[1] GARCIADIEGO-CáZARES D, AGUIRRE-SáNCHEZ HI, ABARCA-BUIS RF, et al. Regulation of α5 and αV Integrin Expression by GDF-5 and BMP-7 in Chondrocyte Differentiation and Osteoarthritis. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0127166.
[2] KANIA K, COLELLA F, RIEMEN A, et al. Regulation of Gdf5 expression in joint remodelling, repair and osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):157.
[3] BUNGARTZ M, KUNISCH E, MAENZ S, et al. GDF5 significantly augments the bone formation induced by an injectable, PLGA fiber-reinforced, brushite-forming cement in a sheep defect model of lumbar osteopenia. Spine J. 2017;17(11):1685-1698.
[4] FITZGERALD M J, MUSTAPICH T, LIANG H, et al. Tendon Transection Healing Can Be Improved With Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Cultured With Growth Differentiation Factor 5 and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor. Hand (N Y). 2021:15589447211028929.
[5] XU H, SUN M, WANG C, et al. GDF5-GelMA injectable microspheres laden with adipose-derived stem cells for disc degeneration repair. Biofabrication. 2020. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/abc4d3.
[6] XIA B, CHEN G, ZOU Y, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound combination with induced pluripotent stem cells-derived neural crest stem cells and growth differentiation factor 5 promotes sciatic nerve regeneration and functional recovery. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(4):625-636.
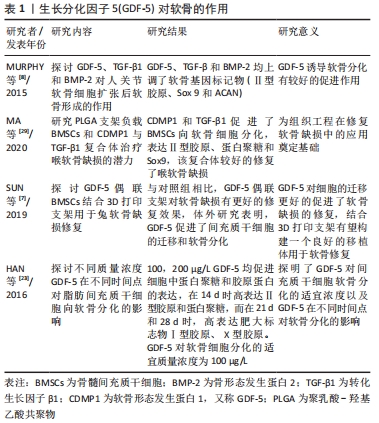
[7] SUN Y, YOU Y, JIANG W, et al. 3D-bioprinting a genetically inspired cartilage scaffold with GDF5-conjugated BMSC-laden hydrogel and polymer for cartilage repair. Theranostics. 2019;9(23):6949-6961.
[8] MURPHY MK, HUEY DJ, HU JC, et al. TGF-β1, GDF-5, and BMP-2 stimulation induces chondrogenesis in expanded human articular chondrocytes and marrow-derived stromal cells. Stem Cells. 2015; 33(3):762-773.
[9] WANG T, NIMKINGRATANA P, SMITH CA, et al. Enhanced chondrogenesis from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2019;39:101497.
[10] 刘振宁,贾长青,韩长旭,等.生长分化因子5诱导兔脂肪干细胞成软骨细胞分化的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009, 23(4):483-489.
[11] MANG T, KLEINSCHMIDT-DOERR K, PLOEGER F, et al. BMPR1A is necessary for chondrogenesis and osteogenesis, whereas BMPR1B prevents hypertrophic differentiation. J Cell Sci. 2020;133(16): jcs246934.
[12] 吴磊,刘洋,谭俊峰,等.生长分化因子5诱导脂肪干细胞向成软骨细胞方向分化的实验研究[J].生物医学工程与临床,2017,21(4): 429-434.
[13] MELROSE J, SHU C, WHITELOCK JM, et al. The cartilage extracellular matrix as a transient developmental scaffold for growth plate maturation. Matrix Biol. 2016;52-54:363-383.
[14] 杨治,张铭,许鹏.生长分化因子5转染对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].贵州医科大学学报,2016,41(10):1197-1203, 1207.
[15] ZHAO X, BIAN R, WANG F, et al. GDF-5 promotes epidermal stem cells proliferation via Foxg1-cyclin D1 signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):42.
[16] 李博,吴慧颖,朴虎林,等.生长分化因子5对血管内皮细胞增殖和运动的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2011,37(6):1062-1064.
[17] 任晓勇,张银刚,陈文弦.hGDF5基因转染对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2006,27(1):15-19.
[18] 卢康荣,朴仲贤,刘真喜,等.生长分化因子5基因转染诱导骨髓基质干细胞分化的研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(8):750-754.
[19] FREYMANN U, METZLAFF S, KRüGER JP, et al. Effect of Human Serum and 2 Different Types of Platelet Concentrates on Human Meniscus Cell Migration, Proliferation, and Matrix Formation. Arthroscopy. 2016; 32(6):1106-1116.
[20] LI X, WANG F, LAN Y, et al. GDF-5 induces epidermal stem cell migration via RhoA-MMP9 signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(4):1939-1948.
[21] SCHIEFER JL, HELD M, FUCHS PC, et al. Growth Differentiation Factor 5 Accelerates Wound Closure and Improves Skin Quality During Repair of Full-Thickness Skin Defects. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2017;30(5):223-229.
[22] COLEMAN CM, VAUGHAN EE, BROWE DC, et al. Growth differentiation factor-5 enhances in vitro mesenchymal stromal cell chondrogenesis and hypertrophy. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(13):1968-1976.
[23] HAN C, REN Y, JIA Y, et al. The effective mode of growth and differentiation factor-5 in promoting the chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2016;17(1):105-115.
[24] PEREIRA D, RAMOS E, BRANCO J. Osteoarthritis. Acta Med Port. 2015; 28(1):99-106.
[25] STUDER D, MILLAN C, ÖZTüRK E, et al. Molecular and biophysical mechanisms regulating hypertrophic differentiation in chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells. Eur Cell Mater. 2012;24:118-135; discussion 135.
[26] 张山锋,勘武生,刘军,等.生长分化因子5促进软骨细胞肥大成熟的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(17):1611-1614.
[27] 许鹏,许珂,张银刚,等.人生长分化因子5重组质粒转染大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外成软骨观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016, 31(9):952-954.
[28] PARRISH WR, BYERS BA, SU D, et al. Intra-articular therapy with recombinant human GDF5 arrests disease progression and stimulates cartilage repair in the rat medial meniscus transection (MMT) model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(4):554-560.
[29] MA L, ZHANG Y, WANG C. Coaction of TGF-β1 and CDMP1 in BMSCs-induced laryngeal cartilage repair in rabbits. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31(12):130.
[30] KATAYAMA R, WAKITANI S, TSUMAKI N, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defects in rabbits using CDMP1 gene-transfected autologous mesenchymal cells derived from bone marrow. Rheumatology(Oxford). 2004;43(8):980-985.
[31] AYERST BI, SMITH RA, NURCOMBE V, et al. Growth Differentiation Factor 5-Mediated Enhancement of Chondrocyte Phenotype Is Inhibited by Heparin: Implications for the Use of Heparin in the Clinic and in Tissue Engineering Applications. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(7-8): 275-292.
[32] STECK E, FISCHER J, LORENZ H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell differentiation in an experimental cartilage defect: restriction of hypertrophy to bone-close neocartilage. Stem Cells Dev. 2009;18(7): 969-978.
[33] LI G, YIN J, GAO J, et al. Subchondral bone in osteoarthritis: insight into risk factors and microstructural changes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013; 15(6):223.
[34] MADRY H, ORTH P, CUCCHIARINI M. Role of the Subchondral Bone in Articular Cartilage Degeneration and Repair. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(4):e45-46.
[35] BARR AJ, CAMPBELL TM, HOPKINSON D, et al. A systematic review of the relationship between subchondral bone features, pain and structural pathology in peripheral joint osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):228.
[36] GOLDRING MB, GOLDRING SR. Articular cartilage and subchondral bone in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192: 230-237.
[37] GOLDRING SR. Alterations in periarticular bone and cross talk between subchondral bone and articular cartilage in osteoarthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2012;4(4):249-258.
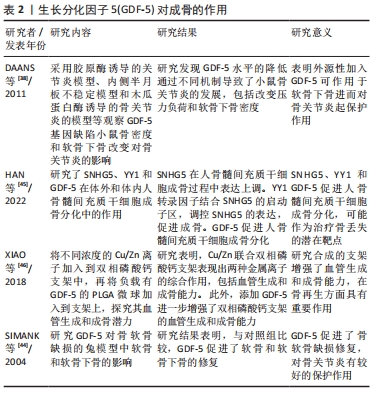
[38] DAANS M, LUYTEN FP, LORIES RJ. GDF5 deficiency in mice is associated with instability-driven joint damage, gait and subchondral bone changes. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(1):208-213.
[39] HU Y, CHEN X, WANG S, et al. Subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis and pain. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):20.
[40] LI B, ASPDEN RM. Material properties of bone from the femoral neck and calcar femorale of patients with osteoporosis or osteoarthritis. Osteoporos Int. 1997;7(5):450-456.
[41] ZENG Q, LI X, BECK G, et al. Growth and differentiation factor-5 (GDF-5) stimulates osteogenic differentiation and increases vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels in fat-derived stromal cells in vitro. Bone. 2007;40(2):374-381.
[42] SENA K, SUMNER DR, VIRDI AS. Modulation of VEGF expression in rat bone marrow stromal cells by GDF-5. Connect Tissue Res. 2007; 48(6):324-331.
[43] KAKUDO N, WANG YB, MIYAKE S, et al. Analysis of osteochondro-induction using growth and differentiation factor-5 in rat muscle. Life Sci. 2007;81(2):137-143.
[44] SIMANK HG, SERGI C, JUNG M, et al. Effects of local application of growth and differentiation factor-5 (GDF-5) in a full-thickness cartilage defect model. Growth Factors. 2004;22(1):35-43.
[45] HAN Y, YANG Q, HUANG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the miR-212-3p/GDF5/SMAD pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022; 13(1):130.
[46] XIAO D, YANG F, ZHAO Q, et al. Fabrication of a Cu/Zn co-incorporated calcium phosphate scaffold-derived GDF-5 sustained release system with enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis properties. RSC Adv. 2018;8(52):29526-29534.
[47] 丁呈彪,周云.膝骨性关节炎患者滑膜炎的发病机制及研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(51):8327-8332.
[48] STOPPIELLO LA, MAPP PI, WILSON D, et al. Structural associations of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(11): 3018-3027.
[49] MIN S, WANG C, LU W, et al. Serum levels of the bone turnover markers dickkopf-1, osteoprotegerin, and TNF-α in knee osteoarthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2017;36(10):2351-2358.
[50] CHANG X, SHEN J, YANG H, et al. Upregulated expression of CCR3 in osteoarthritis and CCR3 mediated activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Cytokine. 2016;77:211-219.
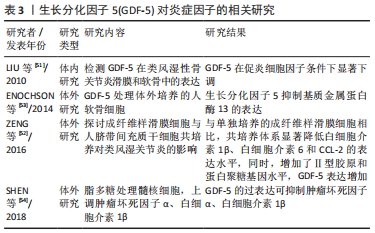
[51] LIU FL, LIN LH, SYTWU HK, et al. GDF-5 is suppressed by IL-1beta and enhances TGF-beta3-mediated chondrogenic differentiation in human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Exp Mol Pathol. 2010;88(1):163-170.
[52] ZENG J, WANG F, MAO M. Co‑culture of fibroblast‑like synoviocytes with umbilical cord‑mesenchymal stem cells inhibits expression of pro‑inflammatory proteins, induces apoptosis and promotes chondrogenesis. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(4):3887-3893.
[53] ENOCHSON L, STENBERG J, BRITTBERG M, et al. GDF5 reduces MMP13 expression in human chondrocytes via DKK1 mediated canonical Wnt signaling inhibition. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(4):566-577.
[54] SHEN L, WU Y, HAN L, et al. Overexpression of growth and differentiation factor-5 inhibits inflammatory factors released by intervertebral disc cells. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(4):3603-3608.
[55] LIU Y, PENG L, LI L, et al. 3D-bioprinted BMSC-laden biomimetic multiphasic scaffolds for efficient repair of osteochondral defects in an osteoarthritic rat model. Biomaterials. 2021;279:121216.
|