液作用后的产物是Mg(OH)2,不会产生氢气,且生物陶瓷可使镁以Mg2+的形式缓慢释放,这样便可研究镁降解导致的碱性环境对体外成骨和血管生成的影响。结果显示MgO掺入量在10%以内时,Mg2+上调成骨基因Runx2的表达,促进成骨细胞的成骨分化,并通过激活PI3K/Akt信号促进内皮细胞的血管生成,镁质量分数超过15%时,高浓度的Mg2+、较强的碱度降低了材料的生物活性。因此,在组织工程设计应用镁相关材料时,不仅要考量镁浓度对生物反应产生的影响,更要考虑不同形式的镁降解时对机体酸碱环境造成的影响,如添加适量的镁,用MgO、MgCl2替代纯镁,用生物陶瓷、生物活性玻璃及有机涂层等材料把控镁降解速率,便可通过提高材料生物活性抵消碱性环境带来不利影响。
金属钛强度高、密度低、抗疲劳、耐腐蚀性能优秀,生物相容性高,常被制造成接骨板、种植体、螺钉及人工关节等医疗器械,在临床治疗中应用非常广泛。研究者通常选择对钛表面进行改性,以赋予惰性金属生物活性,改善钛合金骨整合能力不足的问题。SUN等[40]首先在钛表面固定聚多巴胺,然后用Sr2+取代钙离子制备羟基磷灰石涂层,形成了一种新型复合涂层,并评估了该材料诱导成骨和血管生成的能力。该材料在体内外都表现出良好的成骨和成血管能力,涂层提高了血管紧张素-Ⅰ和血管内皮生长因子的表达,激活了PI3K/Akt通路,促进内皮细胞血管生成分化。然而,近年来研究者发现,钛虽为惰性金属,植入机体后也会与周围环境相互作用,介导细胞生物学功能。MARTINS等[41]主要研究了钛对内皮细胞的影响并分析了其可能的机制,数据显示富含钛的培养基显著上调了内皮型一氧化氮合酶、血管内皮生长因子等基因的表达,PI3K/Akt的磷酸化显著增加,因此作者认为钛通过激活PI3K/Akt通路来改变内皮细胞活性,促进血管生成。此外,在添加PI3K抑制剂处理细胞后,血管生成相关基因表达的显著降低再次证明了PI3K/Akt信号通路驱动钛诱导血管生成。
上述研究皆阐明了金属离子诱导血管生成的PI3K/Akt信号传导机制,为镁、锶等金属植入物应用于临床提供了理论依据。
2.2.3 MAPK信号通路 MAPK是重要的信号转导酶,参与细胞分化、增殖、凋亡和细胞运动的许多方面。MAPK家族包括细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)、c-Jun氨基末端激酶(JNK)和p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 MAPK)。十多年前便有学者研究发现,可溶性钛能诱导大鼠主动脉和人内皮细胞的ERK1/2蛋白磷酸化,促进内皮型一氧化氮合酶表达增加,改变内皮细胞功能,促进成管[42],此后学者们逐渐开始探究金属离子促血管生成的生物学性能与MAPK信号通路之间的关系。
为诱导血管生成和成骨形成加快骨整合,ZHANG等[43]将Sr2+通过微弧氧化(MAO)添加在钛植入体表面以提高钛的生物活性。微弧氧化处理可使材料耐腐蚀性能提升,使Sr2+持续释放,长时间维持一个促成骨与血管生成的微环境。研究证明了微弧氧化Sr涂层可以同时通过MAPK和PI3K/Akt信号通路诱导血管生成和成骨,将成血管和成骨耦合提高到了一个新的水平,但两条信号通路是否起协同作用共同促进血管生成和成骨,二者是否作用于同一个蛋白或调控相同靶基因仍待进一步研究。
除了合金化、表面改性,金属离子还可以各种形式掺入支架材料,进而调控血管生成。SONG等[44]在低温下用3D打印技术铸造制备一种新型的硅酸锌/纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原(ZS/HA/Col)复合支架,Zn2+以硅酸锌的形式被包裹在胶原蛋白中,可以使得Zn2+在体内持续性低浓度释放。实验数据表明,10%ZS/HA/Col支架提取物组中血管内皮生长因子α和血小板衍生因子的表达水平显著升高,且支架提取物激活了p38 MAPK和ERK1/2途径。然而在添加抑制剂对此2条通路进行阻断时,血管生成相关因子的表达明显受到抑制,支架促成骨和血管生成的能力明显受到削弱,上述实验结果从正反两面印证了10%ZS/HA/Col支架可以通过激活p38 MAPK和ERK1/2通路来促进血管的生成。
CHEN等[45]制备了锶-氧化石墨烯纳米生物复合材料
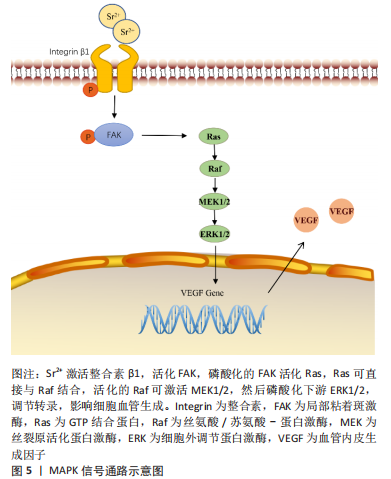
(Sr-GO-Col),评估了其促血管生成和骨再生的潜能并探讨了相关的机制。氧化石墨烯可增强细胞黏附和扩散,在此基础上,锶的掺入一方面能够招募聚集更多的内皮细胞向血管破损处迁移,增强促血管生成因子的分泌来刺激内皮细胞成血管;另一方面,锶还可以协同氧化石墨烯激活整合素β1/FAK信号通路,磷酸化下游ERK1/2和P38 MAPK,激活MAPK通路,进而促进血管内皮生长因子和骨形态发生蛋白2的分泌,从而促进骨和血管的生成及修复,见图5。动物实验中同样发现,将支架植入构建的大鼠颅骨缺损模型,12周后只有掺锶组新生骨组织基本完全覆盖缺损处,血管生成效果也达到最佳,这都归功于氧化石墨烯可使锶缓慢释放,长期维持一个中等浓度。
ZHANG等[46]制备的氧化石墨烯-铜纳米复合材料同样实现了Cu2+的缓慢释放,从而防止了Cu2+爆发积累造成的细胞毒性。实验结果显示氧化石墨烯-铜纳米复合材料可激活ERK1/2和缺氧诱导因子1α信号通路,上调成骨和血管生成基因的表达,体内外血管化程度更高,骨再生的效果也更佳,材料显示出优秀的成骨诱导性和血管生成活性。由于石墨烯降解速度很慢,植入8周后在新生骨组织附近检测到了残余材料,虽未对机体产生毒害作用,但未来需加强对石墨烯生物安全性与生物相容性的研究,弄清石墨烯与细胞之间相互作用的机制后,石墨烯将成为一种用于控制离子释放速率的良好材料。
综上所述,锌、铜和锶可以通过激活MAPK信号通路诱导血管生成,另外锶还可以耦合成骨与血管生成过程,锶激活的MAPK和PI3K/Akt信号通路都可调控成骨与血管生成。由此可见,血管生成和成骨都不是由单一的通路起作用,并且成骨过程与血管生成过程彼此相互联系,有共同的信号通路。目前研究尚未揭示成骨与血管生成信号通路的综合调控机制,值得广大学者深入探究。
2.2.4 缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子信号通路 近年来的研究表明,缺氧信号通路在调节血管生长及其修复方面发挥着重要作用。在正常氧饱和度下,缺氧诱导因子1α翻译后即被蛋白酶水解复合体降解。在缺氧情况下,缺氧诱导因子1α活性发生变化,稳定性提高,降解过程受到抑制,缺氧诱导因子1α与1β结合形成缺氧诱导因子1,接着转入胞核内调节一些基因的转录。血管内皮生长因子是关键的促血管形成因子,血管内皮生长因子编码基因受缺氧诱导因子1的调控。缺氧诱导因子1作用于血管内皮生长因子编码基因和血管内皮生长因子受体编码基因的结合位点,提高血管内皮生长因子 mRNA的表达,促进血管生成[47]。
铜具有改善的血管生成能力,并可提高缺氧诱导因子1α的稳定性,显著上调缺氧诱导因子1α和血管内皮生长因子的表达[48],见图6。
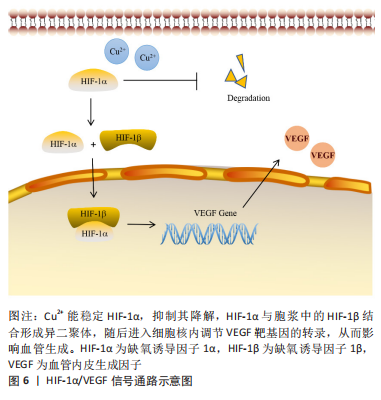
有研究者用Cu2+来人为模拟缺氧环境研究血管生成,将Cu2+掺杂到生物活性支架中来诱导低氧微环境也被证明是可行的[49]。WU等[50]首次将微弧氧化与水热处理结合,成功地将铜引入钛种植体表面,该材料显示出良好的成骨、血管生成活性、生物相容性以及抗菌性能,且再次印证了铜通过激活缺氧信号通路介导血管生成的机制。这次表面改性的成功实践,为制备多功能生物活性植入涂层奠定了基础。
大量研究证明,镁可提高内皮细胞的活性,促进内皮细胞迁移,内皮细胞在体外经镁的刺激生成的管状结构长度更长,数量及节点更多,缺氧诱导因子1α和血管内皮生长因子的表达显著提高[51-53]。HAMUSHAN等[54]在大鼠牵张成骨模型的髓腔内放置高纯镁钉,发现在高纯度镁组中血管内皮生长因子和缺氧诱导因子1α高表达。为了探究牵张成骨过程中Mg2+调控的信号通路,他们选择了与血管生成相关的PCR阵列,并在进一步的Western blot结果中提出了镁促进骨生成和钙化的可能机制是Mg减少缺氧诱导因子1α的降解,促进血管内皮生长因子表达,刺激血管的形成,促进成骨钙化。镁对血管生成的刺激进一步促进了成骨,镁在骨科植入物中的应用潜力巨大。
既往研究发现,在生物材料中添加钴可诱导更高水平的血管生成,并且体外实验显示钴的加入未对内皮细胞活性造成影响,Co2+可诱导缺氧诱导因子1α的高表达,提高缺氧诱导因子1α的转录活性,进一步增强血管内皮生长因子的表达,促进血管生成[55-56]。AZEVEDO等[57]研究了含钴的生物玻璃,揭示了钴通过激活缺氧途径促进血管生成的机制。实验发现在一定浓度范围时,钴对缺氧诱导因子1α活性及表达皆有显著增强作用,且呈浓度依赖性增强,Co2+通过抑制缺氧诱导因子1α的降解来激活缺氧途径,上调血管内皮生长因子等基因的表达,促进血管生成。钴作为治疗离子掺入生物支架,是获得组织修复优质材料的一种可行方法。
综上所述,在关于金属材料促血管生成机制的研究中,缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子信号通路提供了一种合理的解释。但文章发现缺氧诱导因子1可调控血管内皮生长因子编码基因,Wnt、MAPK及PI3K等通路也可影响血管内皮生长因子的表达,这些通路与缺氧诱导因子1α是否为级联关系尚未有研究阐明。
2.3 医用金属材料对血管化的免疫调节 金属材料植入机体时,会触发宿主免疫反应,诱导过度的炎症反应,影响成骨与血管生成效果,限制材料的临床应用。为解决这一问题,需要深入研究金属材料植入后发生的生物免疫反应。
镁缺乏会使炎症细胞因子表达增加,导致内皮细胞功能障碍,细胞增殖减少[58],镁可以有效预防或者治疗血管功能障碍。尽管镁在内皮功能和屏障完整性方面起着关键作用,但镁影响内皮的具体机制目前仍处于探索阶段。Toll样受体跨膜家族在识别病原体和引发先天免疫反应中发挥重要作用,Toll样受体4在内皮细胞和血管平滑肌细胞中表达,损伤可导致Toll样受体4激活特定的炎症反应,诱使内皮细胞功能紊乱[59]。一方面,
ALMOUSA等[60]和JIN等[61]学者研究发现镁可以直接抑制Toll样受体4的表达,逆转脂多糖诱导的MAPK和核转录因子κB的激活,降低了促炎细胞因子白细胞介素8、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子的表达,减轻了炎症反应,且抑制效果与镁浓度呈剂量依赖性。另一方面,由于Ca2+是Toll样受体4激活炎症的主要启动子[62],而Mg2+作为钙离子通道阻滞剂,可以通过降低细胞内Ca2+浓度,从而间接降低Toll受体4活性,进而抑制核转录因子κB激活,降低炎症因子的表达[63]。
镁对Toll样受体4的抑制作用一定程度上解释了镁降低炎症反应的机制。另有研究发现,镁的抗炎性能与其抑制巨噬细胞M1型转化、促进M2型转化有关,镁可抑制巨噬细胞向M1型分化,显著下调炎症因子表达,使促炎细胞因子的产生大幅度减少,M1的低表达促进了体外内皮细胞血管生成[64]。CHENG等[65]在镁表面制造了一种镁铝层状双氢氧化物涂层,该涂层不但可以显著抑制巨噬细胞活化为M1表型,抑制核转录因子κB信号通路的活化减轻炎症反应,并且诱导巨噬细胞分泌的细胞因子还可以进一步改善成骨和血管生成。除此之外,材料植入大鼠体内8周后,重要组织器官切片未发现明显病理变化,血液指标未见异常,展现出优秀的生物安全性。综上所述,镁具有出色的成骨、血管生成、抗炎、生物安全性和可降解性能,可以用于操纵血管生成微环境,开发调节炎症、成骨和血管生成的理想生物材料,镁基合金的植入材料以及镁修饰的生物材料将可能成为未来组织工程的主流材料。一系列研究表明,锶、锌和铜同样也可以与巨噬细胞发生反应,促进巨噬细胞向M2表型转化,并降低促炎基因表达,减少促炎细胞因子分泌,增加抗炎基因表达和抗炎细胞因子分泌[66-68]。
巨噬细胞通过诱导免疫原性反应,调节局部炎症反应,参与组织的修复再生,适当的炎症反应有利于骨与血管的重塑。当前研究尚未彻底揭示金属离子浓度对巨噬细胞增殖分化的影响,改善植入物介导的免疫反应仍是未来研究热点。
2.4 改善金属材料血管生成的方法 金属离子促血管生成的分子机制丰富,为镁、锌、锶、铜等金属应用于临床奠定生物学基础[69-76],见表1-4。
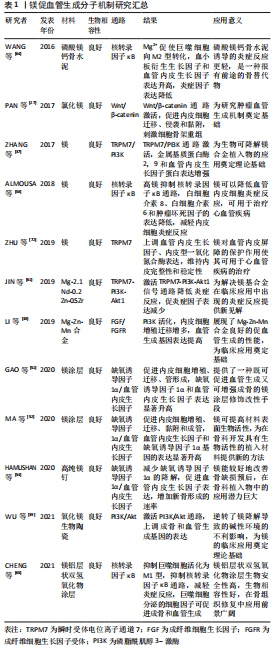

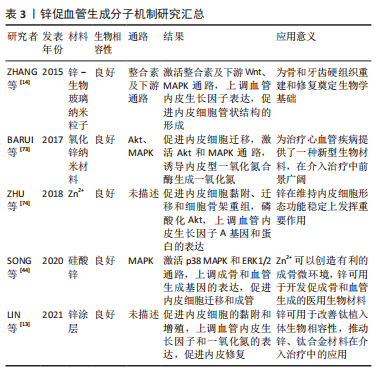
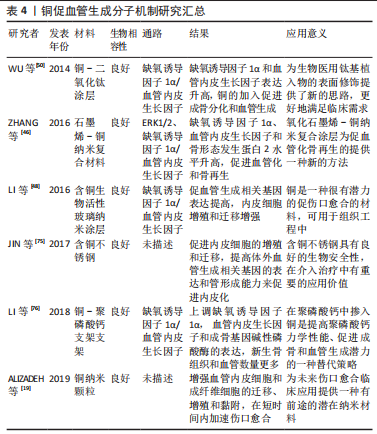
由前文所述可以发现,金属离子浓度是影响金属材料血管诱导性能的重要因素,因此调控金属离子的释放速率对血管生成具有重大意义。调控金属离子的释放速率主要可以从以下几个方面入手:第一,对镁、锌此类生物可降解合金进行改性,提高耐腐蚀性能,减缓降解速率。目前改性的方法主要有:纯化镁、锌合金、合金化、表面涂层及热处理等[69-70]。第二,选择石墨烯、生物陶瓷等材料作为金属离子的载体,控制金属离子以适宜的速度释放[45,71]。金属离子合理持续的释放速率是衡量生物材料促血管化性能优越的标准之一。

| [1] ZHU S, BENNETT S, KUEK V, et al. Endothelial cells produce angiocrine factors to regulate bone and cartilage via versatile mechanisms. Theranostics. 2020;10(13):5957-5965. [2] HU K, OlSEN BR. The roles of vascular endothelial growth factor in bone repair and regeneration. Bone. 2016;91:30-38. [3] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):426-436. [4] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492): 323-328. [5] ŠALANDOVÁ M, VAN HENGEL I, APACHITEI I, et al. Inorganic agents for enhanced angiogenesis of orthopedic biomaterials. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(12):e2002254. [6] BOSE S, FIELDING G, TARAFDER S, et al. Understanding of dopant-induced osteogenesis and angiogenesis in calcium phosphate ceramics. Trends Biotechnol. 2013;31(10):594-605. [7] LIU W, GUO S, TANG Z, et al. Magnesium promotes bone formation and angiogenesis by enhancing MC3T3-E1 secretion of PDGF-BB. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2020;528(4):664-670. [8] GU Y, ZHANG J, ZHANG X, et al. Three-dimensional printed mg-doped β-TCP bone tissue engineering scaffolds: effects of magnesium Ion concentration on osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vitro. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019; 16(4):415-429. [9] ZHANG W, FENG C, YANG G, et al. 3D-printed scaffolds with synergistic effect of hollow-pipe structure and bioactive ions for vascularized bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2017;135:85-95. [10] WANG C, XU D, LIN L, et al. Large-pore-size Ti6Al4V scaffolds with different pore structures for vascularized bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C. 2021; 131:112499. [11] 包庞,刘焕云,王玉清,等.锌离子对人脐静脉内皮细胞生物学功能的影响[J].中华心血管病杂志,2018,46(5):390-395. [12] MA J, ZHAO N, ZHU D. Endothelial cellular responses to biodegradable metal Zinc. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2015;1(11):1174-1182. [13] LIN Y, ZHANG L, YANG Y, et al. Loading Gentamicin and Zn2+ on TiO2 Nanotubes to Improve Anticoagulation, Endothelial Cell Growth, and Antibacterial Activities. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:9993247. [14] ZHANG J, PARK YD, BAE WJ, et al. Effects of bioactive cements incorporating zinc-bioglass nanoparticles on odontogenic and angiogenic potential of human dental pulp cells. J Biomater Appl. 2015;29(7):954-964. [15] HERMAWAN H. Updates on the research and development of absorbable metals for biomedical applications. Prog Biomater. 2018;7(2):93-110. [16] 费倩,尹洪涛,李今朝,等.铜在血管内皮细胞损伤与修复中的作用[J].医学与哲学(B). 2014,35(7):45-47. [17] 靳淑静,王同敏,任玲,等.铜在心血管系统中的有益作用[J].现代生物医学进展,2018,18(16):3196-3200. [18] LI S, XIE H, LI S, et al. Copper stimulates growth of human umbilical vein endothelial cells in a vascular endothelial growth factor-independent pathway. Exp Biol Med. 2012;237(1):77-82. [19] ALIZADEH S, SEYEDALIPOUR B, SHAFIEYAN S, et al. Copper nanoparticles promote rapid wound healing in acute full thickness defect via acceleration of skin cell migration, proliferation, and neovascularization. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2019;517(4):684-690. [20] LI K, XIA C, QIAO Y, et al. Dose-response relationships between copper and its biocompatibility/antibacterial activities. J Trace Elem Med Bio. 2019; 55:127-135. [21] LIU C, FU X, PAN H, et al. Biodegradable Mg-Cu alloys with enhanced osteogenesis, angiogenesis, and long-lasting antibacterial effects. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27374. [22] 蔺艳,张莹茜,盘强文,等.锶矿泉水对人血管内皮细胞的增殖和功能的影响[J].中国食品卫生杂志,2013,25(2):136-139. [23] LIU X, SUN Y, SHEN J, et al. Strontium doped mesoporous silica nanoparticles accelerate osteogenesis and angiogenesis in distraction osteogenesis by activation of Wnt pathway. Nanomedicine. 2022;41:102496. [24] WU X, TANG Z, WU K, et al. Strontium-calcium phosphate hybrid cement with enhanced osteogenic and angiogenic properties for vascularised bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(30):5982-5997. [25] GU Z, XIE H, LI L, et al. Application of strontium-doped calcium polyphosphate scaffold on angiogenesis for bone tissue engineering. J Mater Sci-Mater M. 2013;24(5):1251-1260. [26] GOODWIN AM, SULLIVAN KM, D’AMORE PA. Cultured endothelial cells display endogenous activation of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway and express multiple ligands, receptors, and secreted modulators of Wnt signaling. Dev Dynam. 2006;235(11):3110-3120. [27] PAN S, AN L, MENG X, et al. MgCl(2) and ZnCl(2) promote human umbilical vein endothelial cell migration and invasion and stimulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(5):4663-4670. [28] YU Z, FAN L, LI J, et al. Lithium prevents rat steroid-related osteonecrosis of the femoral head by β-catenin activation. Endocrine. 2016;52(2):380-390. [29] EASWARAN V, LEE SH, INGE L, et al. beta-Catenin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2003; 63(12):3145-3153. [30] HARO DURAND LA, VARGAS GE, VERA-MESONES R, et al. In Vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Response to Ionic Dissolution Products from Lithium-Containing 45S5 Bioactive Glass. Materials. 2017;10(7):740. [31] 崔斌,刘曦,李佳蓓,等.氯化锂通过激活Wnt信号通路促进内皮祖细胞的增殖能力[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2017,25(10):985-988, 1001. [32] ZEILBECK LF, MÜLLER B, KNOBLOCH V, et al. Differential angiogenic properties of lithium chloride in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e95546. [33] LIU W, LI T, YANG C, et al. Lithium-incorporated nanoporous coating formed by micro arc oxidation (MAO) on magnesium alloy with improved corrosion resistance, angiogenesis and osseointegration. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2019;15(6):1172-1184. [34] ERSAHIN T, TUNCBAG N, CETIN-ATALAY R. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR interactive pathway. Mol Biosyst. 2015;11(7):1946-1954. [35] LEE MY, LUCIANO AK, ACKAH E, et al. Endothelial Akt1 mediates angiogenesis by phosphorylating multiple angiogenic substrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(35):12865-12870. [36] KOBIALKA P, GRAUPERA M. Revisiting PI3-kinase signalling in angiogenesis. Vasc Biol. 2019;1(1):H125-H134. [37] ZHANG X, ZU H, ZHAO D, et al. Ion channel functional protein kinase TRPM7 regulates Mg ions to promote the osteoinduction of human osteoblast via PI3K pathway:In vitro simulation of the bone-repairing effect of Mg-based alloy implant. Acta Biomater. 2017;63:369-382. [38] LI D, YUAN Q, YU K, et al. Mg-Zn-Mn alloy extract induces the angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells via FGF/FGFR signaling pathway. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2019;514(3):618-624. [39] WU Q, XU S, WANG F, et al. Double-edged effects caused by magnesium ions and alkaline environment regulate bioactivities of magnesium-incorporated silicocarnotite in vitro. Regen Biomater. 2021;8(6):rbab016. [40] SUN Y, LI Y, ZHANG Y, et al. A polydopamine-assisted strontium-substituted apatite coating for titanium promotes osteogenesis and angiogenesis via FAK/MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Mater Sci Eng C. 2021;131:112482. [41] MARTINS BR, PINTO TS, DA COSTA FERNANDES CJ, et al. PI3K/AKT signaling drives titanium-induced angiogenic stimulus. J Mater Sci-Mater M. 2021; 32(1):18. [42] YANG RS, TZENG HP, HO FM, et al. Titanium implants alter endothelial function and vasoconstriction via a protein kinase C-regulated pathway. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(8):3258-3264. [43] ZHANG W, CAO H, ZHANG X, et al. A strontium-incorporated nanoporous titanium implant surface for rapid osseointegration. Nanoscale. 2016;8(9): 5291-301. [44] SONG Y, WU H, GAO Y, et al. Zinc silicate/nano-hydroxyapatite/collagen scaffolds promote angiogenesis and bone regeneration via the p38 mapk pathway in activated monocytes. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2020;12(14):16058-16075. [45] CHEN Y, ZHENG Z, ZHOU R, et al. Developing a strontium-releasing graphene oxide-/collagen-based organic-inorganic nanobiocomposite for large bone defect regeneration via MAPK signaling pathway. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2019;11(17):15986-15997. [46] ZHANG W, CHANG Q, XU L, et al. Graphene oxide-copper nanocomposite-coated porous cap scaffold for vascularized bone regeneration via activation of Hif-1α. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(11):1299-1309. [47] 王美玲,刘华绪.HIF-VEGF-Notch信号通路在血管生成中的作用[J].中国麻风皮肤病杂志,2021,37(5):332-336. [48] LI J, ZHAI D, LV F, et al. Preparation of copper-containing bioactive glass/eggshell membrane nanocomposites for improving angiogenesis, antibacterial activity and wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2016;36:254-266. [49] WU C, ZHOU Y, XU M, et al. Copper-containing mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with multifunctional properties of angiogenesis capacity, osteostimulation and antibacterial activity. Biomaterials. 2013;34(2):422-433. [50] WU Q, LI J, ZHANG W, et al. Antibacterial property, angiogenic and osteogenic activity of Cu-incorporated TiO(2) coating. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2(39):6738-6748. [51] GAO P, FAN B, YU X, et al. Biofunctional magnesium coated Ti6Al4V scaffold enhances osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo for orthopedic application. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(3):680-693. [52] MA L, CHENG S, JI X, et al. Immobilizing magnesium ions on 3D printed porous tantalum scaffolds with polydopamine for improved vascularization and osteogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;117:111303. [53] YU Y, JIN G, XUE Y, et al. Multifunctions of dual Zn/Mg ion co-implanted titanium on osteogenesis, angiogenesis and bacteria inhibition for dental implants. Acta Biomater. 2017;49:590-603. [54] HAMUSHAN M, CAI W, ZHANG Y, et al. High-purity magnesium pin enhances bone consolidation in distraction osteogenesis model through activation of the VHL/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling. J Biomater Appl. 2020;35(2):224-236. [55] BARRIONI BR, DE LAIA AGS, VALVERDE TM, et al. Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility and structure of cobalt-releasing sol-gel bioactive glass. Ceram Int. 2018;44(16):20337-20347. [56] KULANTHAIVEL S, MISHRA U, AGARWAL T, et al. Improving the osteogenic and angiogenic properties of synthetic hydroxyapatite by dual doping of bivalent cobalt and magnesium ion. Ceram Int. 2015;41(9):11323-11333. [57] AZEVEDO MM, TSIGKOU O, NAIR R, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-stabilizing bioactive glasses for directing mesenchymal stem cell behavior. Tissue Eng Pt A. 2015;21(1-2):382-389. [58] ALMOUSA LA, SALTER AM, LANGLEY-EVANS SC. Magnesium deficiency heightens lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and enhances monocyte adhesion in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Magnesium Res. 2018;31(2):39-48. [59] SALVADOR B, ARRANZ A, FRANCISCO S, et al. Modulation of endothelial function by Toll like receptors. Pharmacol Res. 2016;108:46-56. [60] ALMOUSA LA, SALTER AM, LANGLEY-EVANS SC. Varying magnesium concentration elicits changes in inflammatory response in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Magnesium Res. 2018;31(3):99-109. [61] JIN L, CHEN C, LI Y, et al. A biodegradable mg-based alloy inhibited the inflammatory response of THP-1 cell-derived macrophages through the TRPM7-PI3K-AKT1 signaling axis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2798. [62] CHIANG CY, VECKMAN V, LIMMER K, et al. Phospholipase Cγ-2 and intracellular calcium are required for lipopolysaccharide-induced Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) endocytosis and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) activation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(6):3704-3709. [63] LIBAKO P, NOWACKI W, CASTIGLIONI S, et al. Extracellular magnesium and calcium blockers modulate macrophage activity. Magnesium Res. 2016;29(1):11-21. [64] WANG M, YU Y, DAI K, et al. Improved osteogenesis and angiogenesis of magnesium-doped calcium phosphate cement via macrophage immunomodulation. Biomater Sci-UK. 2016;4(11):1574-1583. [65] CHENG S, ZHANG D, LI M, et al. Osteogenesis, angiogenesis and immune response of Mg-Al layered double hydroxide coating on pure Mg. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(1):91-105. [66] WU T, LIU W, HUANG S, et al. Bioactive strontium ions/ginsenoside Rg1-incorporated biodegradable silk fibroin-gelatin scaffold promoted challenging osteoporotic bone regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2021;12:100141. [67] CHEN B, YOU Y, MA A, et al. Zn-Incorporated TiO(2) Nanotube Surface Improves Osteogenesis Ability Through Influencing Immunomodulatory Function of Macrophages. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15:2095-2118. [68] XU X, LU Y, LI S, et al. Copper-modified Ti6Al4V alloy fabricated by selective laser melting with pro-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory properties for potential guided bone regeneration applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2018;90: 198-210. [69] MEYSAM NA, ABOLFAZL Z, KINGSLEY BO, et al. A review of current challenges and prospects of magnesium and its alloy for bone implant applications. Prog Biomater. 2022;11(1):1-26. [70] 郑玉峰,吴远浩.处在变革中的医用金属材料[J].金属学报,2017,53(3): 257-297. [71] BAINO F, POTESTIO I, VITALE-BROVARONE C. Production and physicochemical characterization of cu-doped silicate bioceramic scaffolds. Materials. 2018;11(9):4524. [72] ZHU D, YOU J, ZHAO N, et al. Magnesium regulates endothelial barrier functions through TRPM7, MagT1, and S1P1. Adv Sci. 2019;6(18):1901166. [73] BARUI AK, NETHI SK, PATRA CR. Investigation of the role of nitric oxide driven angiogenesis by zinc oxide nanoflowers. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(18): 3391-3403. [74] ZHU D, SU Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Zinc regulates vascular endothelial cell activity through zinc-sensing receptor ZnR/GPR39. Am J Physiol-Cell Ph. 2018; 314(4):C404-C414. [75] JIN S, QI X, ZHANG B, et al. Evaluation of promoting effect of a novel Cu-bearing metal stent on endothelialization process from in vitro and in vivo studies. Sci Rep-UK. 2017;7(1):17394. [76] LI Y, WANG J, WANG Y, et al. Transplantation of copper-doped calcium polyphosphate scaffolds combined with copper (II) preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for bone defect repair. J Biomater Appl 2018;32(6):738-753. |
| [1] | 孙可欣, 曾今实, 李佳, 蒋海越, 刘霞. 力学刺激提高生物3D打印软骨构建物基质的形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | 方兴艳, 田侦丽, 赵哲仪, 文平, 谢婷婷. 亚砷酸钠对人脐静脉内皮细胞损伤及鞘氨醇激酶1/1-磷酸鞘氨醇信号轴的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [3] | 贺垠皓, 李晓声, 陈宏文, 陈铁柱. 3D打印多孔钽金属治疗发育性髋关节发育不良:现状及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1455-1461. |
| [4] | 党 祎, 杜成砚, 姚红林, 袁能华, 曹 金, 熊 山, 张顶梅, 王 信. 激素型骨坏死与氧化应激[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [5] | 龙桂月, 李冬冬, 廖红兵. 磷酸钙骨水泥/聚乳酸羟基乙酸降解产物促进小鼠单核细胞破骨向分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1193-1198. |
| [6] | 赵 璐, 赵逸菲, 高 达, 刘艳芳, 付婷婷, 徐江雁. Zeste基因抑制子基因12在糖尿病肾脏病模型大鼠肾组织中的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1179-1186. |
| [7] | 杨怡天, 王 璐, 姚 蔚, 赵 彬. 生物支架与巨噬细胞在骨再生中的相互影响及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [8] | 李 诚, 郑国爽, 蒯贤东, 于炜婷. 海藻酸盐支架修复关节软骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [9] | 唐昊天, 廖荣东, 田 京. 压电材料修复骨缺损的应用及设计思路[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [10] | 许 言, 李 平, 赖春花, 朱培君, 杨 烁, 徐淑兰. 血管化骨再生中压电生物材料的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [11] | 李欣悦, 李熙恒, 毛天娇, 唐 亮, 李 江. 三维培养人牙周膜干细胞的形态、活性及成骨分化能力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| [12] | 袁 维, 刘静东, 徐广辉, 康 健, 李富平, 王英杰, 支中正, 李冠武. 人血管周围干细胞成骨分化及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的调控[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 866-871. |
| [13] | 袁 博, 谢利德, 付秀美. 许旺细胞源性外泌体促进损伤周围神经的修复与再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| [14] | 秦宇星, 任前贵, 李子龙, 全嘉星, 沈佩锋, 孙 韬, 王浩宇. 骨微血管内皮细胞在股骨头坏死中的作用机制及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 955-961. |
| [15] | 邵子晨, 李华南, 顾 兵, 章晓云, 孙伟康, 刘永钱, 甘 斌. 痛风过程中微小RNA、长链非编码RNA和环状RNA介导降尿酸、抗炎及调控骨代谢的协同调节作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(5): 765-771. |
医用金属生物材料因其出色的机械力学性能、良好生物相容性、生物安全性及可降解性能而被广泛应用于临床中,例如心血管支架、骨修复支架和口腔种植材料等,近年来逐渐成为生物组织工程研究的热点。近十年来,研究人员着力于改善植入材料的物理和化学性能以改善成骨,由于快速血管化是促进细胞增殖、成骨分化、形成新生骨组织的先决条件,因此研究金属促血管化机制,开发具有促血管生成特性的金属材料对骨组织修复与再生意义重大。镁、锌、铜、锶及钴等金属离子已经被大多数研究证明能促进血管生成[5-6],这些金属通过影响内皮细胞功能、血管生成过程中的相关因子的分泌与表达,从而参与并调节血管生成过程。镁合金因其良好的生物相容性、机械力学性能、生物可降解性而被广泛研究,成为生物材料领域的研究热点。生物可降解镁合金支架植入初期可提供一定的力学支撑,随着机体的修复及组织的再生而逐渐降解,被人体吸收代谢,不需要经历二次手术取出,减少机体损伤,减轻患者痛苦和经济负担,然其过快的降解速率成为限制其临床应用的瓶颈,对镁、锌此类生物可降解金属的改性是未来研究的重点。绝大多数金属离子在一定浓度范围可产生良好的生物学效应,却在高浓度时表现出细胞毒性,因此控制金属离子在体内的释放速率是发挥其促血管化作用的关键环节。
当骨缺损或骨折时,植入医用金属材料不仅可以提供机械力学支撑,还可以通过降解生成金属离子来诱导血管内皮细胞血管化,生成新生血管,修复损伤血管,加速骨缺损组织再生与愈合。文章就目前金属材料促血管化的特性进行综述,从细胞层面和分子层面,重点总结讨论了不同的医用金属材料促血管化的分子机制,并对金属材料通过免疫调节影响血管生成做一阐述,以期为将来研究金属促血管生成的分子机制提供新方向,为开发加快血管化组织修复与再生的材料提供新思路,为医用金属材料的临床应用提供参考。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者于2022年1月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索2012年1月至2022年1月发表的相关文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、ScienceDirect、中国知网以及万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“医用金属材料、合金、支架、血管化、血管生成、信号通路、内皮细胞”,英文检索词为“medical metal materials OR alloy”“stent OR scaffold”“vascularization OR angiogenesis”“molecular mechanism OR signaling pathway” “endothelial cells”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述和学位论文。
1.1.6 数据库检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。

1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①医用金属材料与血管生成相关的文献;②优先选择近期发表、同一领域中与主题中心相关的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与主题无关的文献;②论点及论据不明确的文章;③重复性研究。
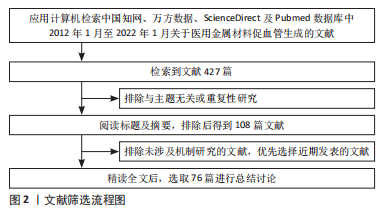
1.3 文献质量评估及数据的提取 通过计算机检索,初步共检索到427篇文献,通过阅读文题及摘要初步筛选;精读全文排除与主题相关性差、质量不高或重复性文献,最终纳入76篇文献(英文文献69篇,中文文献7篇) 进行综述,见图2。
3.2 综述的创新性 目前研究人员的研究方向主要集中于医用金属材料促成骨分化,对成骨分化的信号通路、分子机制研究较多,对促血管化的研究不够深入和全面。该综述总结讨论了近些年几种医用金属材料在血管生成过程中对相关细胞形态功能的影响、对血管生成相关因子的调控、对相关基因表达的影响,以及金属材料诱导的免疫反应对血管生成的影响,分析总结了不同医用金属材料促血管生成的可能分子机制。
3.3 综述的局限性 目前医用金属材料促血管生成的研究较少,大多数研究局限于体外实验和动物实验,缺乏临床实践提供理论依据。文章中总结探讨的大部分都是金属离子对促进血管生成的单条信号通路或者某个基因蛋白的影响,通路与通路之间、蛋白与蛋白之间的具体关系和作用机制尚未阐述清楚,还需进一步深究探讨。金属离子促骨生成和血管生成耦合,具体的分子机制如何,是否有共同的信号通路等未知的问题仍待解决。医用金属材料离子释放速率是影响金属材料血管诱导性能的重要因素,但由于不是此次综述的阐述重点,文中简要提及了一些控制离子释放速率的方法,有其局限性。
3.4 综述的意义 文章综述了不同金属材料诱导调节血管生成可能的分子机制,为成血管信号通路之间相互作用联系提供了新的研究思路,对于治疗心血管疾病、修复骨缺损和血管化组织的修复与再生具有重要意义。随着科学研究的不断深入,有望揭示不同类型的金属支架植入机体后,在血管生成方面所发挥的具体作用,以及成骨-血管生成耦合的具体分子机制,为将来开发各种金属植入材料以加快血管化组织的修复与再生,减少心血管支架植入术后并发症奠定理论基础。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程

文题释义:
医用金属材料:是一类具有良好生物相容性、优秀的力学性能以及方便加工制作的植入机体的生物金属材料,此类材料通常以支架、种植体、赝复体及外科辅助材料的形式广泛应用于骨科、牙科、整形及介入治疗中。
血管生成:血液供应是骨再生的先决条件,植入材料与病损组织相互作用,刺激内皮细胞向病损区迁移增殖,诱导血管生成相关基因的表达,促进血管生成,加快骨再生进程,改善骨再生效果。
医用金属生物材料因其出色的机械力学性能、良好生物相容性、生物安全性及可降解性能而被广泛应用于临床中,例如心血管支架、骨修复支架和口腔种植材料等,近年来逐渐成为生物组织工程研究的热点。近十年来,研究人员着力于改善植入材料的物理和化学性能以改善成骨,由于快速血管化是促进细胞增殖,成骨分化,形成新生骨组织的先决条件,因此研究金属促血管化机制,开发具有促血管生成特性的金属材料对骨组织修复与再生意义重大。镁、锌、铜、锶、钴等金属离子已经被大多数研究证明能促进血管生成,这些金属通过影响内皮细胞功能,血管生成过程中的相关因子的分泌与表达,从而参与并调节血管生成过程。镁合金因其良好的生物相容性,机械力学性能,生物可降解性而被广泛研究,成为生物材料领域的研究热点。生物可降解镁合金支架植入初期可提供一定的力学支撑,随机体的修复,组织的再生而逐渐降解,被人体吸收代谢,不需要经历二次手术取出,减少机体损伤,减轻患者痛苦和经济负担,然其过快的降解速率成为限制其临床应用的瓶颈,对镁、锌此类生物可降解金属的改性是未来研究的重点。绝大多数金属离子在一定浓度范围可产生良好的生物学效应,却在高浓度时表现出细胞毒性,因此控制金属离子在体内的释放速率是发挥其促血管化作用的关键环节。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||