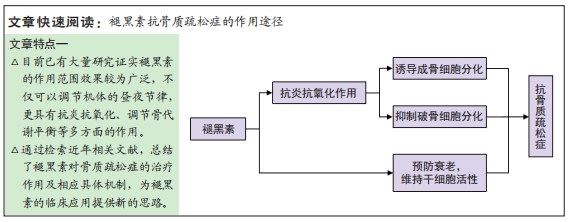
[1] CLARKE B. Normal bone anatomy and physiology. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3(Suppl 3):S131-S139.
[2] NOH JY, YANG Y, JUNG H. Molecular mechanisms and emerging therapeutics for osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7623.
[3] TUMAY S, LALE O, NURSEL CB. An overview and management of osteoporosis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2017;4(1):46.
[4] MARAKA S, KENNEL KA. Bisphosphonates for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. BMJ. 2015;351:h3783.
[5] LIM SY, BOLSTER MB. Current approaches to osteoporosis treatment. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27(3):216-224.
[6] BINKLEY N, BOLOGNESE M, SIDOROWICZ‐BIALYNICKA A, et al. A phase 3 trial of the efficacy and safety of oral recombinant calcitonin: the Oral Calcitonin in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis (ORACAL) trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(8):1821-1829.
[7] LIU Z, GAN L, LUO D, et al. Melatonin promotes circadian rhythm‐induced proliferation through C lock/histone deacetylase 3/c‐M yc interaction in mouse adipose tissue. J Pineal Res. 2017;62(4):e12383.
[8] SONG C, WANG J, KIM B, et al. Insights into the role of circadian rhythms in bone metabolism: a promising intervention target? Biomed Res Int. 2018. doi: 10.1155/2018/9156478.
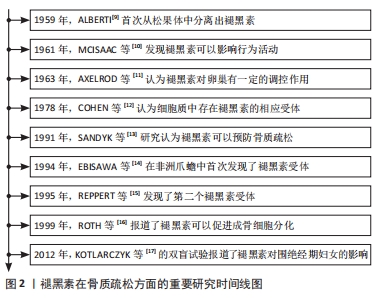
[9] ALBERTI C. Melatonin: the first hormone isolated from the pineal body.Farmaco Sci. 1958;13(8):604-605.
[10] MCISAAC WM, KHAIRALLAH PA, PAGE IH.10-Methoxyharmalan, a potent serotonin antagonist which affects conditioned behavior. Science. 1961; 134(3480):674-675.
[11] AXELROD J, WURTMAN RJ, CHU EW. Effects of melatonin, a pineal substance, on the rat ovary. Science. 1963;140(3565):378.
[12] COHEN M, ROSELLE D, CHABNER B, et al. Evidence for a cytoplasmic melatonin receptor. Nature. 1978;274(5674):894-895.
[13] SANDYK R, ANASTASIADIS PG, ANNINOS PA, et al. Is postmenopausal osteoporosis related to pineal gland functions? Int J Neurosci. 1991;62(3-4): 215-225.
[14] EBISAWA T, KARNE S, LERNER MR, et al. Expression cloning of a high-affinity melatonin receptor from Xenopus dermal melanophores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(13):6133-6137.
[15] REPPERT SM, GODSON C, MAHLE CD, et al. Molecular characterization of a second melatonin receptor expressed in human retina and brain: the Mel1b melatonin receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(19):8734-8738.
[16] ROTH JA, KIM BG, LIN WL, et al. Melatonin promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(31):22041-22047.
[17] KOTLARCZYK MP, LASSILA HC, O’NEIL CK, et al. Melatonin osteoporosis prevention study (MOPS): a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study examining the effects of melatonin on bone health and quality of life in perimenopausal women. J Pineal Res. 2012;52(4):414-426.
[18] HARDELAND R. Melatonin: signaling mechanisms of a pleiotropic agent. Biofactors. 2009;35(2):183-192.
[19] CECON E, LIU L, JOCKERS R. Melatonin receptor structures shed new light on melatonin research.J Pineal Res. 2019;67(4):e12606.
[20] HANSON MA, ROTH CB, JO E, et al. Crystal structure of a lipid G protein–coupled receptor.Science. 2012;335(6070):851-855.
[21] LIU C, WEAVER DR, JIN X, et al. Molecular dissection of two distinct actions of melatonin on the suprachiasmatic circadian clock. Neuron. 1997;19(1): 91-102.
[22] JIN X, GALL CV, PIESCHL RL, et al. Targeted disruption of the mouse mel1b melatonin receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(3):1054-1060.
[23] GIANNONI‐GUZMÁN MA, KAMITAKAHARA A, MAGALONG V, et al. Circadian photoperiod alters TREK‐1 channel function and expression in dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons via melatonin receptor 1 signaling. J Pineal Res. 2021; 70(2):e12705.
[24] LI HY, WANG Y, FENG DX, et al. Alterations in the time course of expression of the Nox family in the brain in a rat experimental cerebral ischemia and reperfusion model: effects of melatonin. J Pineal Res. 2014;57(1):110-119.
[25] BOROS K, FREEMONT T. Physiology of ageing of the musculoskeletal system. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2017;31(2):203-217.
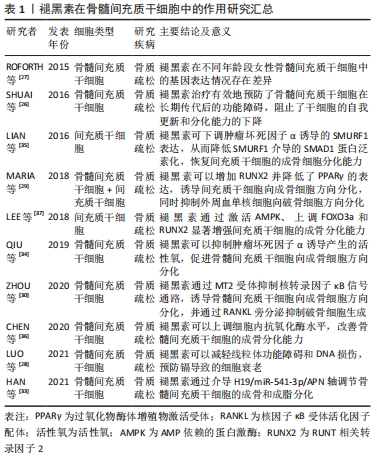
[26] Shuai Y, Liao L, Su X, et al. Melatonin treatment improves mesenchymal stem cells therapy by preserving stemness during long-term in vitro expansion.Theranostics. 2016;6(11):1899-1917.
[27] ROFORTH MM, FARR JN, FUJITA K, et al. Global transcriptional profiling using RNA sequencing and DNA methylation patterns in highly enriched mesenchymal cells from young versus elderly women. Bone. 2015;76:49-57.
[28] LUO H, GU R, OUYANG H, et al. Cadmium exposure induces osteoporosis through cellular senescence, associated with activation of NF-κB pathway and mitochondrial dysfunction. Environ Pollut. 2021;290:118043.
[29] MARIA S, SAMSONRAJ RM, MUNMUN F, et al. Biological effects of melatonin on osteoblast/osteoclast cocultures, bone, and quality of life: implications of a role for MT 2 melatonin receptors, MEK 1/2, and MEK 5 in melatonin‐mediated osteoblastogenesis. J Pineal Res. 2018;64(3):e12465.
[30] ZHOU Y, WANG C, SI J, et al. Melatonin up‐regulates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic action but suppresses their mediated osteoclastogenesis via MT2‐inactivated NF‐κB pathway. Br J Pharmaco. 2020;177(9):2106-2122.
[31] LI G, YUN X, YE K, et al. Long non‐coding RNA‐H19 stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the microRNA‐149/SDF‐1 axis. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(9):4944-4955.
[32] BI H, WANG D, LIU X, et al. Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating microRNA-140-5p/SATB2 axis. J Biosci. 2020;45(1):1-13.
[33] HAN H, TIAN T, HUANG G, et al. The IncRNA H19/miR-541-3p/Wnt/-catenin axis plays a vital role in melatonin-mediated osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. doi: 10. 18632/aging. 203267
[34] QIU X, WANG X, QIU J, et al. Melatonin rescued reactive oxygen species-impaired osteogenesis of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the presence of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019: 6403967.
[35] LIAN C, WU Z, GAO B, et al. Melatonin reversed tumor necrosis factor‐alpha‐inhibited osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells by stabilizing SMAD 1 protein. J Pineal Res. 2016;61(3):317-327.
[36] CHEN W, CHEN X, CHEN AC, et al. Melatonin restores the osteoporosis-impaired osteogenic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by preserving SIRT1-mediated intracellular antioxidant properties. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;146:92-106.
[37] LEE S, LE NH, KANG D. Melatonin alleviates oxidative stress-inhibited osteogenesis of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through AMPK activation. Int J Med Sci. 2018;15(10):1083.
[38] LIU J, CHEN S, BISWAS S, et al. Glucose‐induced oxidative stress and accelerated aging in endothelial cells are mediated by the depletion of mitochondrial SIRTs. Physiol Rep. 2020;8(3):e14331.
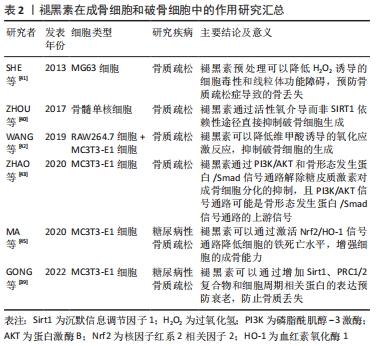
[39] GONG Z, DA W, TIAN Y, et al. Exogenous melatonin prevents type 1 diabetes mellitus–induced bone loss, probably by inhibiting senescence. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(2):453-466.
[40] ZHOU L, CHEN X, YAN J, et al. Melatonin at pharmacological concentrations suppresses osteoclastogenesis via the attenuation of intracellular ROS. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(12):3325-3337.
[41] SHE F, WANG W, WANG Y, et al. Melatonin protects MG63 osteoblast-like cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity by maintaining mitochondrial function. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(2):493-498.
[42] WANG X, LIANG T, ZHU Y, et al. Melatonin prevents bone destruction in mice with retinoic acid–induced osteoporosis. Mol Med. 2019;25(1):1-14.
[43] ZHAO R, TAO L, QIU S, et al. Melatonin rescues glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of osteoblast differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells via the PI3K/AKT and BMP/Smad signalling pathways. Life Sci. 2020;257:118044.
[44] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072.
[45] MA H, WANG X, ZHANG W, et al. Melatonin suppresses ferroptosis induced by high glucose via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:1-18.
[46] KRASSAS GE, PAPADOPOULOU P. Oestrogen action on bone cells. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2001;2(2):143-152.
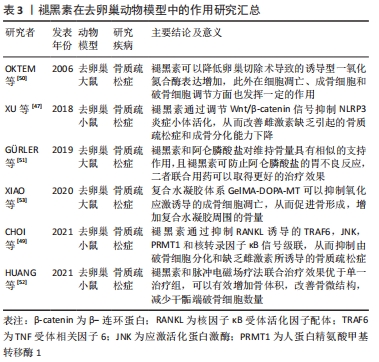
[47] XU L, ZHANG L, WANG Z, et al. Melatonin suppresses estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis and promotes osteoblastogenesis by inactivating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;103(4):400-410.
[48] CHOI JH, JANG AR, KIM D, et al. PRMT1 mediates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and contributes to bone loss in ovariectomized mice. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50(8):1-15.
[49] CHOI JH, JANG AR, PARK MJ, et al. Melatonin inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone loss in ovariectomized mice by regulating PRMT1-mediated signaling. Endocrinology. 2021;162(6):bqab057.
[50] OKTEM G, USLU S, VATANSEVER SH, et al. Evaluation of the relationship between inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) activity and effects of melatonin in experimental osteoporosis in the rat. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006; 28(2):157-162.
[51] GÜRLER EB, ÇILINGIR‐KAYA ÖT, PEKER EYÜBOGLU I, et al. Melatonin supports alendronate in preserving bone matrix and prevents gastric inflammation in ovariectomized rats. Cell Biochem Funct. 2019;37(2):102-112.
[52] HUANG J, LI Y, WANG L, et al. Combined effects of low‐frequency pulsed electromagnetic field and melatonin on ovariectomy‐induced bone loss in mice. Bioelectromagnetics. 2021;42(8):616-628.
[53] XIAO L, LIN J, CHEN R, et al. Sustained release of melatonin from GelMA liposomes reduced osteoblast apoptosis and improved implant osseointegration in osteoporosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020(4):1-20.
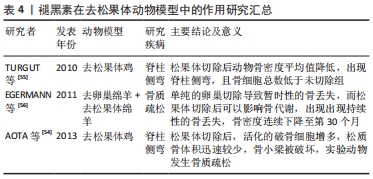
[54] AOTA Y, TERAYAMA H, SAITO T, et al. Pinealectomy in a broiler chicken model impairs endochondral ossification and induces rapid cancellous bone loss. Spine J. 2013;13(11):1607-1616.
[55] TURGUT M, SÜLEYMAN KAPLAN, TURGUT A T, et al. Morphological, stereological and radiological changes in pinealectomized chicken cervical vertebrae. J Pineal Res. 2010;39(4):392-399.
[56] EGERMANN M, GERHARDT C, BARTH A, et al. Pinealectomy affects bone mineral density and structure-an experimental study in sheep. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12(1):1-9.
[57] JING HF, WANG XM. Effects of aerobic exercise combined with melatonin on osteoporosis of type II diabetic rats. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2017;33(3):252-256.
[58] AMSTRUP AK, SIKJAER T, HEICKENDORFF L, et al. Melatonin improves bone mineral density at the femoral neck in postmenopausal women with osteopenia: a randomized controlled trial. J Pineal Res. 2015;59(2):221-229.
[59] AMSTRUP AK, SIKJAER T, MOSEKILDE L, et al. The effect of melatonin treatment on postural stability, muscle strength, and quality of life and sleep in postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial. Nutr J. 2015;14(1):1-8.
[60] OSTROWSKA Z, ZIORA K, KOS-KUDŁA B, et al. Melatonin, the RANKL/RANK/OPG system, and bone metabolism in girls with anorexia nervosa. Endokrynol Pol. 2010;61(1):117-123.
[61] SHIGEMATSU T, MURAOKA R, SUGIMOTO T, et al. Risedronate therapy in patients with mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease with osteoporosis: post-hoc analysis of data from the risedronate phase III clinical trials. BMC Nephrol. 2017;18(1):1-8.
[62] REN H, SUN R, WANG J. Relationship of melatonin level, oxidative stress and inflammatory status with osteoporosis in maintenance hemodialysis of chronic renal failure. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(6):5183-5188.
|