1.1 设计 随机对照动物实验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2020年9月至2021年7月在河南省中医药大学SPF级实验动物中心完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 40只雄性SPF级SD大鼠,鼠龄6-8周,体质量(190±10) g,购自河南中医药大学,动物生产许可证号:SYXK(豫)2020-0004。所有动物被饲喂于12 h光照/
12 h黑暗交替环境下,可随意获得常规食物和水。实验方案经河南省中医药大学动物实验伦理委员会批准(批准号为HNUCM-2020037)。实验过程遵循了国际兽医学编辑协会《关于动物伦理与福利的作者指南共识》和本地及国家法规。实验动物在麻醉下进行所有的手术,并尽一切努力最大限度地减少其疼痛、痛苦和死亡。
1.3.2 主要试剂与仪器 当归甙购自美国GLPBIO公司;血管紧张素Ⅱ、一氧化氮、丙二醛、血管细胞黏附分子1、细胞间黏附分子1和E-选择素酶联免疫吸附(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)试剂盒均购自北京BioTeke公司;活性氧检测试剂盒购自北京百奥莱博公司;凋亡细胞检测试剂盒购自德国Miltenyi Biotec公司;兔单克隆FOXO1抗体和鼠单克隆甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶(glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase,GAPDH)抗体购自英国Abcam公司;HRP标记的兔抗鼠和羊抗兔二抗购自美国Sigma公司;实时荧光定量PCR反应试剂盒TRIzol购自美国Invitrogen公司;噻唑蓝(3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide,MTT)染色液和过氧化氢(H2O2)购自大连Takara Biotechnology公司;ECL发光液、碘化丙啶(propidium Iodide,PI)染色液和TUNEL检测试剂盒购自美国Thermo公司;胎牛血清(fetal bovine serum,FBS)和DMEM培养液购自美国Gibco公司;FOXO1过表达载体(pcDNA-FOXO1)、FOXO1小干扰RNA(si-FOXO1)和对应阴性对照载体Vector或Scramble购自美国Bio-Rad公司。智能无创血压仪Softron BP-98AL购自北京软隆生物技术有限公司;凝胶成像分析仪购自广州瑞丰实验设备有限公司;BD LSRFortessa细胞分析仪购自美国BD Biosciences公司;酶标仪购自美国ELX800公司。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 动物实验
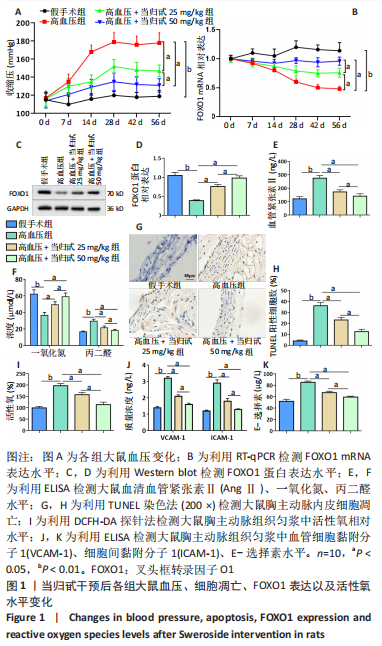
(1)动物模型建立:将40只SD大鼠随机分为假手术组、高血压组、高血压+当归甙25 mg/kg组和高血压+当归甙(50 mg/kg)组,每组10只。使用2%戊巴比妥钠(50 mg/kg)腹腔注射麻醉大鼠,将大鼠取右侧卧位固定于操作台,在左肋缘下方肾脏体表投影区域内消毒,剪去毛发,充分暴露手术区域,沿左肋弓下缘平行于脊柱约 1 cm处纵向切开皮肤1.0-2.0 cm,逐层分离皮肤、筋膜、肌层后充分暴露左肾,将左肾移出腹腔,用含生理盐水的纱布包裹,在肾门处用钝头镊小心分离肾动脉和肾静脉,利用内径0.25 mm的U形银夹缩窄左肾动脉,充分固定后将肾脏还纳腹腔并缝合建立高血压大鼠模型。假手术组仅分离血管,但不缩窄,其余操作与高血压组相同。建模4周后,若大鼠收缩压> 160 mmHg且解剖后左肾无坏死、萎缩或纤维化则建模成功。此时,利用当归甙(25 mg/kg或50 mg/kg)每天腹腔注射建模成功的大鼠,持续4周。手术后8周,在麻醉下断头处死所有大鼠。高血压建模成功率为100%。该动物模型通过减少肾血流量引起肾素-血管紧张素系统过度激活,并伴随血浆肾素活性和循环血管紧张素Ⅱ水平显著升高,以及血管壁中活性氧大量累积。

(2)大鼠血压监测:使用无创血压仪检测大鼠血压,血压监测前维持环境温度24 ℃左右,将大鼠放置于固定囊袋中,露出鼠尾,用乙醇擦拭使其尾动脉充分扩张,将加压尾套放置于鼠尾根部,使其与尾动脉紧密贴合。在大鼠安静的状态下,打开血压监测系统,待屏幕上的脉搏波信号出现并持续稳定5 min后开始测血压,连续测量5次,取平均值并记录。所有大鼠术前均进行基础血压测定,术后每周定期进行血压测定。
(3)测定大鼠血清血管紧张素Ⅱ、一氧化氮和丙二醛水平以评估建模的成功以及建模后的氧化应激水平:各组大鼠在手术后8周采用针刺心脏法采集血液并分离血清,破碎各组细胞并收集培养液上清,使用相应的ELISA试剂盒检测血清中血管紧张素Ⅱ、一氧化氮和丙二醛的水平和细胞中一氧化氮和丙二醛的水平。
(4)测定大鼠血管组织中的黏附分子水平以评估血管内皮细胞功能:手术后8周处死大鼠,收集大鼠胸主动脉组织使用液氮研磨法结合PBS制作组织匀浆,使用ELISA试剂盒检测组织匀浆中血管细胞黏附分子1、细胞间黏附分子1和E-选择素水平。
(5)TUNEL染色法:手术后8周收集大鼠胸主动脉,用镊子分离胸主动脉内皮,使用40 g/L多聚甲醛固定48 h,用乙醇脱水,二甲苯透明,石蜡浸润包埋,使用切片机将其切成2 μm左右的薄片,将切片放入45 ℃ 恒温箱烘干,二甲苯脱蜡,乙醇脱水。按TUNEL检测试剂盒的说明检测大鼠胸主动脉内皮细胞的凋亡,每个组从3个深度的切片组织中随机取10个切片,染色后,每个切片至少有100个细胞被评估。标记的细胞数表示为细胞总数的百分比,对平均百分比进行统计评估。使用光学显微镜观察并记录凋亡细胞。
(6)组织活性氧水平检测:手术后8周收集大鼠胸主动脉,并于冰上制作组织匀浆。按照说明书,在组织匀浆中加入5 μmol/L 2’,7’-二氯二氢-荧光素二乙酸酯(2′,7′-dichlorodihy-drofluorescein diacetate,DCFH-DA)探针,置于37 ℃环境下孵育20 min。使用荧光酶标仪测定荧光强度。
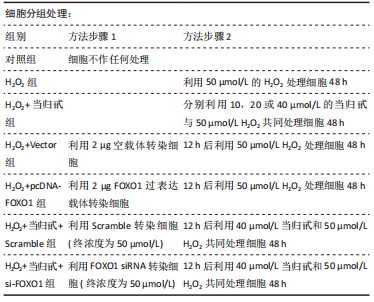
1.4.2 细胞实验
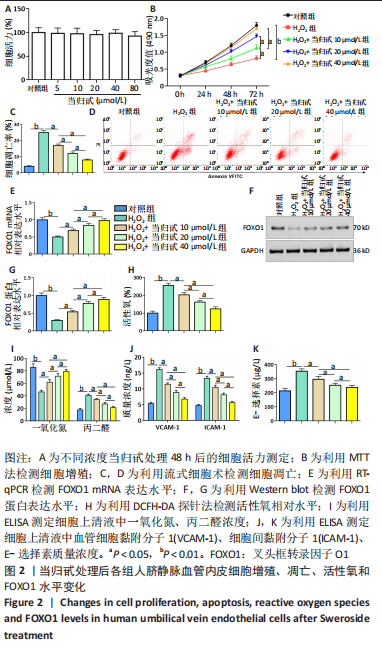
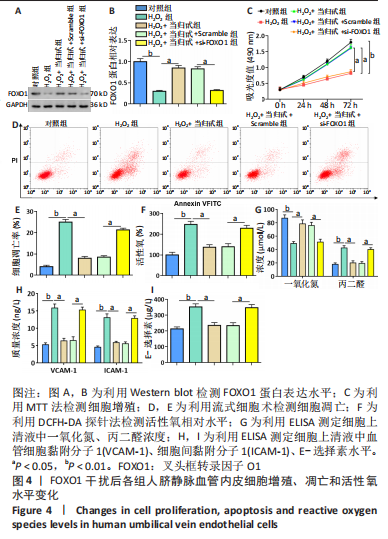
(1)细胞氧化损伤模型建立及处理:人脐静脉血管内皮细胞(human umbilical vein endothelial cells,HUVECs)购自美国ATCC细胞库。H2O2作为机体产生的一种活性氧,在自身浓度较高时可诱导大量活性氧生成,与动物模型一致可对内皮细胞造成氧化损伤。将细胞接种于6孔板,每孔约1.2×106细胞,每孔加入2 mL含体积分数10% FBS的DMEM培养液。
(2)MTT法检测HUVECs增殖:在细胞培养的第0,24,48和72 小时分别加入20 μL 5 g/L MTT, 于37 ℃孵育4 h,吸出培养液并加入150 μL二甲基亚砜,待结晶全部溶解后,使用酶标仪检测A值,检测波长为 490 nm。
(3)流式细胞术检测HUVECs凋亡:以2×108 L-1的细胞浓度接种于培养基孵育24 h后。收集细胞并用预冷PBS洗涤3次。将细胞重悬在含有PI的缓冲液中,室温培养15 min后,使用BD LSRFortessa细胞分析仪进行流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡。
(4)RT-qPCR检测细胞和组织中FOXO1 mRNA水平:使用TRIzol试剂按照说明书提取细胞的总RNA,使用TaqMan试剂盒将提取的总RNA反转录成cDNA。引物由生工生物工程(上海)有限公司合成,FOXO1上游引物:5′-GGC TGA GGG TTA GTG AGC AG-3′,下游引物: 5′-AAA GGG AGT TGG TGA AAG ACA-3′;GAPDH上游引物:5′-GTC GGA GTC AAC GGA TTT GGT-3′,下游引物:5′-GCC ATG GGT GGA ATC ATA TTG G-3′。qPCR反应体系为20 μL,包含2 μL模板,2 μL 10×TaqMan酶,1 μL引物1,1 μL引物2和14 μL ddH2O。qPCR反应条件:95 ℃ 1 min,90 ℃ 30 s, 56 ℃ 1 min,72 ℃ 90 s,30个循环,72 ℃延伸10 min。用SYBR Green Mater Mix试剂检测待检基因的mRNA水平,重复检测3次,mRNA水平以GAPDH作为内参。
(5)Western blot法检测FOXO1蛋白表达水平:使用RIPA裂解液裂解细胞并提取总蛋白,使用BCA试剂盒测定样品蛋白浓度。电泳结束后用蛋白转膜仪将蛋白转印至PVDF膜上,用5%脱脂牛奶将膜封闭1 h,TBST洗膜完成后,用一抗FOXO1(1∶500稀释)和GAPDH(1∶500稀释)于4 ℃孵育过夜,TBST洗膜,加入HRP标记的兔抗鼠二抗(1∶1 000稀释)室温孵育2 h,洗膜完成后在ECL中显色。目的蛋白表达水平=目的蛋白条带灰度值/内参GAPDH条带灰度值。
(6)细胞活性氧水平检测:按照说明书的要求将DCFH-DA稀释至10 μmol/L,弃掉细胞培养液,加入DCFH-DA(1×109L-1)并置于37 ℃环境下孵育20 min。使用荧光酶标仪测定荧光强度。
(7)ELISA检测一氧化氮、丙二醛及黏附分子水平:各组细胞按分组方法分别处理48 h后取细胞上清液,利用ELISA测定细胞上清液中一氧化氮、丙二醛、血管细胞黏附分子1、细胞间黏附分子1及E-选择素水平。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①大鼠建模后血压和FOXO1表达水平;②大鼠血清血管紧张素Ⅱ、一氧化氮和丙二醛水平;③大鼠胸主动脉组织中血管细胞黏附分子1、细胞间黏附分子1和E-选择素的水平;④当归甙干预各组HUVECs 增殖、凋亡和FOXO1 mRNA和蛋白的表达;⑤FOXO1过表达干预各组HUVECs增殖、凋亡和FOXO1蛋白的表达;⑥FOXO1干扰各组HUVECs增殖、凋亡和FOXO1蛋白表达。
1.6 统计学分析 使用SPSS 22.0软件对实验数据进行统计分析,结果采用x±s表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较用 LSD-t检验,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。文章统计学方法已经河南省中医药大学生物统计学专家的审核。