中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (17): 2692-2698.doi: 10.12307/2023.157
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇
针灸与康复疗法干预脑缺血模型大鼠神经功能及肠道菌群的变化
崔振华,林夏妃,陈永敏,林 烨,李关羽,宋振华
- 中南大学湘雅医学院附属海口医院康复医学科,海南省海口市 570208
Acupuncture and moxibustion combined with rehabilitation therapy improve neurological function and intestinal flora following cerebral ischemia in rats
Cui Zhenhua, Lin Xiafei, Chen Yongmin, Lin Ye, Li Guanyu, Song Zhenhua
- Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Haikou Hospital Affiliated to Xiangya Medical College of Central South University, Haikou 570208, Hainan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
缺血性卒中:是由于脑血管狭窄或闭塞引起供血不足造成的脑组织损伤,可引发神经功能障碍。此文采用Longa法建立脑缺血大鼠模型,分离并结扎左侧颈总动脉,并插入线栓导致局灶永久性缺血,模拟人缺血性卒中状况。
肠道菌群:是肠道的正常微生物,具有辅助消化、调节免疫等多种作用,维持肠道菌群动态平衡有利于激活免疫因子,提高抗病能力。此文缺血性卒中大鼠肠道菌群紊乱,炎性因子水平升高,说明缺血性卒中确实与肠道菌群紊乱相关。
背景:针灸与康复训练均能够有效缓解脑缺血患者症状,目前有关两者联合治疗是否对脑缺血患者神经功能障、肠道菌群失调具有调控作用尚不明确。
目的:探究针灸联合康复疗法对脑缺血大鼠神经功能、肠道菌群的影响。
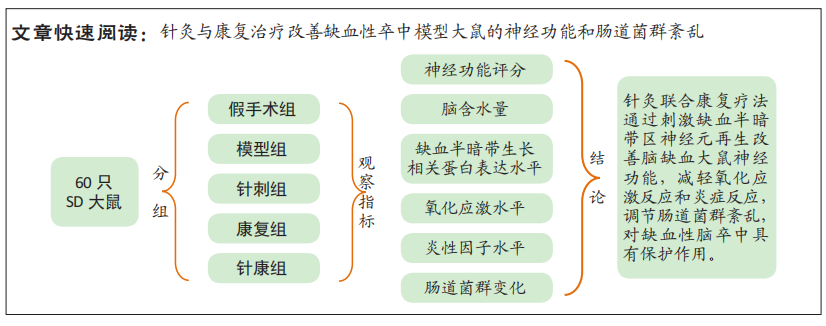
方法:将60只SD大鼠按随机数表法随机分为假手术组、模型组、针刺组、康复组和针康组(n=12)。除假手术组外,其余各组建立脑缺血大鼠模型;假手术组仅分离左侧颈总动脉;针刺组用头穴丛刺干预,康复组进行任务导向性跑台训练,针康组同时给予头穴丛针刺和任务导向性跑台训练干预,干预14 d。观察造模后4 h及1,7,14 d各组大鼠神经功能情况,检测干预14 d后大鼠脑含水量变化,Western blot检测缺血半暗带神经元生长相关蛋白(生长相关蛋白43、神经丝蛋白200、排斥指导分子a)表达,试剂盒检测脑组织乳酸脱氢酶、超氧化物歧化酶、丙二醛水平,酶联免疫吸附法检测脑组织肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β质量浓度,实时荧光定量PCR检测大鼠粪便中大肠杆菌、双歧杆菌、乳酸杆菌和肠球菌变化。
结果与结论:①造模后4 h及1,7,14 d,假手术组无神经功能障碍,模型组大鼠出现明显神经功能障碍(P < 0.05);②与同时段模型组相比,针刺组和康复组大鼠神经功能缺损随着干预时间延长有所改善(P < 0.05),而针康组大鼠神经功能改善更显著(P < 0.01);③与模型组比较,针刺组、康复组大鼠缺血半暗带生长相关蛋白43、神经丝蛋白200表达上调(P < 0.05),排斥指导分子a表达下调(P < 0.05);大鼠脑组织含水量和脑组织中乳酸脱氢酶、丙二醛、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β质量浓度降低(P < 0.05),超氧化物歧化酶活性升高(P < 0.05);粪便中大肠杆菌、肠球菌数量明显增多(P < 0.05),双歧杆菌、乳酸菌数量明显降低(P < 0.05);且针康组上述指标改善更为显著(P < 0.01);④提示针灸联合康复疗法可通过刺激缺血半暗带区神经元再生改善脑缺血大鼠神经功能,减轻氧化应激反应和炎症反应,调节肠道菌群紊乱,对缺血性脑卒中具有保护作用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0856-9360 (崔振华)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: