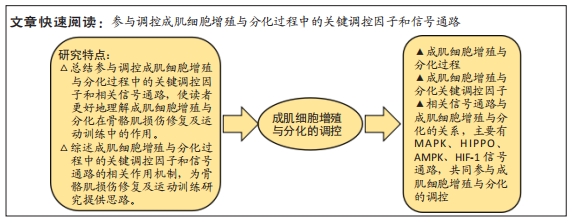
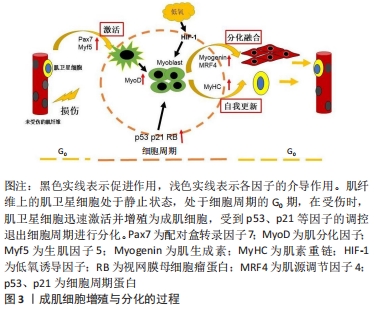
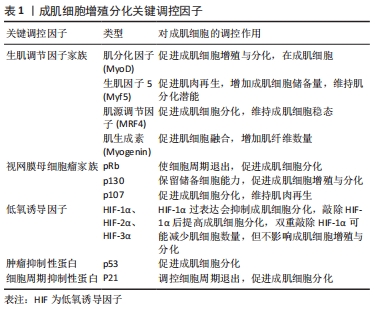
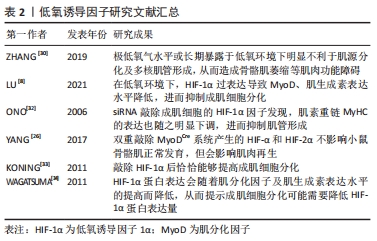
[1] OLGUIN HC, OLWIN BB. Pax-7 up-regulation inhibits myogenesis and cell cycle progression in satellite cells: a potential mechanism for self-renewal. Dev Biol. 2004;275(2):375-388.
[2] XIONG G, HINDI SM, MANN AK, et al. The PERK arm of the unfolded protein response regulates satellite cell-mediated skeletal muscle regeneration. Elife. 2017;6:e22871.
[3] GUITART M, LLORETA J, MAÑAS-GARCIA L, et al. Muscle regeneration potential and satellite cell activation profile during recovery following hindlimb immobilization in mice. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(5):4360-4372.
[4] ZHANG J, XU X, LIU Y, et al. EPA and DHA Inhibit Myogenesis and Downregulate the Expression of Muscle-related Genes in C2C12 Myoblasts. Genes (Basel). 2019;10(1):64.
[5] 王震,蔺海旗,何霏,等.运动激活骨骼肌卫星细胞:增龄性肌衰减症及肌肉损伤修复的运动预防和治疗[J].中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(23):3752-3759.
[6] 周静,郑孝众,姚婉贞,等.骨骼肌运动损伤的MRI研究进展[J].中华放射学杂志,2021,55(3):324-328.
[7] 蒲荣喜. AMPK对成肌细胞功能活性的影响及其代谢调节研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2017.
[8] LU Y, MAO J, HAN X, et al. Downregulated hypoxia-inducible factor 1α improves myoblast differentiation under hypoxic condition in mouse genioglossus. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(3):1351-1364.
[9] DUMONT NA, RUDNICKI MA. Characterizing Satellite Cells and Myogenic Progenitors During Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1560:179-188.
[10] 从晓霞. mTOR信号通路在肌肉再生和肌腱分化中的作用和调控机制研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2018.
[11] HERNÁNDEZ-HERNÁNDEZ JM, GARCÍA-GONZÁLEZ EG, BRUN CE, et al. The myogenic regulatory factors, determinants of muscle development, cell identity and regeneration. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;72:10-18.
[12] ZAMMIT PS. Function of the myogenic regulatory factors Myf5, MyoD, Myogenin and MRF4 in skeletal muscle, satellite cells and regenerative myogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;72:19-32.
[13] 张安宁,罗雪林,黄思琴,等.PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路在大鼠急性骨骼肌钝挫伤修复中的作用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(7):594-600.
[14] JUNG EM, JEUNG EB. Rapamycin-induced au-tophagy decreases Myf5 and MyoD proteins in C2C1myoblast cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2019;58: 132-141.
[15] YAMAMOTO M, LEGENDRE NP, BISWAS AA, et al. Loss of MyoD and Myf5 in Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells Results in Altered Myogenic Programming and Failed Regeneration. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;10(3): 956-969.
[16] ZAPPIA MP, ROGERS A, ABMMK I, et al. Rbf Activates the Myogenic Transcriptional Program to Promote Skeletal Muscle Differentiation. Cell Rep. 2019;26(3):702-719.e6.
[17] ASFOUR HA, ALLOUH MZ, SAID RS. Myogenic regulatory factors: The orchestrators of myogenesis after 30 years of discovery. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018;243(2):118-128.
[18] 汪瑞婷.骨骼肌特异转录调控因子MyoD通过相分离机制调控基因表达[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2019.
[19] YANG ZJ, BROZ DK, NODERER WL, et al. p53 suppresses muscle differentiation at the myogenin step in response to genotoxic stress. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22(4):560-573.
[20] MASCIULLO V, VALDIVIESO P, AMADIO G, et al. Role of Retinoblastoma Protein Family (Rb/p105 and Rb2/p130) Expression in the Histopathological Classification of Borderline Ovarian Tumors. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:596226.
[21] SCHNEIDER JW, GU W, ZHU L, et al. Reversal of terminal differentiation mediated by p107 in Rb-/- muscle cells. Science. 1994;264(5164):1467-1471.
[22] SIDLE A, PALATY C, DIRKS P, et al. Activity of the retinoblastoma family proteins, pRB, p107, and p130, during cellular proliferation and differentiation. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1996;31(3):237-271.
[23] DE FALCO G, COMES F, SIMONE C. pRb: master of differentiation. Coupling irreversible cell cycle withdrawal with induction of muscle-specific transcription. Oncogene. 2006;25(38):5244-5249.
[24] NOVITCH BG, SPICER DB, KIM PS ,et al. pRb is required for MEF2-dependent gene expression as well as cell-cycle arrest during skeletal muscle differentiation. Curr Biol. 1999;9(9):449-459.
[25] ROUFAYEL R, MEZHER R, STOREY KB. The Role of Retinoblastoma Protein in Cell Cycle Regulation: An Updated Review. Curr Mol Med. 2021;21(8):620-629.
[26] YANG X, YANG S, WANG C, et al. The hypoxia-inducible factors HIF1α and HIF2α are dispensable for embryonic muscle development but essential for postnatal muscle regeneration. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(14): 5981-5991.
[27] GENOVESE C, TRANI D, CAPUTI M, et al. Cell cycle control and beyond: emerging roles for the retinoblastoma gene family. Oncogene. 2006; 25(38):5201-5209.
[28] CARNAC G, FAJAS L, L’HONORÉ A, et al. The retinoblastoma-like protein p130 is involved in the determination of reserve cells in differentiating myoblasts. Curr Biol. 2000;10(9):543-546.
[29] WANG C, LIU W, LIU Z, et al. Hypoxia Inhibits Myogenic Differentiation through p53 Protein-dependent Induction of Bhlhe40 Protein. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(50):29707-29716.
[30] ZHANG Z, ZHANG L, ZHOU Y, et al. Increase in HDAC9 suppresses myoblast differentiation via epigenetic regulation of autophagy in hypoxia. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(8):552.
[31] 宋亚琼,周播江.低氧诱导因子-1在调控骨骼肌缺氧时能量代谢发生适应性变化的机制研究进展[J].解剖学报,2017,48(2):236-240.
[32] ONO Y, SENSUI H, SAKAMOTO Y, et al. Knockdown of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by siRNA inhibits C2C12 myoblast differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98(3):642-649.
[33] KONING M, WERKER PM, VAN LUYN MJ, et al. Hypoxia promotes proliferation of human myogenic satellite cells: a potential benefactor in tissue engineering of skeletal muscle. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(13-14): 1747-1758.
[34] WAGATSUMA A, KOTAKE N, YAMADA S. Spatial and temporal expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α during myogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;347(1-2):145-155.
[35] LIU X, WANG Y, ZHAO S, et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Promotes C2C12 Cells Myogenic Differentiation by Enhancing Cell Cycle Exit. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:1648715.
[36] FLAMINI V, GHADIALI RS, ANTCZAK P, et al. The Satellite Cell Niche Regulates the Balance between Myoblast Differentiation and Self-Renewal via p53. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;10(3):970-983.
[37] LI H, HOU L, ZHANG Y, et al. PFN2a Suppresses C2C12 Myogenic Development by Inhibiting Proliferation and Promoting Apoptosis via the p53 Pathway. Cells. 2019;8(9):959.
[38] ADHIKARI A, MAINALI P, DAVIE JK. JARID2 and the PRC2 complex regulate the cell cycle in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(51): 19451-19464.
[39] MAL A, CHATTOPADHYAY D, GHOSH MK, et al. p21 and retinoblastoma protein control the absence of DNA replication in terminally differentiated muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 2000;149(2):281-292.
[40] WANG S, ZUO H, JIN J, et al. Long noncoding RNA Neat1 modulates myogenesis by recruiting Ezh2. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(7):505.
[41] SUN W, HU S, HU J, et al. Akirin1 promotes myoblast differentiation by modulating multiple myoblast differentiation factors. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(3):BSR20182152.
[42] GUO Y, WANG M, GE J, et al. Bioactive biodegradable polycitrate nanoclusters enhances the myoblast differentiation and in vivo skeletal muscle regeneration via p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(3):486-495.
[43] SUN Y, LIU WZ, LIU T, et al. Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2015;35(6):600-604.
[44] CHEN TH, CHEN CY, WEN HC, et al. YAP promotes myogenic differentiation via the MEK5-ERK5 pathway. FASEB J. 2017;31(7):2963-2972.
[45] CONTRERAS O, VILLARREAL M, BRANDAN E. Nilotinib impairs skeletal myogenesis by increasing myoblast proliferation. Skelet Muscle. 2018; 8(1):5.
[46] YOO M, LEE SJ, KIM YK, et al. Dehydrocorydaline promotes myogenic differentiation via p38 MAPK activation. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(4): 3029-3036.
[47] JUDSON RN, TREMBLAY AM, KNOPP P, et al. The Hippo pathway member Yap plays a key role in influencing fate decisions in muscle satellite cells. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 24):6009-6019.
[48] 赵莉娟,张宏,张国辉,等.Hippo信号通路在骨骼肌损伤修复中作用的研究进展[J].山东医药,2020,60(1):109-112.
[49] WATT KI, JUDSON R, MEDLOW P, et al. Yap is a novel regulator of C2C12 myogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;393(4):619-624.
[50] KNYAZEVA A, KHUDIAKOV A, VAZ R, et al. FLNC Expression Level Influences the Activity of TEAD-YAP/TAZ Signaling. Genes (Basel). 2020; 11(11):1343.
[51] ZHANG T, GUAN X, CHOI UL, et al. Phosphorylation of TET2 by AMPK is indispensable in myogenic differentiation. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2019;12(1):32.
[52] 吕欣,周达岸.PI3K/AKT信号通路对骨骼肌再生的影响研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(11):908-912.
[53] ZHANG ZK, LI J, LIU J, et al. Icaritin requires Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling to counteract skeletal muscle atrophy following mechanical unloading. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20300.
[54] MAJMUNDAR AJ, LEE DS, SKULI N, et al. HIF modulation of Wnt signaling regulates skeletal myogenesis in vivo. Development. 2015; 142(14):2405-2412.
|