中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (17): 2708-2712.doi: 10.12307/2022.539
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
钙敏感受体可影响持续性肺动脉高压新生模型小鼠的肺血管重塑
朱亚平1,李 翔1,陈志文1,刘 莹1,赵文卓1,马克涛2,谷 强1
- 1石河子大学医学院第一附属医院儿科,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832000;2石河子大学医学院,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832000
Calcium-sensitive receptors influence pulmonary vascular remodeling in neonatal mice with persistent pulmonary hypertension
Zhu Yaping1, Li Xiang1, Chen Zhiwen1, Liu Ying1, Zhao Wenzhuo1, Ma Ketao2, Gu Qiang1
- 1Department of Pediatrics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University School of Medicine, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Shihezi University School of Medicine, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
钙敏感受体:是经典的G蛋白偶联受体,通过一系列信号转导通路影响细胞的病理生理功能。钙敏感受体不仅在维持机体钙和其他金属离子的稳态中发挥重要作用,而且也参与激素分泌调节、离子通道激活、基因表达、细胞分化、增殖及凋亡等过程。
小凹蛋白:是构成细胞质膜小凹结构的核心蛋白,可与多种信号分子结合形成复合体,调控信号分子的活性状态,进而控制细胞的跨膜信号转导,参与细胞的生命活动,如细胞增殖、细胞内吞、胆固醇运输、细胞膜组装及信号转导等。
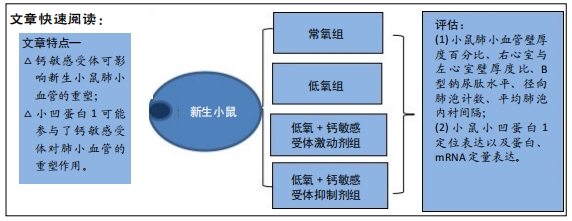
背景:课题组早期研究结果显示在新生小鼠持续性肺动脉高压模型中钙敏感受体的表达上调,在钙敏感受体激动剂组该上调趋势更加明显,而在钙敏感受体抑制剂组有所下降。
目的:探讨钙敏感受体在低氧诱导的持续肺动脉高压新生小鼠肺血管重塑中的机制。
方法:将80只刚出生的C57BL/6小鼠随机平均分成4个组。其中,低氧组、低氧+激动剂组(以下简称激动剂组)和低氧+抑制剂组(以下简称抑制剂组)同时放置于低氧箱中(氧浓度为12%),后2组分别每天1次腹腔内注射钙敏感受体激动剂GdCl3(16 mg/kg)或抑制剂NPS2390(1 mg/kg);常氧组小鼠暴露在空气中,与低氧组一样每天注射等量的生理盐水,共注射14 d,第15天麻醉后取出小鼠心肺组织。显微镜下测量各组小鼠心室壁及肺血管壁的厚度、观察肺泡形态学变化;使用酶联免疫吸附实验检测B型钠尿肽水平;使用Western bolt和免疫组化检测小鼠肺组织中小凹蛋白1蛋白的表达和定位,并使用qRT-PCR检测小凹蛋白1 mRNA的表达。实验方案经石河子大学医学院第一附属医院实验动物伦理委员会批准(批准号为2018-172-01)。
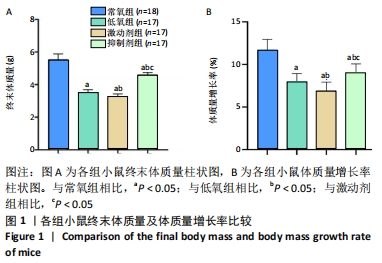
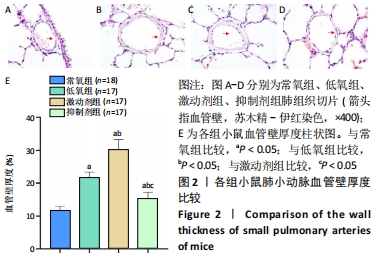
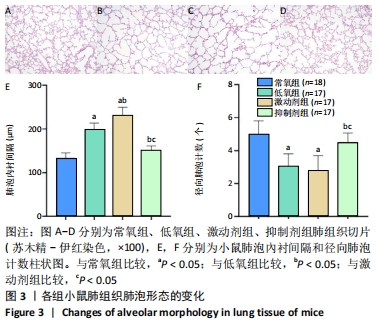
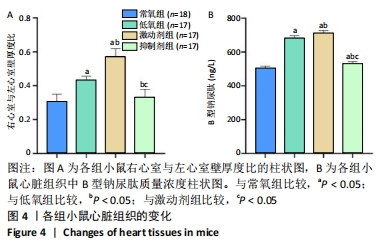
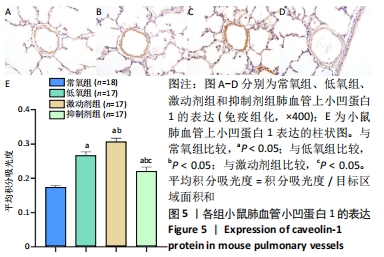
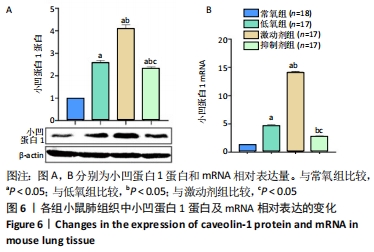
结果与结论:①与常氧组比较,低氧14 d后低氧组小鼠肺小动脉血管壁增厚、右心室与左心室壁厚度比及B型钠尿肽水平增加,平均肺泡内衬间隔变宽、径向肺泡计数减少,Western bolt和qRT-PCR显示小凹蛋白1蛋白和mRNA表达上调(P < 0.05);激动剂组变化更为显著(P < 0.05);抑制剂组可逆转低氧所致的变化(P < 0.05);②结果提示,钙敏感受体影响持续肺动脉高压新生小鼠肺组织血管的重塑,其作用机制可能与改变了小凹蛋白1的表达有关。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3454-1038 (朱亚平)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: