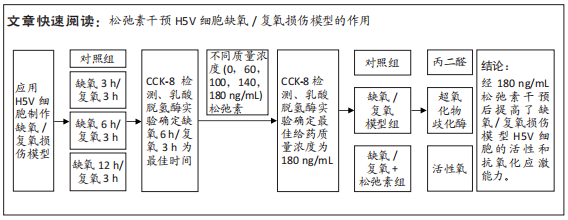
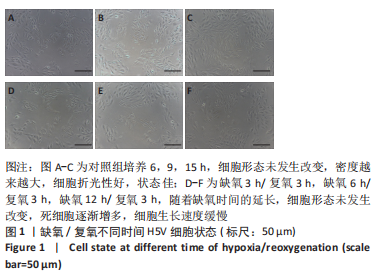
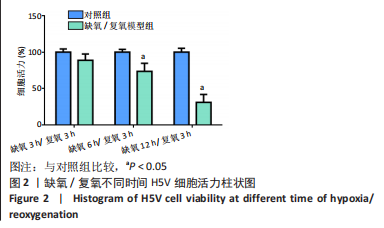
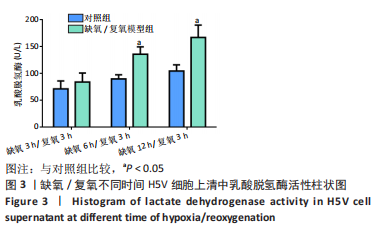
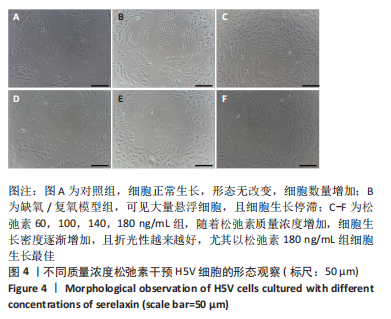
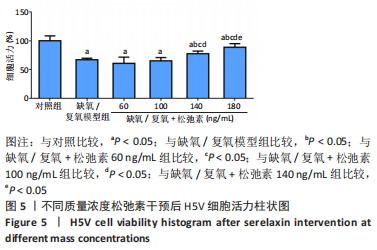
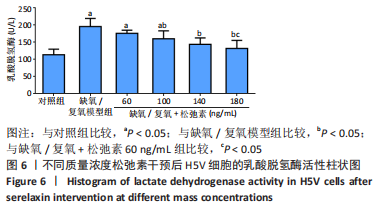
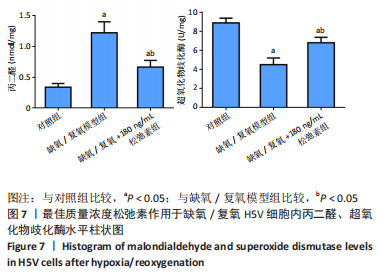
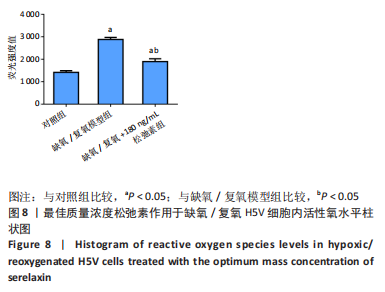
[1] VALLE RALEIGH J, MAURO AG, DEVARAKONDA T, et al. Reperfusion therapy with recombinant human relaxin-2 (Serelaxin) attenuates myocardial infarct size and NLRP3 inflammasome following ischemia/reperfusion injury via eNOS-dependent mechanism. Cardiovasc Res. 2017;113(6):609-619.
[2] YU F, LIU Y, XU J. Pro-BDNF Contributes to Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury in Myocardial Microvascular Endothelial Cells: Roles of Receptors p75NTR and Sortilin and Activation of JNK and Caspase 3. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:3091424.
[3] YANG HH, CHEN Y, GAO CY, et al. Protective Effects of MicroRNA-126 on Human Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells Against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Injury and Inflammatory Response by Activating PI3K/Akt/eNOS Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(2):506-518.
[4] ROCCO E, GRIMALDI MC, MAINO A, et al. Advances and Challenges in Biomarkers Use for Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction: From Bench to Clinical Practice. J Clin Med. 2022;11(7):2055.
[5] JAKUBAUSKIENE L, JAKUBAUSKAS M, LEBER B, et al. Relaxin Positively Influences Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Solid Organ Transplantation: A Comprehensive Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):631.
[6] BANI D. Recombinant human H2 relaxin (serelaxin) as a cardiovascular drug: aiming at the right target. Drug Discov Today. 2020;25(7): 1239-1244.
[7] METRA M, TEERLINK JR, COTTER G, et al. Effects of Serelaxin in Patients with Acute Heart Failure. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(8):716-726.
[8] SUNO K, SHINGU Y, WAKASA S. Protective effects of trehalose preconditioning on cardiac and coronary endothelial function through eNOS signaling pathway in a rat model of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022;477(10):2403-2414.
[9] 姜彤伟,郝珍珠,王冰梅,等.心肌缺血再灌注损伤中西医机制及相关药物治疗的研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2019,16(9):43-46.
[10] 朱明辉,朱骏昌,殷琚妹,等.心肌缺血患者再灌注损伤的发生机制及临床治疗[J].医学信息,2022,35(13):49-52.
[11] ZHANG D, WU H, LIU D, et al. Research Progress on The Mechanism and Treatment of Inflammatory Response in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Heart Surg Forum. 2022;25(3):E462-E468.
[12] 张云盛,滕天明,康毅,等.药物后处理对离体大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤影响的对比研究[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2016,24(10): 579-586.
[13] 何小奇,邓莉.抗心肌缺血再灌注损伤多肽类药物的研究进展[J].医学综述,2019,25(17):3473-3478.
[14] SUN M, JIN L, BAI Y, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against pathological cardiac remodeling by modulating galectin-3 expression. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(12):19529-19540.
[15] MARINS FR, OLIVEIRA AC, QADRI F, et al. Alamandine but not angiotensin-(1-7) produces cardiovascular effects at the rostral insular cortex. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021;321(3):R513-R521.
[16] RAJAPAKSHA IG, GUNARATHNE LS, ANGUS PW, et al. Update on New Aspects of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Hepatic Fibrosis and Portal Hypertension: Implications for Novel Therapeutic Options. J Clin Med. 2021;10(4):702.
[17] ZAMAN A, BANDAY AA. Angiotensin (1-7) protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via regulating expression of NRF2 and microRNAs in Fisher 344 rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022;323(1): F33-F47.
[18] 朱勇,杨德林.谷胱甘肽S-转移酶P1基因甲基化在前列腺癌发生、诊治和预后预测中的作用研究进展[J].山东医药,2022,62(9):109-111.
[19] 侯凯,谭昊宇,刘静,等.心肌缺血再灌注损伤的防治新靶点寻找及其研究进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2022,53(2):164-170.
[20] 彭石,马茜钰,张丹,等.铁死亡在心肌缺血再灌注损伤中的作用及靶向治疗研究进展[J].心血管病学进展,2022,43(4):357-361.
[21] XU MM, SEYLER L, BAUERLET, et al. Serelaxin activates eNOS, suppresses inflammation, attenuates developmental delay and improves cognitive functions of neonatal rats after germinal matrix hemorrhage. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):8115.
[22] CHUNDURI P, PATEL SA, LEVICK SP. Relaxin/serelaxin for cardiac dysfunction and heart failure in hypertension. Adv Pharmacol. 2022; 94:183-211.
[23] LIU ZH, ZHANG Y, WANG X, et al. SIRT1 activation attenuates cardiac fibrosis by endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;118:109227.
[24] HE X, LI S, LIU B, et al. Major contribution of the 3/6/7 class of TRPC channels to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion and cellular hypoxia/reoxygenation injuries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(23): E4582-E4591.
[25] ABDUL KSM, FAIZ N, JOVANOVIC A, et al. Isosteviol Protects H9c2 Cells Against Hypoxia-reoxygenation by Activating ERK1/2. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2021;21(1):73-77.
[26] 姜涛,吴硕,李志强,等.血小板衍生生长因子BB促进SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(13):1976-1981.
[27] 阴文超,罗春琼,王春燕,等.右美托咪定对大鼠心脏缺血再灌注损伤及小窝蛋白3的影响[J].四川医学,2020,41(1):20-23.
[28] WILHELMI T, XU X, TAN X, et al. Serelaxin alleviates cardiac fibrosis through inhibiting endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition via RXFP1. Theranostics. 2020;10(9):3905-3924.
[29] NISTRI S, FIORILLO C, BECATTI M, et al. Human Relaxin-2 (Serelaxin) Attenuates Oxidative Stress in Cardiac Muscle Cells Exposed In Vitro to Hypoxia-Reoxygenation. Evidence for the Involvement of Reduced Glutathione Up-Regulation. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(9):774.
[30] TEERLINK JR, DAVISION BA, COTTER G, et al. Effects of serelaxin in patients admitted for acute heart failure: a meta-analysis. Eur J Heart Fail. 2020; 22(2):315-329.
[31] CACERES FT, GASPARI TA, SAMUEL CS, et al. Serelaxin inhibits the profibrotic TGF-β1/IL-1β axis by targeting TLR-4 and the NLRP3 inflammasome in cardiac myofibroblasts. FASEB J. 2019;33(12):14717-14733.
[32] GAO XM, SU Y, MOORE S, et al. Relaxin mitigates microvascular damage and inflammation following cardiac ischemia-reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol. 2019;114(4):30.
[33] 李瑞龄,赵志强.松弛素在心房颤动中的应用研究进展[J].天津医药,2021,49(4):441-443.
[34] 骆莹莹,姚树桐,王大新,等.氧化应激在动脉粥样硬化发生发展中作用的研究新进展[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2013,21(1):46-50.
[35] 李雪惠,张阳,吉世禹.红参对H2O2诱导 H9C2 大鼠心肌细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用[J].吉林中医药,2019,39(6):772-776.
[36] 雷蕾,雷燕,胡厚祥.番茄红素对SD大鼠在体心脏缺血再灌注损伤的影响及其作用机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2022,42(11):2787-2790.
[37] 沈莹,柳湘洁,雷超.黄芪总苷对H2O2诱导的衰老心肌细胞氧化应激及PI3K/AKT通路的影响[J].广州中医药大学学报,2019,36(3): 391-395.
[38] 田耀博,赵大庆,李香艳,等.人参多糖通过抑制ROS水平和凋亡保护H2O2诱导的心肌细胞氧化应激损伤[J].华中师范大学学报(自然科学版),2018,52(2):240-247.
|