中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (23): 3635-3639.doi: 10.12307/2023.588
• 血管组织构建 vascular tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
NICD/Hes1影响心肌梗死后小鼠缺血心肌的血管新生
卢鹏飞1,施伟丽2
- 1河南中医药大学第三附属医院心血管科,河南省郑州市 450003;2河南中医药大学第二临床医学院(河南省中医院),河南省郑州市 450002
NICD/Hes1 affects angiogenesis in the ischemic myocardium of myocardial infarction mice
Lu Pengfei1, Shi Weili2
- 1Cardiovascular Division, Third Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China; 2The Second Clinical Medical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine (Henan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
血管新生:是在原有毛细血管或微静脉基础上,通过内皮细胞的增殖、分化和迁移,以芽生或非芽生的形式生成新血管的过程。血管新生既参与机体生理情况下的血管生成,同时是伤口愈合和缺血组织修复的重要保障。Notch信号:是血管正常发育必需的关键信号通路之一,参与组织血管新生过程多个步骤,包括尖端细胞和柄细胞分化、柄细胞增殖、内皮细胞迁移和黏附、血管重塑以及动静脉分化,同时参与间充质干细胞向内皮细胞分化,在缺血性心脑血管相关疾病的发生发展过程中发挥重要作用。
背景:心肌缺血是心肌梗死后心功能受损的主要原因之一,Notch通路参与血管新生过程,但其下游分子Notch受体胞内部分(Notch intracellular domain,NICD)/Hes1在心肌梗死后缺血心肌血管新生中发挥何种作用,研究尚少。
目的:借助Notch γ分泌酶抑制剂RO4929097,探讨NICD/Hes1对心肌梗死后小鼠心功能及缺血心肌血管新生的影响。
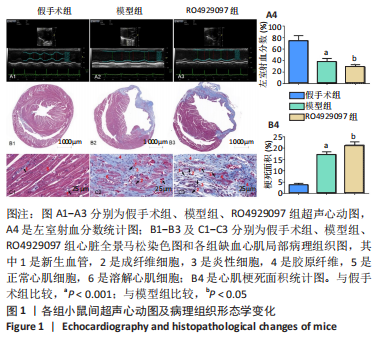
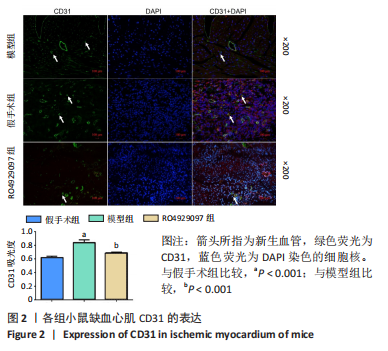
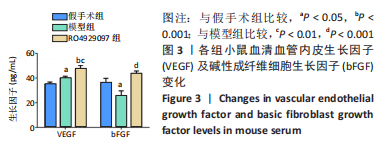
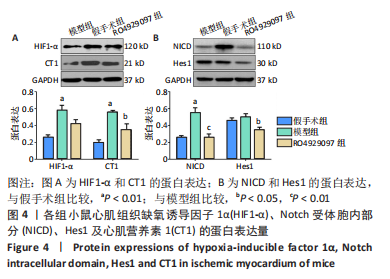
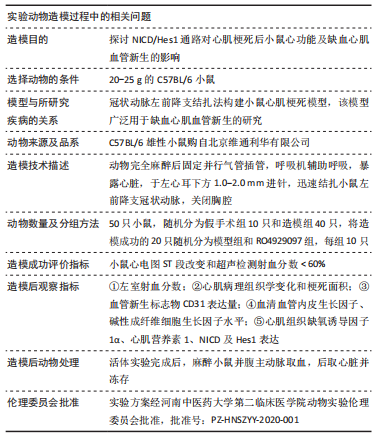
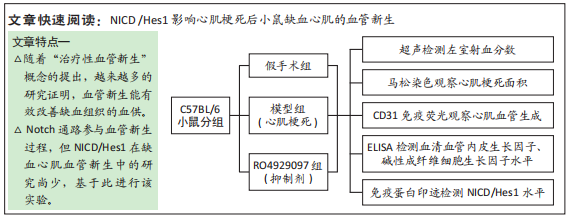
方法:按随机数字表法将C57BL/6小鼠分为假手术组、模型组和RO4929097组,每组10只,后2组C57BL/6小鼠通过结扎左前降支冠状动脉建立心肌梗死模型,RO4929097组小鼠术后第2天按10 mg/(kg·d)每天灌胃1次,假手术组和模型组小鼠给予等体积生理盐水,灌胃20 d。第21天超声检测小鼠左室射血分数,马松染色观察心肌梗死面积及病理组织学变化,免疫荧光法检测缺血心肌CD31水平,酶联免疫吸附法检测血清血管内皮生长因子和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子水平,免疫蛋白印迹技术检测心肌组织缺氧诱导因子1α、心肌营养素1及NICD、Hes1蛋白表达量。
结果与结论:①模型组小鼠左室射血分数较假手术组显著降低(P < 0.001),与模型组比较,RO492909组左室射血分数降低更明显(P < 0.05);②马松染色后,模型组及RO492909组小鼠梗死面积较假手术组显著增加(P < 0.001),RO492909组梗死面积较模型组增加明显(P < 0.05);③模型组小鼠心肌CD31平均吸光度值较假手术组升高明显(P < 0.001),RO492909组CD31平均吸光度值较模型组明显降低(P < 0.001);④模型组、RO4929097组小鼠血清血管内皮生长因子水平较假手术组明显升高(P < 0.05),RO492909组血管内皮生长因子较模型组升高明显(P < 0.01);⑤模型组小鼠心肌组织缺氧诱导因子1α、心肌营养素1水平较假手术组明显增加(P < 0.01),RO492909组两者表达量较模型组均降低;与假手术组比较,模型组小鼠NICD蛋白表达明显增加(P < 0.01),RO492909组NICD表达量较模型组降低(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,RO492909组小鼠Hes1水平降低(P < 0.05);⑥结果说明,RO4929097可能通过抑制Notch γ分泌酶活性,降低NICD/Hes1表达,从而减少缺血心肌血管新生,降低心肌梗死小鼠左室射血分数。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1434-6136(卢鹏飞)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: