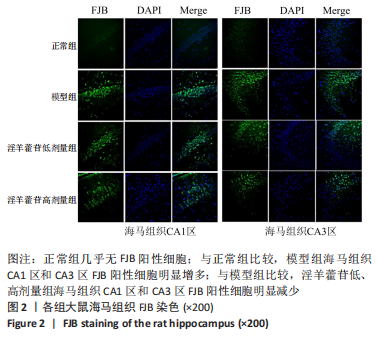
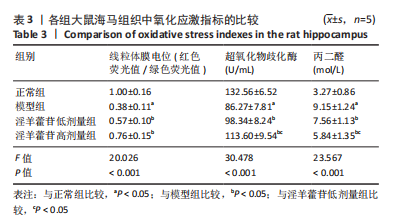
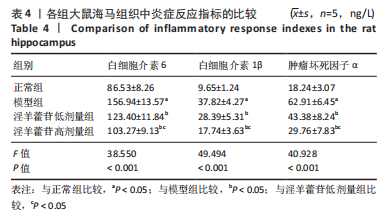
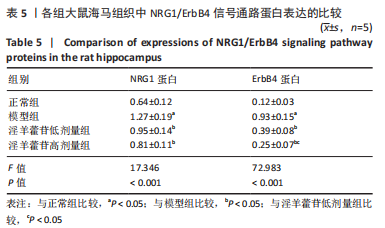
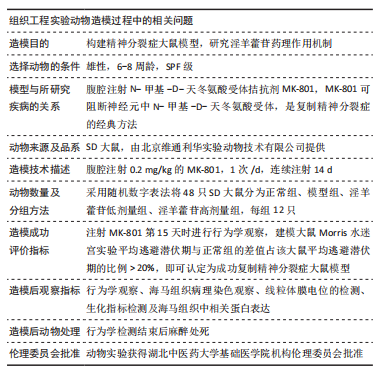
[1] McCUTCHEON RA, MARQUES TR, HOWES OD. Schizophrenia-an overview. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020;77(2):201-210.
[2] SRIVASTAVA A, DADA O, QIAN J, et al. Epigenetics of schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2021;305:114218.
[3] RICHETTO J, MEYER U. Epigenetic modifications in schizophrenia and related disorders: molecular scars of environmental exposures and source of phenotypic variability. Biol Psychiatry. 2021;89(3):215-226.
[4] 彭兴,马辛,任艳萍,等. 精神分裂症患者语义距离与认知功能的相关性研究[J].中华行为医学与脑科学杂志,2020,29(9):797-801.
[5] GAMA MARQUES J, OUAKININ S. Schizophrenia–schizoaffective–bipolar spectra: an epistemological perspective. CNS Spectr. 2021;26(3):197-201.
[6] 陈彦霖,陈诚,李泽平,等. NRG1/ErbB4信号通路与精神疾病关联的研究进展[J].中国现代医学杂志,2020,30(15):44-49.
[7] HASAN A, ROEH A, LEUCHT S, et al. Add-on spironolactone as antagonist of the NRG1-ERBB4 signaling pathway for the treatment of schizophrenia: Study design and methodology of a multicenter randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2020;17:100537.
[8] LIN E, LIN CH, LANE HY. Logistic ridge regression to predict bipolar disorder using mRNA expression levels in the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor genes. J Affect Disord. 2022;297:309-313.
[9] WANG M, GAO H, LI W, et al. Icariin and its metabolites regulate lipid metabolism: From effects to molecular mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110675.
[10] 路宇仁,陈昳冰,崔元璐,等.淫羊藿苷药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2018,24(17):209-220.
[11] 陈静,高瑜,夏海建,等.淫羊藿苷调节大鼠脑内N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体分子机制研究[J].中国药业,2020,29(11):18-21.
[12] WANG S, MA J, ZENG Y, et al. Icariin, an up-and-coming bioactive compound against neurological diseases: network pharmacology-based study and literature review. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:3619-3641.
[13] ZHOU D, LV D, WANG Z, et al. GLYX-13 ameliorates schizophrenia-like phenotype induced by MK-801 in mice: role of hippocampal NR2B and DISC1. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018;11:121.
[14] 万争艳,李宁,向玲玲,等.精神分裂症模型大鼠前额叶皮质PKA和内皮细胞趋化因子-5的表达变化[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2019,29(10):92-97.
[15] JAARO-PELED H, SAWA A. Neurodevelopmental factors in schizophrenia. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2020,43(2):263-274.
[16] PARK HJ, CHOI I, LEEM KH. Decreased brain pH and pathophysiology in schizophrenia. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(16):8358.
[17] MATSUDA Y, MAKINODAN M, MORIMOTO T, et al. Neural changes following cognitive remediation therapy for schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019; 73(11):676-684.
[18] WRIGHT AC, BROWNE J, SKIEST H, et al. The relationship between conventional clinical assessments and momentary assessments of symptoms and functioning in schizophrenia spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Schizophr Res. 2021; 232(13):11-27.
[19] HE C, WANG Z, SHI J. Pharmacological effects of icariin. Adv Pharmacol. 2020;87: 179-203.
[20] 陈溪,谷洪顺,张兰,等.淫羊藿苷对MK-801致精神分裂症小鼠模型的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2016,22(4):395-398.
[21] 刘运琴,刘燕芹,戢汉斌,等.淫羊藿苷对精神分裂症模型大鼠认知功能的改善作用及机制[J].中国药房,2021,32(7):812-818.
[22] WINSHIP IR, DURSUN SM, BAKER GB, et al. An overview of animal models related to schizophrenia. Can J Psychiatry. 2020;64(1):5-17.
[23] 陈溪,马登磊,李林.淫羊藿苷对cuprizone诱导精神分裂症样小鼠模型行为学变化,髓鞘脱失及神经炎性反应的影响[J].首都医科大学学报,2021, 42(5):761-767.
[24] KÖŞGER F, YİĞİTASLAN S, EŞSİZOĞLU A, et al. Inflammation and oxidative stress in deficit schizophrenia. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2020;57(4):303-307.
[25] UPTHEGGROVE R, KHANDAKER GM. Cytokines, oxidative stress and cellular markers of inflammation in schizophrenia. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2020;44: 49-66.
[26] PRESTWOOD TR, ASGARIROOZBEHANI R, WU S, et al. Roles of inflammation in intrinsic pathophysiology and antipsychotic drug-induced metabolic disturbances of schizophrenia. Behav Brain Res. 2021;402:113101.
[27] CJIEN YL, HWU HG, HANG TJ, et al. Clinical implications of oxidative stress in schizophrenia: Acute relapse and chronic stable phase. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020;99:109868.
[28] 范瑜,吴嘉,林静.集体心理干预对精神分裂症患者氧化应激、细胞凋亡及炎症反应的影响[J].海南医学院学报,2017,23(16):2299-2302.
[29] JING X, DU T, CHEN K, et al. Icariin protects against iron overload-induced bone loss via suppressing oxidative stress. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(7):10123-10137.
[30] WANG P, MENG Q, WANG W, et al. Icariin inhibits the inflammation through down-regulating NF-κB/HIF-2α signal pathways in chondrocytes. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(11):BR20203107.
[31] RAJASEKARAN A, SHIVAKUMAR V, KALMAADY SV, et al. Impact of NRG1 HapICE gene variants on digit ratio and dermatoglyphic measures in schizophrenia. Asian J Psychiatry. 2020;54:102363.
[32] LI C, TAO H, YANG X, et al. Assessment of a combination of serum proteins as potential biomarkers to clinically predict Schizophrenia. Int J Med Sci. 2018;15(9): 900-906.
[33] ZHANG Z, LI Y, HE F, et al. Sex differences in circulating neuregulin1-beta1 and beta-secretase 1 expression in childhood-onset schizophrenia. Compr Psychiatry. 2020;100:152176.
[34] ZIEBA J, MPRRIS MJ, WEICKERT CS, et al. Behavioural effects of high fat diet in adult Nrg1 type III transgenic mice. Behav Brain Res. 2020;377:112217.
[35] JAHN K, HEESE A, KEBIR O, et al. Differential methylation pattern of schizophrenia candidate genes in tetrahydrocannabinol-consuming treatment-resistant schizophrenic patients compared to non-consumer patients and healthy controls. Neuropsychobiology. 2021;80(1):36-44.
[36] XIE R, HONG S, YE Y, et al. Ketamine affects the expression of ErbB4 in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of rats. J Mol Neuroscie. 2020;70(6):962-967.
[37] SKIRZEWSKI M, CRONIN ME, MURPHY R, et al. ErbB4 null mice display altered mesocorticolimbic and nigrostriatal dopamine Levels, as well as deficits in cognitive and motivational behaviors. eNeuro. 2020;7(3):ENEURO.0395-19.2020.
[38] YANG JZ, KANG CY, WU C, et al. Pharmacogenetic associations of NRG1 polymorphisms with neurocognitive performance and clinical symptom response to risperidone in the untreated schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2021;231(1-3):67-69.
[39] ZHANG C, NI P, LIU Y, et al. GABAergic abnormalities associated with sensorimotor corticostriatal community structural deficits in ErbB4 knockout mice and first-episode treatment-naive patients with schizophrenia. Neurosci Bull. 2020;36(2): 97-109.
[40] DABBAH-ASSADI F, ALON D, GOLANI I, et al. The influence of immune activation at early vs late gestation on fetal NRG1-ErbB4 expression and behavior in juvenile and adult mice offspring. Brain Behav Immun. 2019;79:207-215.
|