1.1 设计 体外细胞观察对比实验,采用单因素方差分析进行多组间比较,组间两两比较采用LSD-t检验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2020年9月至2021年6月在广西中医药大学科学实验中心进行,细胞实验于分子生物学实验室完成,动物实验于动物实验中心进行,实验许可证编号:SYXK(桂)2019-0001。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验细胞株和动物 HepG2细胞(iCell-h092)提供商为赛百慷(上海)生物技术股份有限公司。含药血清制备所需雌性SPF级Wistar大鼠32只,6-8周龄,体质量160-250 g,均购买于湖南斯莱克景达实验动物有限公司,生产许可证编号:SCXK(湘)2016-0002。实验方案经广西中医药大学动物伦理委员会批准(动物伦理审查号:2019010)。实验过程遵循了国际兽医学编辑协会《关于动物伦理与福利的作者指南共识》和本地及国家法规。实验动物在麻醉下进行所有的手术,并尽一切努力最大限度减少其疼痛、痛苦和死亡。
1.3.2 实验药物 江阴天江药业有限公司生产的免煎中药配方颗粒进行药物制备,敷和备化方由17味中草药组成,其中白花蛇舌草30 g,茵陈蒿30 g,牛膝30 g,鳖甲24 g,茯苓15 g,白术15 g,制香附12 g,柴胡12 g,杭白芍12 g,制半夏12 g,当归12 g,莪术12 g,西洋参10 g,三七10 g,枳实10 g,生姜10 g,甘草6 g。将所有中药颗粒充分加入ddH2O进行溶解后于广西中医药大学第一附属医院制剂室使用120目网筛将药液过滤。过滤完成后蒸馏浓缩,将药物浓缩成1 g/mL含药液,高温灭菌法灭菌后进行封装,于4 ℃环境中保存。雷帕霉素(美国Sigma-Aldrich公司,货号:D8371)。
1.3.3 实验试剂 胰蛋白酶-EDTA消化液、青链霉素混合液(100×)、BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒、PBS、RIPA裂解液(北京索莱宝科技有限公司,批号分别为 T1300、P1400、PH0326、sv300160.03、P0013B);乳铁蛋白、N2、B27、DMEM(美国 Gibco 公司,批号分别为yb-E12455、17502048、17504-004、MD202);DMEM/F12(中国武汉BOSTER公司,批号:11330032);表皮生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子(美国PEPROTECH公司,批号分别为HZ-4567R、Rs-6706R);PE MOUSE ANTI-HUMAN CD133(北京BD Biosciences公司,批号:12-1331-82);CD133 microbead kit、MACS Buffer(德国美天旎生物技术公司,批号分别为130-097-049、130-091-221);CCK-8试剂盒(中国上海东仁化学科技有限公司,批号:ab228554);Nuclease-Free Water(莫纳生物科技有限公司,批号:AM9932);山羊抗鼠IgG、山羊抗兔IgG(美国Sigma-Aldrich公司,批号分别为1010-04、12-448);脱脂奶粉(中国光明牌, 批号:080922 DN7);SDS-PAGE凝胶配制试剂盒、SDS-PAGE上样缓冲液、干样细胞消化液、ECL发光液 (碧云天上海生物技术有限公司,批号分别为 P1200、YT050-CWN、MX2001、PH0353);β-肌动蛋白、兔抗PI3K单克隆抗体、兔抗AKT单克隆抗体、兔抗p-AKT单克隆抗体、兔抗mTOR单克隆抗体、兔抗p-mTOR单克隆抗体、兔抗LC3单克隆抗体、兔抗LC3-Ⅱ单克隆抗体(英国Abcam公司,批号分别为:ab8226、ab278545、ab38449、ab8805、ab32028、ab32028、ab128025、ab192890);引物(中国武汉金开瑞公司,批号:D3118);FastKing RT Kit、SuperReal PreMix Plus(TIANGE,批号分别为 FP205、KR116-02);Scientific TRIzolTM Reagent (Thermo 中国公司,批号:15596026)。
1.3.4 实验仪器 BBS-H1500型超净工作台(中国山东博科生物产业有限公司);MCO175M型CO2细胞培养箱(日本Sanyo公司);DMi1型倒置生物显微镜(德国Leica公司);高压蒸汽灭菌锅(中国上海三申医疗器械厂);电泳仪、全波长酶标仪、CL10型离心机、Multiskan FC型酶标仪、磁力搅拌器(美国Thermo 公司);制冰机(美国Bio-Rad公司);PCR循环仪、GE多功能成像仪(美国通用);CytoFLEX流式细胞仪(美国贝克曼公司);水平摇床(北京市六一仪器厂);170-4158型转膜仪(美国Bio-Rad公司)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 HepG2 细胞培养 HepG2细胞株采用含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM 培养基,在CO2培养箱中孵育,细胞融合至85%左右,加入0.25%胰酶消化,每3 d以1∶3的比例传代,传代后取对数生长期的细胞用于后续实验。
1.4.2 CD133+ HepG2 肝癌干细胞的分离、纯化
(1)干样细胞诱导:配备干样细胞培养液,包括成纤维细胞生长因子(20 μg/L)+人白血病抑制因子(10 μg/L)+表皮生长因子(20 μg/L)+DMEM/F12+ B27(1×)+N2(1×)。取对数生长期的HepG2细胞,加入PBS充分洗涤3次后,加入1 mL 0.25%胰酶+0.02%EDTA干样细胞消化液(0.25%胰酶+0.02%EDTA),充分消化后加入DMEM终止消化,在离心机上以1 000 r/min、4 ℃低温离心5 min,离心后吸弃上清液,于低黏度6孔板中加入细胞(2×104个/孔)进行培养,待细胞总数达108个,进行磁珠分选。
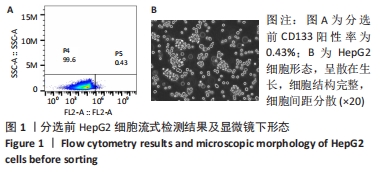
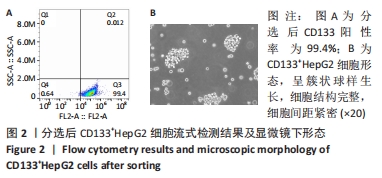
(2)磁珠分选:取出细胞加入1 mL干样细胞消化液进行消化,于离心机上以1 000 r/min、4 ℃低温条件离心5 min收集细胞沉淀,加入300 μL的buffer缓冲液混匀后重悬。低黏度6孔板每孔加入100个细胞,于避光4 ℃环境下加入FCR Blocking Reagent 100 μL、CD133 Micro Beads 100 μL孵育30 min。置LS柱于MACS磁选机,以buffer液冲洗干净,加入细胞悬液进行缓慢滴落,收集滴落细胞后以2 mL的buffer液冲洗干净。将滴落的细胞悬液于离心机上以1 000 r/min、4 ℃低温条件离心5 min,离心后PBS清洗2遍。将清洗后的细胞用DMEM/F12培养基(不含酚红)进行悬浮培养6 d,培养后于镜下观察细胞形态,离心、收集干样细胞球,收集后胰酶消化并重悬,重悬静置5 min后将细胞球反复吹打至单个细胞,再次以PBS清洗后进行离心。离心后收集细胞沉淀,将细胞重悬培养于干细胞专用培养基,于6孔悬浮细胞培养板中按1∶2比例进行传代。细胞培养21 d后采用流式细胞术鉴定CD133+HepG2细胞纯度。
(3)流式鉴定:取出细胞,1 000 r/min、4 ℃离心5 min,加1 mL的PBS重悬细胞,加10 μL细胞悬液于计数板A孔,计数,总数超过106 即可下一步实验。按照实验要求将细胞分为空白对照管、同型对照管、实验管,每管加入100 μL细胞悬液,实验管、空白对照管、同型对照组管分别加入PE CD133抗体、染色剂、同型对照抗体,于4 ℃环境下避光反应30 min,反应后离心收集细胞沉淀,PBS反复清洗2遍,再次离心后加入PBS对细胞进行重悬,重悬后使用流式细胞仪检测CD133阳性表达率。
1.4.3 敷和备化方含药血清制备及保存 严格按照中药复方血清药理学的研究方法进行含药血清的制备。将大鼠随机分为空白组和中药组,每组16只,分为4笼饲养,参考成人(60 kg)的临床计量,大鼠按100 g/mL的药量进行灌胃,以同等标准用生理盐水对空白组大鼠进行灌胃,连续灌胃1周,1次/d,末次灌胃2 h后腹主动脉采血。收集血液后静置4 h,300 r/min离心15 min收集血清。将血清于56 ℃水浴锅水浴30 min灭活。灭活后于无菌操作台以0.22 μm微孔滤膜注射滤器对血清进行过滤、灭菌,用无菌EP管分装敷和备化方含药血清和正常大鼠血清,置-20 ℃保存备用,并应用色谱与质谱联用技术对敷和备化方含药血清进行鉴定。
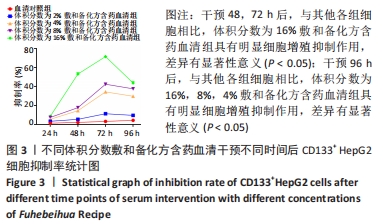
1.4.4 敷和备化方含药血清最佳干预浓度测定 参照前期研究结果和相应中药含药血清细胞实验规范,配制体积分数为2%,4%,8%,16%含药血清以备后续使用。取对数生长期第2代或第3代CD133+HepG2细胞,制备细胞悬液,按105个/孔的密度接种于96孔板,每孔1 mL细胞悬液,每组6个复孔,于37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中培养,镜下观察细胞生长状况,加入体积分数为2%,4%,8%,16%含药血清,每孔1 mL,对照组加体积分数为10%的正常大鼠血清,每孔1 mL,于37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中培养24,48,72,96 h,取出孔板,吸弃旧的培养液,PBS洗涤2次,加入CCK-8溶液,每孔10 μL,于培养箱中培养1-4 h,用酶标仪检测波长450 nm处吸光度值,计算敷和备化方含药血清对CD133+HepG2细胞的抑制率,抑制率=(对照孔吸光度值-试验孔吸光度值)/(对照孔吸光度值-空白孔吸光度值)×100%,筛选出最佳体积分数的含药血清用于后续实验。
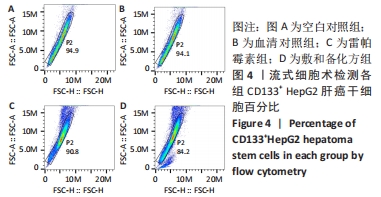
1.4.5 流式细胞术检测各组CD133+HepG2细胞百分比 将第2代或第3代CD133+ HepG2肝癌干细胞分为血清对照组、空白对照组、雷帕霉素组和敷和备化方组,将细胞以每孔106个接种于低黏度6孔板中,血清对照组加入2 mL含体积分数为16%正常大鼠血清的DMEM/F12培养基,空白对照组加入等量无血清DMEM/F12培养基,雷帕霉素组加入2 mL含0.05%雷帕霉素的DMEM/F12培养基,敷和备化方组加入2 mL含体积分数为16%敷和备化方含药血清的DMEM/F12培养基,于37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中培养6 d后进行流式鉴定。倒置显微镜下观察细胞形态,采用细胞计数器进行计数,待细胞总数超过106进行下一步实验。每孔吸取100 μL细胞悬液分装至无菌EP管中,分别加入CD133抗体、染色剂4 ℃避光反应30 min,离心收集细胞进行重悬后于流式细胞仪检测。
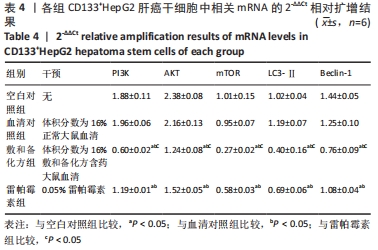
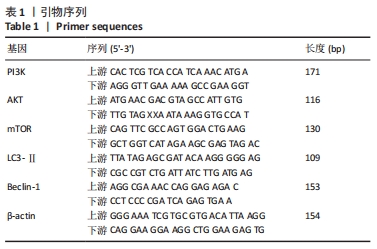
1.4.6 RT-PCR法检测各组细胞中PI3K、AKT、mTOR、LC3-Ⅱ、Beclin-1的mRNA表达 将第2代或第3代CD133+HepG2肝癌干细胞分为血清对照组、空白对照组、雷帕霉素组和敷和备化方组,将细胞以每孔106个接种于低黏度6孔板中,血清对照组加入2 mL含体积分数为16%正常大鼠血清的DMEM/F12培养基,空白对照组加入等量无血清DMEM/F12培养基,雷帕霉素组加入2 mL含0.05%雷帕霉素的DMEM/F12培养基,敷和备化方组加入2 mL含体积分数为16%敷和备化方含药血清的DMEM/F12培养基,于37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中培养6 d后提取RNA,反转录为cDNA,RT-PCR检测各组细胞PI3K、AKT、mTOR、LC3-Ⅱ和Beclin-1的mRNA表达水平,严格按说明书操作。引物序列见表1。
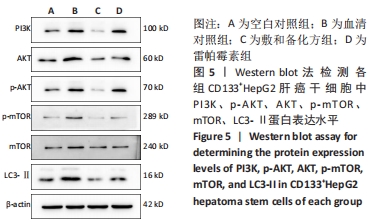
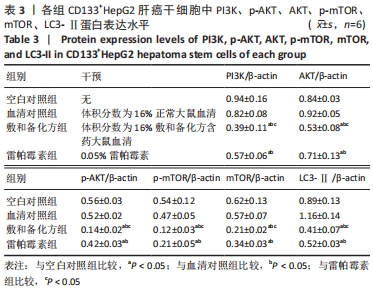
1.4.7 Western blot 法检测各组细胞中PI3K、p-AKT、AKT、p-mTOR、mTOR、LC3-Ⅱ蛋白表达水平 将第2代或第3代处于对数生长期CD133+ HepG2细胞分为血清对照组、空白对照组、雷帕霉素组和敷和备化方组,将细胞以每孔106个接种于低黏度6孔板中,血清对照组加入2 mL含体积分数为16%正常大鼠血清的DMEM/F12培养基,空白对照组加入等量无血清DMEM/F12培养基,雷帕霉素组加入 2 mL含0.05%雷帕霉素的DMEM/F12培养基,敷和备化方组加入2 mL含体积分数为16%敷和备化方含药血清的DMEM/F12培养基,37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2条件下继续培养6 d后进行Western blot检测。离心收集细胞,加入RIPA裂解液充分反应,离心取上清进行BCA蛋白定量。每孔取等量蛋白加入到8% SDS-PAGE胶中进行电泳分离,再将分离后的蛋白以300 mA,1.5 h的转膜条件转膜至PVDF膜;PBS漂洗3次,将膜在室温条件下用5%脱脂奶粉封闭2 h,PBS洗涤5 min;加入PI3K、p-AKT、AKT、p-mTOR、mTOR、LC3-Ⅱ、β-actin一抗(1∶300)室温孵育2 h,PBS洗涤3次,每次5 min,将膜置于双色红外激光发光显色仪中进行发光检测,凝胶成像系统拍照,用Quantity One软件测量各蛋白条带平均吸光度值。
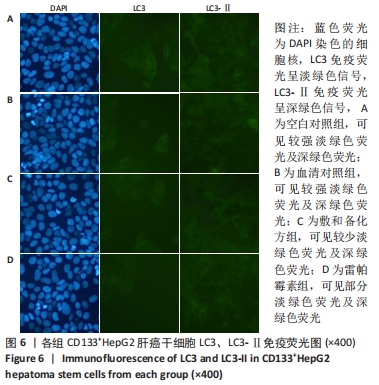
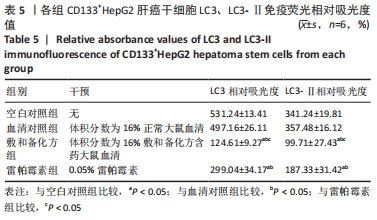
1.4.8 免疫荧光法检测各组细胞中LC3、LC3-Ⅱ的表达 将处于对数生长期第2代或第3代CD133+HepG2细胞分为血清对照组、空白对照组、雷帕霉素组和敷和备化方组,将细胞以每孔106个接种于低黏度6孔板中,血清对照组加入2 mL含体积分数为16%正常大鼠血清的DMEM/F12培养基,空白对照组加入等量无血清DMEM/F12培养基,雷帕霉素组加入2 mL含0.05%雷帕霉素的DMEM/F12培养基,敷和备化方组加入2 mL含体积分数为16%敷和备化方含药血清的DMEM/F12培养基,于37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2条件下继续培养6 d后进行免疫荧光检测。将各组CD133+ HepG2细胞以每孔106个接种于6孔板爬片,37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中孵育24 h,取出6孔板,弃培养基,PBS清洗3次,加入40 g/L多聚甲醛2 mL,常温固定20 min,自然干燥10 min,PBS洗3次,每次5 min,0.2% Triton X-100透膜,室温放置20 min,体积分数为10%羊血清室温封闭30 min,PBS洗3次,每次5 min,滴加LC3、LC3-Ⅱ一抗,4 ℃孵育过夜,PBS洗3次,每次5 min,滴加二抗,避光室温孵育2 h,PBS洗3次,每次5 min,滴加DAPI(0.5 mg/L)避光孵育5 min,PBS洗涤3 次,树脂封固剂封固、烘干,爬片于荧光显微镜下观察并采集图像。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①CD133+HepG2细胞增殖水平;②CD133+HepG2细胞百分比;③CD133+HepG2细胞中PI3K、p-AKT、AKT、p-mTOR、mTOR、LC3-Ⅱ的蛋白表达水平;④CD133+HepG2细胞中PI3K、AKT、mTOR、LC3-Ⅱ和Beclin-1的mRNA表达水平;⑤CD133+HepG2细胞中LC3、LC3-Ⅱ免疫荧光表达水平。
1.6 统计学分析 所有实验数据以EXCEL 2013版录入,采用SPSS 25.0软件作统计学数据分析,用GraphPad Prism 8软件统计作图。所有实验数据结果以x±s表示,采用单因素方差分析(one-way analysis of variance,ANOVA)进行多组间比较比较,组间两两比较采用LSD-t检验。检验水准设定为 α=0.05,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。