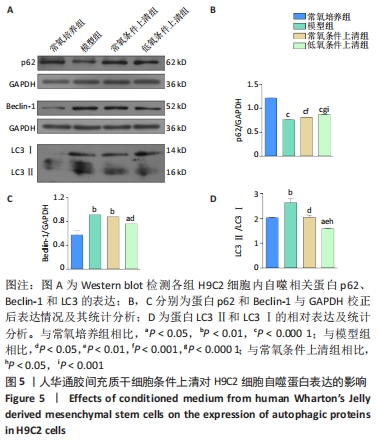
[1] YELLON DM, HAUSENLOY DJ. Myocardial reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(11):1121-1135.
[2] ABBASZADEH H, GHORBANI F, DERAKHSHANI M, et al. Regenerative potential of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells: A new horizon of stem cell therapy. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(12):9230-9240.
[3] RANJBARAN H, ABEDIANKENARI S, MOHAMMADI M, et al. Wharton’s Jelly Derived-Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Isolation and Characterization. Acta Med Iran. 2018;56(1):28-33.
[4] MARINO L, CASTALDI MA, ROSAMILIO R, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells from the Wharton’s Jelly of the Human Umbilical Cord: Biological Properties and Therapeutic Potential. Int J Stem Cells. 2019;12(2):218-226.
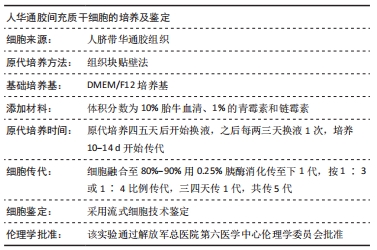
[5] 张宁坤,陈宇,王志国,等.华通胶源间充质干细胞经冠状动脉移植治疗慢性缺血性心肌病的实验研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2015, 40(11):885-891.
[6] LI L, LI L, ZHANG Z, et al. Hypoxia promotes bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell proliferation through apelin/APJ/autophagy pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015;47(5):362-367.
[7] LIU H, SUN X, GONG X, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes exert antiapoptosis effect via activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway on H9C2 cells. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(9):14455-14464.
[8] SCIARRETTA S, MAEJIMA Y, ZABLOCKI D, et al. The Role of Autophagy in the Heart. Annu Rev Physiol. 2018;80:1-26.
[9] GAO LR, ZHANG NK, DING QA, et al. Common expression of stemness molecular markers and early cardiac transcription factors in human Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells and embryonic stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(10):1883-1900.
[10] ISHIUCHI N, NAKASHIMA A, DOI S, et al. Hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells prevent renal fibrosis and inflammation in ischemia-reperfusion rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):130.
[11] ZHANG Z, YANG C, SHEN M, et al. Autophagy mediates the beneficial effect of hypoxic preconditioning on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for the therapy of myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):89.
[12] QIAN L, SHI J, ZHANG C, et al. Downregulation of RACK1 is associated with cardiomyocyte apoptosis after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in adult rats. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2016;52(3):305-313.
[13] 中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组.中国心血管健康与疾病报告2020概要[J].中国循环杂志,2021,36(6):521-545.
[14] ARSLAN F, LAI RC, SMEETS MB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;10(3):301-312.
[15] WANG M, YAN L, LI Q, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell secretions improve donor heart function following ex vivo cold storage. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020;(20):32487-32489.
[16] LEE TL, LAI TC, LIN SR, et al. Conditioned medium from adipose-derived stem cells attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury through the microRNA-221/222/PUMA/ETS-1 pathway. Theranostics. 2021;11(7):3131-3149.
[17] NAZARINIA D, SHARIFI M, DOLATSHAHI M, et al. FoxO1 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway: Molecular targets of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells-derived conditioned medium (hAMSC-CM) in protection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Chem Neuroanat. 2021;112:101918.
[18] ZHANG Q, LIU X, PIAO C, et al. Effect of conditioned medium from adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells on endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipid metabolism after hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury and hepatectomy in swine. Life Sci. 2022;289:120212.
[19] 张蘋,郭莹,高亚杰,等.低氧预处理人脐带间充质干细胞促进其源性外泌体对心肌梗死后心肌损伤的修复[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(17):2630-2636.
[20] LEE JH, YOON YM, LEE SH. Hypoxic Preconditioning Promotes the Bioactivities of Mesenchymal Stem Cells via the HIF-1alpha-GRP78-Akt Axis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(6):1320.
[21] HU X, XU Y, ZHONG Z, et al. A Large-Scale Investigation of Hypoxia-Preconditioned Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Myocardial Repair in Nonhuman Primates. Circulation Research. 2016;118(6):970-983.
[22] OBRADOVIC H, KRSTIC J, TRIVANOVIC D, et al. Improving stemness and functional features of mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton’s jelly of a human umbilical cord by mimicking the native, low oxygen stem cell niche. Placenta. 2019;82:25-34.
[23] MENG SS, XU XP, CHANG W, et al. LincRNA-p21 promotes mesenchymal stem cell migration capacity and survival through hypoxic preconditioning. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):280.
[24] ZHAO D, LIU L, CHEN Q, et al. Hypoxia with Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cell coculture maintains stemness of umbilical cord blood-derived CD34(+) cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):158.
[25] YU H, XU Z, QU G, et al. Hypoxic Preconditioning Enhances the Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Conditioned Medium in Switching Microglia toward Anti-inflammatory Polarization in Ischemia/Reperfusion. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021;41(3):505-524.
[26] LI X, HE S, MA B. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):12.
[27] YOSHII SR, MIZUSHIMA N. Monitoring and Measuring Autophagy. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(9):1865.
[28] MARTANO M, ALTAMURA G, POWER K, et al. Beclin 1, LC3 and P62 Expression in Equine Sarcoids. Animals (Basel). 2021;12(1):20.
[29] LI Q, HAN Y, DU J, et al. Alterations of apoptosis and autophagy in developing brain of rats with epilepsy: Changes in LC3, P62, Beclin-1 and Bcl-2 levels. Neurosci Res. 2018;130:47-55.
[30] LI Y, LIANG P, JIANG B, et al. CARD9 promotes autophagy in cardiomyocytes in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via interacting with Rubicon directly. Basic Res Cardiol. 2020;115(3):29.
[31] KANG X, LI C, XIE Y, et al. Hippocampal ornithine decarboxylase/spermidine pathway mediates H2S-alleviated cognitive impairment in diabetic rats: Involving enhancment of hippocampal autophagic flux.J Adv Res. 2021;27:31-40.
[32] GUAN G, YANG L, HUANG W, et al. Mechanism of interactions between endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in hypoxia/reoxygenationinduced injury of H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(1):350-358.
[33] CHEN G, WANG M, RUAN Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-143-3p suppresses myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating autophagy. Life Sci. 2021;280:119742.
|