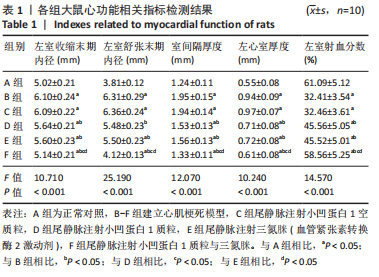
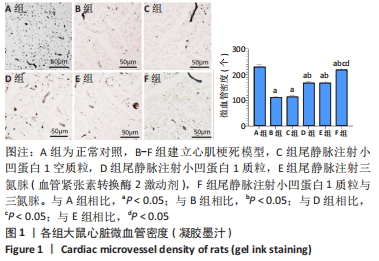
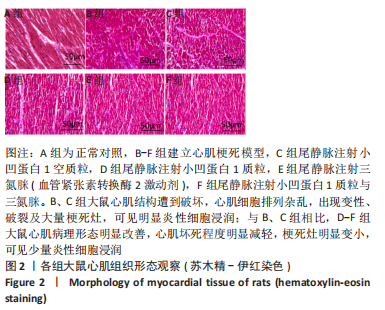
[1] JIANG K, XU Y, WANG D, et al. Cardioprotective mechanism of SGLT2 inhibitor against myocardial infarction is through reduction of autosis. Protein Cell. 2022;13(5):336-359.
[2] KAYIKCIOGLU M, OZKAN HS, YAGMUR B. Premature Myocardial Infarction: A Rising Threat. Balkan Med J. 2022;39(2):83-95.
[3] BERNARDI M, SPADAFORA L, BIONDI-ZOCCAI G, et al. Juvenile myocardial infarction: Sex matters. Int J Cardiol. 2022;361:18-19.
[4] Merlo AC, Bona RD, Ameri P, et al. Type 2 myocardial infarction: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge in contemporary cardiology. Intern Emerg Med. 2022;17(2):317-324.
[5] 鞠帆,袁昕,李宝童,等.心肌梗死后室间隔穿孔的手术时机探讨[J].中国循环杂志,2022,37(3):256-264.
[6] ZHANG CH, LI TT, CHEN X. Acute Myocardial Infarction or Not? JAMA Intern Med. 2022;182(6):668-669.
[7] MERLO AC, ROSA GM, PORTO I. Pregnancy-related acute myocardial infarction: a review of the recent literature. Clin Res Cardiol. 2022; 111(7):723-731.
[8] HIOKI H, KOZUMA K, KOBAYASHI Y, et al. Wearable cardioverter-defibrillators after myocardial infarction: a review of its clinical utility and unmet needs in current clinical practice. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2022;37(1):53-59.
[9] 王英伟,曹永刚,孟丽娜,等.游泳对心肌梗死大鼠心脏微血管的保护作用及机制研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2021,36(9):1060-1067.
[10] ZHANG Y, YANG N, HUANG X, et al. Melatonin Engineered Adipose-Derived Biomimetic Nanovesicles Regulate Mitochondrial Functions and Promote Myocardial Repair in Myocardial Infarction. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;23(9):789203.
[11] 王婷,陈安琪,薛雅馨,等.急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者血清中sACE2、AngⅡ、Ang1-7表达水平及临床意义[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2021,13(5):619-622.
[12] ZHAO K, ZHANG J, XU T, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound ameliorates angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis by alleviating inflammation via a caveolin-1-dependent pathway. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2021;22(10):818-838.
[13] TURKIEH A, EL MASRI Y, PINET F, et al. Mitophagy Regulation Following Myocardial Infarction. Cells. 2022;11(2):199.
[14] TEHRANI BN, DAMLUJI AA, BATCHELOR WB. Acute Myocardial Infarction and Cardiogenic Shock Interventional Approach to Management in the Cardiac Catheterization Laboratories. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2022;18(2):e251121198293.
[15] XIAO L, LIU J, LI G, et al. Acute myocardial infarction after a local anesthetic procedure in a middle-aged patient. Am J Med Sci. 2022; 364(1):106-110.
[16] AKKAN G, ÖZDEMIR E. Subacute Myocardial Infarction Complication: Partial Myocardial Rupture. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars. 2022;50(3): 233-234.
[17] AMBROSE JA, MCENROE DJ. In Search of Coronary Thrombosis as the Cause of Myocardial Infarction: Unraveling a 20th-Century Mystery. Am J Med. 2022;135(5):560-565.
[18] 孙科.螺内酯联合美托洛尔对改善急性心肌梗死后左心室重构的作用[J].中国现代药物应用,2022,16(5):99-101.
[19] SHAH T, KAPADIA S, LANSKY AJ, et al. ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Sex Differences in Incidence, Etiology, Treatment, and Outcomes. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2022;24(5):529-540.
[20] KUBIELAS G, HYDZIK P, RYPICZ Ł. Comprehensive Care after Myocardial Infarction (CCMI): Long-Term Investment in the Health of Polish Citizens. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(12):7518.
[21] LI D, TIAN K, GUO J, et al. Growth factors: avenues for the treatment of myocardial infarction and potential delivery strategies. Regen Med. 2022;17(8):561-579.
[22] JUNG KT, BAPAT A, KIM YK, et al. Therapeutic hypothermia for acute myocardial infarction: a narrative review of evidence from animal and clinical studies. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2022;75(3):216-230.
[23] ALONAIZAN R, CARR C. Cardiac regeneration following myocardial infarction: the need for regeneration and a review of cardiac stromal cell populations used for transplantation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022; 50(1):269-281.
[24] LIAO Z, CHEN Y, DUAN C, et al. Cardiac telocytes inhibit cardiac microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis through exosomal miRNA-21-5p-targeted cdip1 silencing to improve angiogenesis following myocardial infarction. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):268-291.
[25] 王自贵,闫强,黄幸.益气化瘀汤对急性心肌梗死再灌注后心肌微血管的保护作用[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2021,31(13):77-79.
[26] 唐湘宇,洪华山,谭华清,等.心肌梗死前后联合运动对大鼠心梗微血管密度和血管内皮细胞生长因子及其受体通路的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2020,42(9):775-781.
[27] 邢胜.由SETD4调控的静息c-Kit~+细胞在激活后对心脏微血管生成作用的研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2021.
[28] ZHU JZ, BAO XY, ZHENG Q, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction Exerts Cardioprotective Effects through Targeting Angiogenesis via Caveolin-1/VEGF Signaling Pathway in Mice with Acute Myocardial Infarction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:4275984.
[29] 戎李.血清窖蛋白-1和C-反应蛋白水平与急性冠脉综合征病变严重程度和预后的相关性分析[D].蚌埠:蚌埠医学院,2020.
[30] 关雪莹,李红岩,尚海巍,等.芪冬颐心颗粒对心肌梗死大鼠心肌细胞凋亡及心脏微血管功能的影响[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2019, 53(6):565-570.
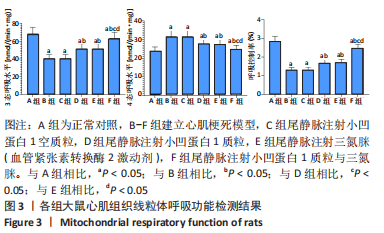
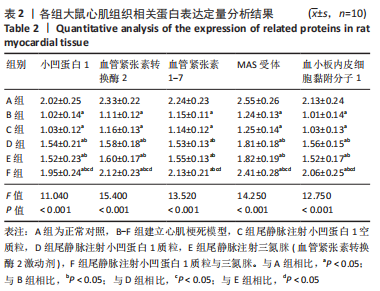
[31] ZHOU Z, LIU Z, GAO X, et al. Mitochondrial respiration in C57BL/6 substrains varies in response to myocardial infarction. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2021;53(2):119-127.
[32] 刘子勤,李文文,吴敬珍,等.Liguzinediol调控心肌细胞线粒体动力学和自噬改善心肌梗死后大鼠心功能的机制[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2022,42(6):768-779.
[33] 曹亚选,郑荣菲,王贺,等.参附益心颗粒对急性心肌梗死后心力衰竭大鼠心肌细胞线粒体自噬的影响[J].中国药房,2022,33(10): 1183-1188.
[34] 郑霞.线粒体靶向性H_2S供体AP39通过抑制过度线粒体自噬改善心肌梗死大鼠心肌纤维化[D].衡阳:南华大学,2021.
[35] 王丽艳.锌转运体Zip2(SLC39A2)对再灌注小鼠心肌线粒体呼吸的调控作用[D].天津:天津医科大学,2020.
[36] 谢世阳,王幼平,崔琳,等.参附益心颗粒对心肌梗死后心力衰竭大鼠心肌线粒体呼吸功能的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2020, 40(1):59-64.
[37] XIAO M, ZENG W, WANG J, et al. Exosomes Protect Against Acute Myocardial Infarction in Rats by Regulating the Renin-Angiotensin System. Stem Cells Dev. 2021;30(12):622-631.
[38] 郝正燕.慢性心力衰竭中医辨证分型与Ang(1-7)、NT-proBNP的相关性研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2018.
[39] 温展鹏.替米沙坦-血管紧张素1-7纳米组装体治疗小鼠心肌梗死的作用及机制研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2021.
[40] 李世超,王志军,杨秀红.ACE2/Ang(1-7)Mas受体轴对心脏重塑、心功能影响及其机制的研究进展[J].山东医药,2016,56(12):96-98. |