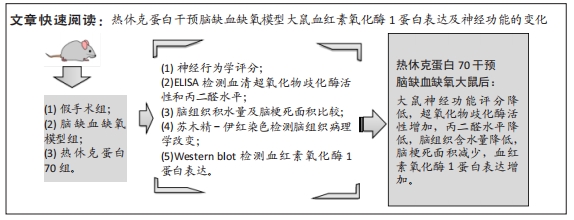
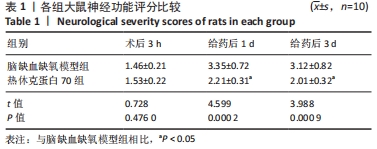
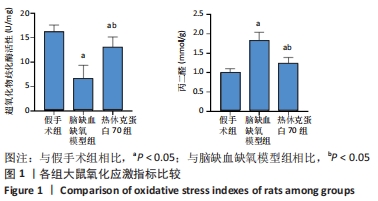
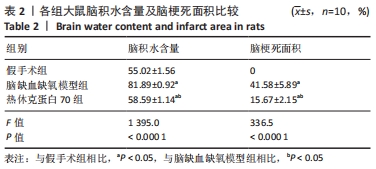
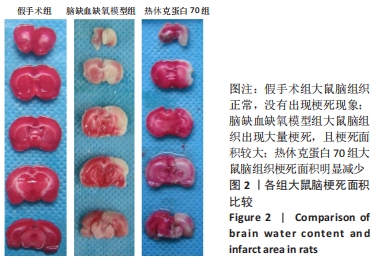
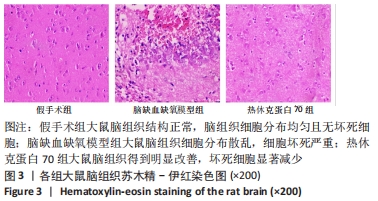
[1] DIÉGUEZ-HURTADO R, KATO K, GIAIMO BD, et al. Loss of the transcription factor RBPJ induces disease-promoting properties in brain pericytes. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2817.
[2] CHEN J, ZHU C, JIA W, et al. MiR-455-5p Attenuates Cerebral Ischemic Reperfusion Injury by Targeting FLT3. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020; 76(5):627-634.
[3] WANG KJ, ZHANG WQ, LIU JJ, et al. Piceatannol protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusioninduced apoptosis and oxidative stress via the Sirt1/FoxO1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(6):5399-5411.
[4] DONG C, WEN S, ZHAO S, et al. Salidroside Inhibits Reactive Astrogliosis and Glial Scar Formation in Late Cerebral Ischemia via the Akt/GSK-3β Pathway. Neurochem Res. 2021;46(4):755-769.
[5] 李永刚. 通窍活血汤对急性缺血性脑卒中患者氧化应激反应及脑血流的影响[J]. 湖南中医杂志,2020,36(3):42-43.
[6] 赵丰, 徐志云. 老年急性缺血性脑卒中患者炎症因子,血脂和氧化应激水平的变化[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2020,40(21):4515-4517.
[7] 沈晓东,张天,宋文.热休克蛋白70在家族性腺瘤性息肉病中的表达及意义[J].医学研究杂志,2020,49(2):143-148.
[8] 潘郭海容, 梁群. 热休克蛋白对脓毒症病理机制的新认识[J]. 中国急救医学,2020,40(4):356-361.
[9] SUBRAMANIAN C, GORNEY R, WANG T, et al. A novel heat shock protein inhibitor KU757 with efficacy in lenvatinib-resistant follicular thyroid cancer cells overcomes up-regulated glycolysis in drug-resistant cells in vitro. Surgery. 2020;169(1):34-42.
[10] GOYAL L, CHAUDHARY SP, KWAK EL, et al. A phase 2 clinical trial of the heat shock protein 90 (HSP 90) inhibitor ganetespib in patients with refractory advanced esophagogastric cancer. Invest New Drugs. 2020;38(5):1533-1539.
[11] 张秀琴,李敬华. 热休克蛋白对2型糖尿病发病的作用机制研究进展[J]. 武警医学,2020,31(11):81-85.
[12] 彭伟,刘畅,李勇,等.慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重患者血清热休克蛋白70和硫化氢水平变化及其与炎症因子关系[J].临床急诊杂志,2020,21(1):74-78.
[13] SUN X, LI X, JIA H, et al. Effect of heat-shock protein B7 on oxidative stress in adipocytes from preruminant calves. J Dairy Sci. 2019;102(6): 5673-5685.
[14] CHIONH YT, CUI J, KOH J, et al. High basal heat-shock protein expression in bats confers resistance to cellular heat/oxidative stress. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2019;24(4):835-849.
[15] 赵静, 袁瑞华, 王海芳,等. 活血胶囊激活PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1通路对血管内皮细胞发挥抗氧化损伤作用[J]. 云南中医学院学报, 2019,42(3):10-16.
[16] 刘凤, 刘增长. 茯苓酸通过激活Nrf2/HO-1信号通路改善OX-LDL诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞损伤[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2020,36(2):164-168,179.
[17] EL-EMAM SZ, SOUBH AA, AL-MOKADDEM AK, et al. Geraniol activates Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathway mediating protection against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020;393(10):1849-1858.
[18] TARZJANI S, FAZELI S, SANATI MH, et al. Heat Shock Protein 70 and The Risk of Multiple Sclerosis in The Iranian Population. Cell J. 2019; 20(4):599-603.
[19] KONG Q, MA X, WANG C, et al. Patients with Acute Ischemic Cerebrovascular Disease with Coronary Artery Stenosis Have More Diffused Cervicocephalic Atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019; 26(9):792-804.
[20] MA X, KONG Q, WANG C, et al. Predicting asymptomatic coronary artery stenosis by aortic arch plaque in acute ischemic cerebrovascular disease: beyond the cervicocephalic atherosclerosis? Chin Med J. 2019; 132(8):905-913.
[21] ZHANG ZB, XIONG LL, XUE LL, et al. MiR-127-3p targeting CISD1 regulates autophagy in hypoxic–ischemic cortex. Cell Death Dis. 2021; 12(3):279.
[22] CHO S, FUCHS P, SARMAH D, et al. Cerebral ischemia in diabetics and oxidative stress. J Breast Cancer. 2020;23(1):59-68.
[23] KAUSAR S, ABBAS MN, YANG L, et al. Biotic and abiotic stress induces the expression of Hsp70/90 organizing protein gene in silkworm, Bombyx mori. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;143(7):610-618.
[24] 刘天宇, 夏斌, 任冠桦,等. 热休克蛋白70对H9C2细胞免受氧糖剥夺损伤的保护作用及分子机制[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2021, 38(4):689-691.
[25] 姜美子, 宗堪堪, 李莉,等. 肉豆蔻提取物对慢性缺血缺氧模型大鼠脑膜及脑组织结构损伤的影响研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2020, 38(4):64-66+270-272.
[26] JIA Q, YAN L, PING Y, et al. Heat shock protein 90 inhibition by 17-Dimethylaminoethylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin protects blood-brain barrier integrity in cerebral ischemic stroke. Am J Transl Res. 2020;7(10):1826-1837.
[27] ZHOU ZB, HUANG GX, LU JJ, et al. Up-regulation of heat shock protein 27 inhibits apoptosis in lumbosacral nerve root avulsion-induced neurons. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):11468.
[28] 祝淑贞,潘速跃.格列苯脲调控HSP70/p-Akt/MMP-9/COX-2炎性信号通路保护脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠的神经血管单元[J]. 中华神经医学杂志,2019,18(8):767-778.
[29] 赵宗刚,金辉,王胜男.奥拉西坦对大鼠脑梗死的脑保护作用及机制[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2019,27(11):944-949.
[30] 高迎春,孟盼盼,郭建魁,等. 急性减压缺氧对大鼠氧化应激损伤的研究[J]. 解放军医药杂志,2020,32(4):19-23.
[31] 唐祎偌,胡秋慧,邹飞.硫化氢对脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].生命的化学,2020,40(4):528-534.
[32] 曾超, 刘文兵, 梁康,等. 电针对脑缺血再灌注损伤小鼠脑组织氧化应激的影响[J]. 中华内分泌外科杂志,2020,14(6):471-475.
[33] 马竞, 何文龙, 高重阳,等. 虫草素对大脑中动脉局灶性脑缺血模型大鼠氧化应激和脑损伤的影响[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2020, 38(3):40-45.
[34] 张玥, 陈林, 谢春,等. 灵芝三萜类化合物对砷中毒大鼠脑组织氧化应激损伤的影响[J]. 贵州医科大学学报,2020,45(3):277-280.
[35] 周海燕, 周俐红, 张彩霞,等. 吴茱萸次碱对局灶性脑缺血模型大鼠脑组织病理,免疫失衡和氧化应激的调节作用及机制研究[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2020,36(6):677-681.
[36] 夏洁,刘丽,陈燕. ERK信号通路在瑞芬太尼减轻失血性休克复苏大鼠脑组织的氧化应激损伤的作用[J]. 脑与神经疾病杂志,2020, 28(12):38-44.
[37] Zhang S, Liu W, Wang P, et al. Activation of HSP70 impedes tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced apoptosis and senescence of human nucleus pulposus stem cells via inhibiting the JNK/c-Jun pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(5):1979-1994.
[38] 陈建国, 黄柳雯, 李杰,等. 4种天然温石棉致大鼠肺损伤及对HO-1和HSP-70的影响[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,2020,39(3):52-60.
[39] 董贝贝, 张智申, 杨永妍,等. HO-1在血红素结合蛋白减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤中的作用[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志,2020,40(3):342-346.
[40] 池宁娟, 刘明义, 冯娟,等. 乐尔脉胶囊对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠大脑皮层组织中HO-1、SOD1、SOD2和Nrf2蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中国药房,2019,30(11):1525-1529.
[41] 刘英存,李飞,黄毅,等.Sestrin2蛋白通过Nrf2/HO-1信号通路保护大鼠心肌细胞缺氧复氧损伤[J].第三军医大学学报,2020,42(15): 1536-1542.
[42] 陈人豪, 王琦, 李俊,等. 刺五加提取物对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2020,31(1):43-48.
[43] DUKAY B, WALTER FR, VIGH JP, et al. Neuroinflammatory processes are augmented in mice overexpressing human heat-shock protein B1 following ethanol-induced brain injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2021; 18(1):22.
|