中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (32): 5201-5208.doi: 10.12307/2022.884
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
下丘脑:运动改善骨代谢的关键控制器
陆鹏程,刘 波,金圣杰,田志凯,曾炘瑜,陈祥和
- 扬州大学体育学院,江苏省扬州市 225127
-
收稿日期:2021-11-23接受日期:2022-01-06出版日期:2022-11-18发布日期:2022-05-14 -
通讯作者:陈祥和,博士,副教授,扬州大学体育学院,江苏省扬州市 225127 -
作者简介:陆鹏程,男,1999年生,江苏省盐城市人,汉族,扬州大学在读硕士,主要从事运动与骨代谢的研究。 -
基金资助:中国博士后科学基金特别资助(2021T140580),项目负责人:陈祥和;中国博士后科学基金(2019M661957),项目负责人:陈祥和;扬州大学“青蓝工程”,项目负责人:陈祥和;扬州大学“高端人才支持计划”,项目负责人:陈祥和
Hypothalamus: the key controller for exercise-improved bone metabolism
Lu Pengcheng, Liu Bo, Jin Shengjie, Tian Zhikai, Zeng Xinyu, Chen Xianghe
- College of Physical Education, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225127, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2021-11-23Accepted:2022-01-06Online:2022-11-18Published:2022-05-14 -
Contact:Chen Xianghe, PhD, Associate professor, College of Physical Education, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225127, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Lu Pengcheng, Master candidate, College of Physical Education, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225127, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2021T140580 (to CXH); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2019M661957 (to CXH); “Ultramarine Blue Engineering” Project of Yangzhou University (to CXH); High-end Talent Support Program of Yangzhou University (to CXH)
摘要:

文题释义:
骨代谢:作为骨组织的正常生理性代谢,主要包括成骨细胞、破骨细胞和骨细胞的代谢,3者的功能活性和代谢平衡均直接影响骨质和骨量,病理性骨代谢常会形成动态平衡紊乱,进而导致出现骨质疏松。
“脑-骨”串联:人体各组织和器官中常存在着交互作用,进而影响机体的正常生理代谢,“脑-骨”之间存在的串联关系在运动改善骨代谢中发挥了重要作用。
背景:骨代谢一直都是骨组织工程研究的热点,研究发现下丘脑是运动改善骨代谢的主要调控中枢。
目的:综述下丘脑在骨代谢中的作用,探讨运动介导下丘脑改善骨代谢的机制。
方法:检索1983年1月至2021年12月CNKI和PubMed等中英文数据库,中文检索词:运动;下丘脑;骨代谢;英文检索词:exercise,hypothalamus,bone metabolism。选择下丘脑与骨代谢相关的文献以及运动介导下丘脑改善骨代谢的相关文献,对入选的72条文献进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:①下丘脑作为调控机体生理活动的关键中枢,其下游的下丘脑-垂体-靶腺轴发挥了重要调控作用,影响神经肽Y、瘦素、骨钙素以及降钙素等激素的分泌,进而调控骨代谢调节因子和信号通路,改善骨质疏松等常见骨类疾病;②近年来,“脑-骨”串联介导的运动健骨作用受到医学、生物学和体育学研究领域的普遍关注,但其具体的发生和作用机制仍在探索中,运动通过机械力刺激和细胞内电信号的传导,激活骨代谢信号通路。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5058-0101 (陆鹏程)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
陆鹏程, 刘 波, 金圣杰, 田志凯, 曾炘瑜, 陈祥和. 下丘脑:运动改善骨代谢的关键控制器[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(32): 5201-5208.
Lu Pengcheng, Liu Bo, Jin Shengjie, Tian Zhikai, Zeng Xinyu, Chen Xianghe. Hypothalamus: the key controller for exercise-improved bone metabolism[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5201-5208.
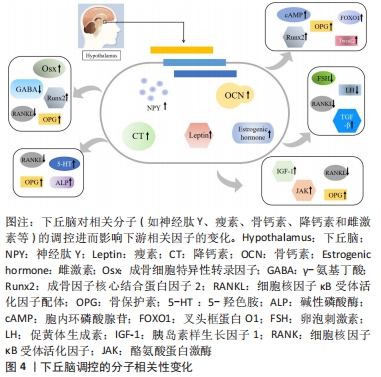
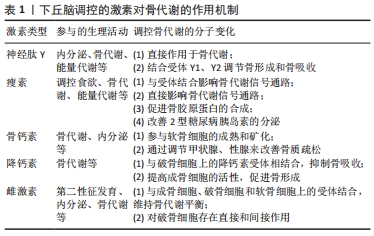
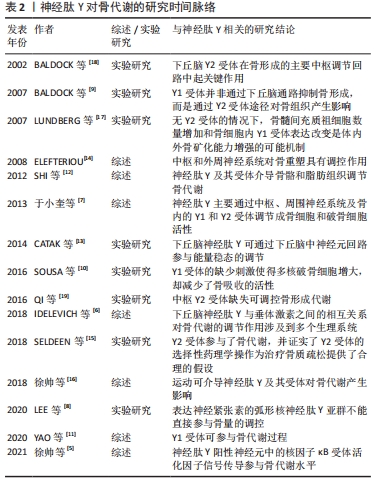
2.1.1 神经肽Y对骨代谢的影响 神经肽Y是一种存在于中枢及外周神经中的肽类激素,可参与调节机体的内分泌、骨代谢以及能量代谢等一系列生理活动。研究发现,神经肽Y作为下丘脑参与调节骨量的重要神经递质,其不仅在下丘脑弓状核中大量生成,而且在骨组织中的成骨细胞、破骨细胞和软骨细胞中也同样发现了神经肽Y的存在[5-6]。此外,于小奎等[7]也发现神经肽Y不仅可以直接抑制成骨细胞中细胞核因子κB受体活化因子配体(nuclear factor kappa B receptor activator ligand,RANKL)表达,使骨髓间充质干细胞中骨保护素的表达增加,骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化受到抑制;还可以间接抑制由RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化和骨吸收。有实验在敲除小鼠神经肽Y基因后,发现成骨细胞的活性明显提高;此外,神经肽Y基因缺失小鼠骨质改善明显、骨量明显增多,成骨因子核心结合蛋白因子2(Runt-related transcription factor 2,Runx2)和成骨细胞特异性转录因子(osterix,Osx)的表达也显著增强[8];而在神经肽Y敲除小鼠的下丘脑中注射补充神经肽Y却发现不能恢复到原有骨代谢水平,同时神经肽Y的过量表达也会导致成骨细胞活性下降,以致出现骨矿含量生成率降低,骨基质和骨量流失严重。以上实验均说明了敲除神经肽Y可促进小鼠骨量增加,骨形成能力提升,但神经肽Y的过高水平表达会导致骨代谢紊乱。
神经肽Y除了对成骨细胞活性有调控作用外,其受体在此过程中也对成骨细胞、破骨细胞活性和骨代谢有着重要影响。研究发现,神经肽Y的受体主要有Y1受体(Y1R)、Y2受体(Y2R)、Y4受体(Y4R)、Y5受体(Y5R)和Y6受体(Y6R)5类G蛋白偶联受体,其中对骨代谢影响较大的是Y1R和Y2R。研究发现,Y1R基因抑制小鼠会出现骨形成和骨吸收代谢失衡,而下丘脑缺失Y1R基因却不能对骨代谢平衡产生影响[9],即下丘脑中Y1R基因不参与调节骨代谢。在应激状态下,神经肽Y激活杏仁核和海马中Y1R抵消促肾上腺皮质激素释放激素产生的应激反应;此外,还可激活下丘脑室旁核中Y1R介导的促肾上腺皮质激素释放激素调控下丘脑-垂体-肾上腺轴,进而改善骨代谢紊乱。而在成骨细胞缺失Y1R基因小鼠中,SOUSA等[10]却发现骨形成和骨吸收水平均显著上调,且成骨能力更为明显。除此之外,神经肽Y不仅可直接促进骨保护素表达并抑制成骨祖细胞中RANKL表达,而且神经肽Y可与小鼠骨髓细胞上Y1R相结合,抑制胞内环磷酸腺苷(cyclic adenosine monophosphate,cAMP)和RANKL的表达,进而抑制破骨细胞骨吸收[7]。此外,还发现成骨细胞中Y1R、中枢中Y2R与骨细胞之间存在神经介导的连接,Y1R缺失也会导致骨量增加和骨形成能力增强[11]。
Y2R广泛存在于脂肪细胞、肝脏和肌肉等组织中,且在下丘脑、海马和脑干中大量表达。研究发现,中枢Y2R与成骨细胞中Y1R之间有着密切联系,成骨细胞中Y1R可以直接参与Y2R敲除小鼠的骨形成,且两者均可抑制骨形成,同时也是参与维持骨代谢平衡的关键因素[12-13]。实验发现小鼠敲除Y2R会提高成骨细胞的骨形成能力,进而导致小鼠骨量增加[14-15]。与下丘脑Y1R不能参与骨代谢不同,下丘脑特异性Y2R缺失的小鼠表现出与Y2R种系缺失小鼠相同的骨形成代谢模式[16]。研究发现,体外去神经培养的Y2R-/-小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞与对照组相比,其矿化作用明显增强[17];并且,无论是部分还是全部敲除下丘脑中Y2R基因,小梁骨的体积和成骨矿化沉积率都有明显增加[18],均可在一定程度上提高成骨细胞的活性。此外,还发现下丘脑中Y2R会导致γ-氨基丁酸表达受抑制,胰岛素样生长因子活性降低,进而成骨细胞分化受到抑制;与此同时,抑制γ-氨基丁酸还会促进白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达增加,并同时作用于OPG/RANKL/细胞核因子κB受体活化因子(receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B,RANK)信号通路,使得RANKL浓度升高,破骨细胞破骨能力增强[19]。以上研究均证明下丘脑神经元Y2R是神经肽Y在下丘脑调控骨代谢的重要因子。总之,神经肽Y作为广泛分布于中枢和周围神经系统的神经肽,可通过“脑-骨”串联刺激下丘脑来显著抑制骨形成,其受体Y1R、Y2R也可以直接作用于成骨细胞和破骨细胞,促进骨细胞分化,维持骨代谢平衡,见表2。
2.1.2 瘦素对骨代谢的影响 瘦素是由脂肪组织分泌的一类激素,是骨代谢、能量代谢中的重要信号分子,其主要作用发生于下丘脑弓状核,与中枢和周围神经系统中的瘦素受体结合参与生理活动,并且抑制神经肽Y表达[20]。研究发现,瘦素主要作用于下丘脑,并与受体结合激活了OPG/RANKL/RANK信号通路、细胞磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(serine-threonine kinase,Akt)/哺乳动物雷帕霉素蛋白(mechanistic target of rapamycin,mTOR)信号通路、酪氨酸蛋白激酶(janus activated kinase,JAK)/信号传导和转录激活子(signal transducer and activator of transcription,STAT)信号通路等,即阐述了瘦素与其受体在中枢和周围神经系统中的重要作用[21]。目前,大量研究数据表明瘦素通过调控下丘脑中枢神经系统来抑制骨形成进而影响骨代谢过程,具体表现为瘦素可以与脑干上的长型瘦素蛋白受体结合,并减少5-羟色胺能神经元的生成,进而调控骨代谢;此外,瘦素还可以调控下丘脑中的肽类物质如神经肽U与神经肽Y的表达来影响骨代谢[22-23]。除此之外,外周神经系统中瘦素受体在成骨细胞、破骨细胞及软骨细胞中大量存在,这就意味着瘦素可在外周神经系统中调控骨代谢[24]。研究发现,敲除小鼠瘦素基因会影响OPG/RANKL/RANK信号通路,通过分析其机制可知,敲除瘦素后会抑制小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向脂肪细胞的转化,诱导成骨基因的表达并促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化[25];此外,瘦素可作用于骨髓间充质干细胞使人间质细胞中RANKL分泌减少,并使骨保护素分泌增加,阻碍RANK与RANKL的结合,促进胰岛素样生长因子1的合成,抑制破骨细胞的分化,从而降低骨吸收的活性[26]。
除此之外,瘦素促进骨胶原蛋白合成,刺激软骨细胞分化和矿化,同时维持成骨细胞活性,促使成骨细胞分化形成骨细胞。成骨细胞周围还存在大量胰岛素受体,而2型糖尿病导致的胰岛素缺乏则会造成骨代谢紊乱,骨形成弱于骨吸收,进而表现为骨量减少,出现骨质疏松,而瘦素在此过程中可以改善胰岛素分泌;对此,DIMITRI等[27]发现,瘦素可刺激成骨细胞分化,促进胰岛素样生长因子1表达,激活PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路,并且下游哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1(mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1,mTORC1)/核糖体蛋白S6激酶多肽1(ribosomal protein S6 kinase polypeptide 1,S6K1)被激活可促进成骨细胞介导的骨形成,抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收能力,由此说明瘦素在2型糖尿病骨代谢中也发挥了重要作用。另外,瘦素与其受体相结合可激活JAK使JAK受体磷酸化,并激活JAK/STAT信号通路,进而提高成骨细胞的成骨能力[28]。人体研究发现,不同性别人群血清中瘦素的表达水平也存在差异,即女性表达水平明显高于男性,且女性血清中瘦素的表达与骨密度呈正相关,这就意味着女性血清中瘦素的增加会造成骨形成能力增强,骨密度提高[23];与之相反,男性血清中瘦素的增加会导致骨吸收能力提高,骨密度下降。这些发现对进一步了解瘦素参与并改善骨代谢的作用机制的研究有着重要意义,同时血清中瘦素与骨密度之间的模糊关系,是否是由于受到机体内病理的影响而发生改变,这也值得深入研究和探讨,见表3。

2.1.3 骨钙素对骨代谢的影响 骨钙素是一种由成熟成骨细胞合成、分泌的特异性非胶原基质蛋白,是骨组织细胞中非胶原蛋白的主要成分。骨钙素在骨代谢过程中扮演了重要角色,尤其在骨形成和骨吸收过程中,大量成熟骨钙素会在骨细胞外的基质中沉积,并在血循环中作少量释放;而且对软骨细胞的矿化和成熟存在影响。除此以外,骨钙素不仅参与了骨组织的正常发育,维持骨量平衡,而且骨钙素的分泌水平还可代表着骨组织的代谢水平。上述均可说明骨钙素与骨骼的生长和发育有非常密切的联系[29-30]。
除此之外,骨钙素缺失常见于甲状腺功能衰退、肾上腺功能减退以及血糖过高等情况,而下丘脑促垂体区肽能神经元分泌的一些肽类激素,如可以通过分泌促甲状腺激素释放激素、促性腺激素释放激素、生长素释放抑制激素、促肾上腺皮质激素释放激素以及生长素释放激素等一系列激素来调控甲状腺、性腺与肾上腺等腺垂体激素的分泌。针对此类研究发现,骨代谢紊乱致使的骨质疏松与神经-内分泌-免疫网络有着密切联系[31]。有研究还发现,血清中骨钙素的表达水平与年龄有着一定关系,即年龄越大,骨钙素的表达水平越低[32],尤其在女性绝经后,下丘脑-垂体-靶腺轴会出现中枢神经系统和激素分泌系统紊乱,骨钙素、脂质运载蛋白2(lipocalin-2,LCN2)和雌激素分泌能力下降,而这些发生机制的调控中枢都在下丘脑中,其中LCN2可通过丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)信号通路促进Runx2磷酸化,进而促进骨形成;并且LCN2可与下丘脑中MC4R黑素细胞皮质激素受体4(melanocortin 4 receptor,MC4R)结合,进而激活cAMP信号途径,使得cAMP活性升高,促进成骨细胞的分化和增殖[33]。就此,董万涛等[34]通过检测去卵巢小鼠的血清骨钙素水平和下丘脑、腺体以及骨组织细胞中的游离Ca2+水平,探讨中枢神经-内分泌-免疫网络对骨质疏松发生的影响和发生机制,结果发现,游离Ca2+量与骨钙素含量呈正相关,当骨钙素含量升高时,游离Ca2+可加速与钙调蛋白(calmodulin,CaM)的结合,通过激活CaMKⅡ/NFATc信号通路中的CaMKⅡ,随后与钙神经素(calcineurin,CaN)结合,使活化的T细胞核因子c(nuclear factor of activated T cell c,NFATc)去磷酸化,进而促进Osx的转录,使成骨细胞成骨能力提高。除此之外,小鼠敲除骨钙素会导致胰岛素敏感性增强,胰岛素抵抗增加,而胰岛素可抑制成骨细胞中骨保护素的合成,加速了RANKL和RANK结合,从而提高破骨细胞的骨吸收能力[35]。
下丘脑能够通过调控相关激素分泌来影响下游甲状腺、肾上腺等腺体,且机体内激素分泌水平是否可对骨钙素的表达水平产生影响,进而影响骨骼的正常发育,目前尚缺少直接证据证明下丘脑能够影响骨钙素分泌进而作用于骨代谢。机体内甲状腺激素的分泌水平会影响骨代谢,甲状腺激素不仅可以直接作用于成骨细胞和破骨细胞,而且可介导骨钙素来影响成骨细胞和破骨细胞的分化能力。甲亢患者因甲状腺激素分泌水平在不断提高,使成骨细胞产生大量的骨钙素、胰岛素样生长因子和碱性磷酸酶;并且在此过程中,p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 Mitogen activated protein kinase,p38MAPK)也可加速成骨细胞中MC3T3-E1合成骨钙素,但同时也可通过cAMP信号通路抑制p38MAPK进而抑制骨钙素的合成[36]。苏俊平等[37]发现甲亢患者血清中游离甲状腺素与骨钙素的分泌水平呈正相关,当下丘脑通过减少促甲状腺激素释放激素分泌后,甲状腺腺体分泌功能受限,甲状腺激素分泌减少,骨钙素含量降低,并抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收能力。以上均说明,下丘脑可通过下丘脑-垂体-甲状腺轴提高促甲状腺激素的分泌水平,促进甲状腺激素的分泌,并使得骨钙素的分泌增加,进而改善骨代谢紊乱。除此之外,在研究胰岛素对骨钙素反馈作用时,发现骨钙素会由原来的羧化无活性形式(cOCN)脱羧化为活性形式(ucOCN),并促进胰岛素分泌,此时胰岛素受体在接受胰岛素信号刺激后会抑制叉头框蛋白O1(Forkhead box protein O1,FOXO1)和Twist2的表达,其中FOXO1将启动骨保护素,进而抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收能力,Twist2则提高Runx2的活性,进而促进成骨细胞分化[38]。下丘脑-垂体-肾上腺轴是中枢神经-内分泌系统的重要组成部分,同时也作为另一证明下丘脑通过分泌激素刺激下游腺体进而实现改善骨代谢的重要通路。机体受到刺激后造成下丘脑-垂体-肾上腺轴失稳状态,下丘脑合成促肾上腺皮质激素释放激素,促肾上腺皮质激素释放激素刺激脑下垂体分泌促肾上腺皮质激素,促肾上腺皮质激素入血促进糖皮质激素的释放[39]。糖皮质激素过多释放导致氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ表达上调,抑制骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨的分化和骨形成活性;同时糖皮质激素还刺激RANKL分化,减少骨保护素的表达,进而提高骨吸收的活性[40]。
2.1.4 降钙素对骨代谢的影响 降钙素是一种哺乳动物体内由甲状腺滤泡旁细胞分泌、参与钙磷骨质代谢的多肽类激素,尤其在人体下丘脑中的浓度最高;降钙素是一种优质骨吸收抑制剂,因此也常作为药剂广泛运用于缓解和治疗骨质疏松。降钙素主要的生理作用是可以抑制破骨细胞活性,降低骨吸收代谢水平,同时刺激成骨细胞的分化,提高骨形成能力。对此,MANGLANI等[41]发现,降钙素在OPG/RANKL/RANK系统中对骨代谢的意义在于能够通过增强该系统的持久性以及形成超分子降钙素组装,并提高骨保护素活性,促进骨形成代谢,同时下调RANKL的表达,抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收。研究认为降钙素可以缓解和改善大部分由于骨组织代谢紊乱导致的骨类疾病[42],并且可以影响小肠对钙的吸收,减少血清中Ca2+的游离,分析其分子机制可知,降钙素可提高下丘脑中5-羟色胺的表达,降低血清中5-羟色胺的活性,其中脑源性5-羟色胺可促进成骨细胞骨形成,小肠中5-羟色胺受到抑制可间接促进骨形成[43]。而且还发现降钙素亦可作用于破骨细胞,并与破骨细胞上的降钙素受体相结合,直接抑制破骨细胞骨吸收,并且有效地改善骨代谢紊乱;此外,降钙素还可影响成骨细胞的活性,提高骨形成能力,促进骨组织中软骨细胞的矿化和沉积。降钙素还通过cAMP-蛋白激酶A(protein kinase A,PKA)信号通路对骨代谢产生影响,降钙素作用于G激活蛋白,使腺苷酸环化酶活化后产生cAMP,并促使依赖于cAMP的蛋白激酶A激活,碱性磷酸酶活性上升,进而抑制破骨细胞的破骨能力,提高成骨细胞的成骨能力[44]。
研究证明,降钙素抑制破骨细胞分化不仅与其分泌量有关,而且血清中降钙素的含量会随年龄变化而改变,尤其在儿童的生长期、妇女的妊娠期和哺乳期,血液中钙磷以及降钙素含量明显增多,进而促使骨组织细胞的分化和硬化,骨量和骨质进一步增加,并达到保护骨骼的作用。尤其在妇女进入绝经期后,血清内降钙素表达水平会显著下降,破骨细胞的骨吸收能力增强,进而造成骨量大量丢失。在动物造模实验中,同样观察到小鼠血清中降钙素对破骨细胞骨吸收能力的抑制作用也会随着年龄的增加而更加显著。有研究发现,在机体内降钙素的活性可以由下丘脑进行调控,并且可以与下丘脑网状结构上的降钙素受体进行结合,抑制破骨细胞活性,降低骨吸收能力,防止骨量流失[45]。
上述的一些观点都表明了下丘脑对降钙素浓度存在调控作用,而降钙素在抑制破骨细胞骨吸收的同时又促进成骨细胞的骨形成,对影响和改善骨代谢紊乱产生了积极作用。
2.1.5 雌激素对骨代谢的影响 雌激素是由雌性动物卵巢和胎盘分泌产生的促进女性生殖器官和第二性发育特征的重要激素,对人体生理活动具有重要调控作用。研究认为机体内大部分代谢紊乱都与下丘脑有关,对此,刘锡仪等[46]提出了骨质疏松的发病环节主要在下丘脑的观点。研究发现,下丘脑-垂体-性腺轴和下丘脑-垂体-肾上腺轴均可直接刺激女性生殖器官(即卵巢)分泌雌激素,而在成骨细胞、破骨细胞和软骨细胞上都有雌激素受体,且雌激素通过结合细胞上的受体可对骨组织产生直接刺激,进而维持骨形成和骨吸收之间的平衡。而女性绝经后机体内雌激素的分泌水平明显下降,其中活性最强的雌二醇也会随之下降,并促使卵泡刺激素和促黄体生成素的生成增加,下丘脑-垂体-性腺轴的负反馈抑制降低,进而会使成骨细胞和破骨细胞之间发生紊乱,骨吸收能力强于骨形成能力,骨量丢失,骨密度下降。而雌激素可以与骨细胞上的受体结合,抑制氧化作用,保持成骨细胞的活性,预防骨量和骨质减少[47]。雌激素对成骨细胞的作用主要体现在雌激素能够诱导细胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular regulating kinase,ERK)和CCAAT/增强子结合蛋白β(CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein β gene,C/EBPβ)磷酸化,并激活Src/Shc/ERK信号通路,维持成骨细胞的活性,增加其存活时间[48]。除此之外,范金柱等[49]对绝经后骨质疏松患者骨髓间充质干细胞进行雌激素刺激,发现干细胞内的Notch通路活性提高,Notch1受体、Jagged1配体表达均有所升高,下游分子Hes1表达也显著上升,骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨分化能力加强,即表明在雌激素作用下可以促进绝经后患者的骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞转化。而雌激素对破骨细胞的作用可分为直接作用和间接作用,直接作用为雌激素与受体结合,阻断RANKL/巨噬细胞集落刺激因子对破骨细胞的诱导;间接作用为提高转化生长因子β的表达水平,阻断RANK与RANKL的结合,进而实现抑制破骨细胞的活性,降低骨吸收能力[50]。此外,雌激素抑制骨细胞的氧化应激反应是通过促进Wnt信号通路,并影响通路中β-catenin信号因子来保证骨内基质的沉积。以上都表明雌激素可以同时作用于成骨细胞、破骨细胞和软骨细胞,维持3者间的动态平衡。总之,下丘脑在人体激素分泌过程中起到了关键的调控作用,并在下丘脑-垂体-靶腺轴中对不同腺体产生刺激后,使得腺体激素分泌发生变化,从而影响成骨细胞和破骨细胞的分化能力,改善骨代谢紊乱。
综上所述,下丘脑可分泌或刺激相关腺体分泌蛋白和激素,如神经肽Y、瘦素、骨钙素、降钙素及雌激素等,并在分子机制上介导“脑-骨”串联调控成骨细胞和破骨细胞的分化,刺激骨细胞内基质的沉积,进而调控骨代谢。
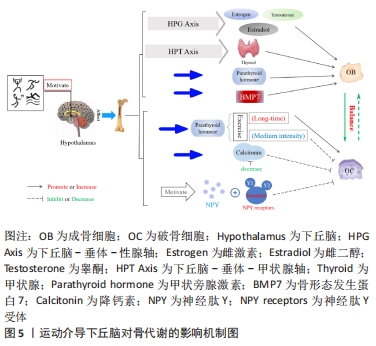
2.2 下丘脑介导运动改善骨代谢 目前普遍认为,骨质疏松的发生与基因表达、激素分泌水平以及不规律的饮食和生活方式存在密切联系,机体会因缺乏运动锻炼、腺体功能水平下降以及随年龄增长带来一系列慢性疾病的影响,使得成骨细胞和破骨细胞分化速度不均衡,骨吸收水平提高,导致骨代谢紊乱[51]。部分激素的分泌与骨代谢有着密切的联系,机体在应激、炎症和病理状态下,性激素、甲状腺素、生长激素、肾上腺素和胰岛素等激素的分泌都会发生紊乱,而运动可以改善机体内的组织和器官分泌相关激素,进而影响和调控骨代谢。研究发现,下丘脑可以通过刺激相关腺体分泌激素进而影响骨代谢,在运动时受到外部刺激或机体内发散电信号后会激活下丘脑分泌激素应对生理活动的代谢紊乱,尤其对维持成骨细胞和破骨细胞之间的平衡发挥重要作用[52]。而运动可以通过下丘脑调控下游器官和组织的生理功能,促使应激和病理状态下功能的恢复和代谢的正常[53]。但运动是否可以通过下丘脑机制实现对骨代谢紊乱的调控,防止骨量的流失,缓解和改善骨质疏松,甚至是否因此实现影响骨骼发育,也需要进一步的研究和讨论,具体机制图,见图5。
2.2.1 下丘脑介导运动对成骨细胞的影响 运动在介导下丘脑对成骨细胞骨形成能力有重要的调控作用。有研究发现运动可以作用于下丘脑-垂体-性腺轴,并介导性激素在一定程度上影响骨组织细胞的形成和吸收,且在不同性别体内的表现也存在一定差异。雌激素是由女性卵巢分泌的一种激素,女性在绝经后因卵巢功能的衰退会致使雌激素分泌减少,并打破成骨细胞和破骨细胞之间的平衡,使得骨量的流失增加,进而导致骨质疏松的出现。秦晋泽等[54]发现,绝经后女性在经过6个月广场舞运动干预后骨密度明显提高,并提出广场舞运动与有氧运动相似,可以直接作用于下丘脑-垂体-卵巢轴,刺激卵巢中腺体的分泌,提高内分泌系统的功能,进而有效促进成骨细胞的骨形成能力,增加骨基质的堆积。此外,运动还使血清中雌二醇和睾酮水平提高,刺激成骨细胞的分化,有效地改善骨代谢紊乱[55]。PEREIRA等[56]发现,体育运动在下丘脑-垂体-性腺轴和下丘脑-垂体-肾上腺轴中可以促进生长激素及胰岛素样生长因子1的释放,并激活骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞的分化,具体表现为碱性磷酸酶、Runx2、Osx以及骨保护素等成骨标记物的增加,此时胰岛素样生长因子1与肌生长抑制素比率升高,进而引起骨形成的增加。而由男性睾丸分泌的雄性激素——睾酮会随着年龄的增长而发生变化,男性在20岁左右达到睾酮分泌的峰值,而后分泌水平会逐渐下降,随之会造成机体内破骨细胞介导的骨吸收能力占据明显优势,进而促使原发性骨质疏松的出现。此外还发现运动可以介导雄性激素并通过影响下丘脑垂体来提高睾酮分泌水平,增强机体蛋白合成能力,促使钙、磷等物质的沉积,进而提高骨密度[57],具体表现为下丘脑-垂体-性腺轴可调控睾酮的分泌,而且在下丘脑弓状核、前腹侧脑室周围和核团中的Kisspeptin-GPR54系统也可通过调控下丘脑-垂体-性腺轴刺激促性腺激素释放激素分泌,进而影响性激素的分泌,GPR54表达上调可促进机体性激素分泌,进而促进骨钙素分泌[58]。骨钙素的活化形式羧化不全骨钙素激活PI3K后,上调靶基因Akt促进成骨细胞对Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、骨桥蛋白等有机质分泌,促进骨形成。
除此之外,李良等[59]研究有氧运动和抗阻运动对大鼠下丘脑中骨形态发生蛋白7的影响,发现有氧运动可以通过促进白色脂肪棕色化来提高机体的能量代谢水平,尤其在进行8周的有氧运动干预后,大鼠下丘脑中骨形态发生蛋白7蛋白表达水平显著提高[60],而对大鼠进行抗阻运动干预却发现下丘脑中骨形态发生蛋白7蛋白的表达没有显著提高,即说明有氧运动在一定程度上可以介导下丘脑来作用于骨相关蛋白的表达,进而影响骨代谢,分析其分子机制可知运动可使下丘脑中骨形态发生蛋白7蛋白含量显著上升,下调AMPK的表达,并抑制Runx2,进而促进成骨细胞的骨形成能力;同时,也有研究发现骨形态发生蛋白7可在脊髓受损后恢复神经元和运动系统功能[61]。REID[62]发现下丘脑可以分泌促甲状腺激素作用于下丘脑-垂体-甲状腺轴提高甲状腺激素的表达水平,而过多甲状腺激素分泌会同时促进成骨细胞和破骨细胞的活性,但此时骨吸收能力较强,进而造成高转换型骨质疏松。但近年来的研究却发现血清中促甲状腺激素的分泌水平与骨密度呈正相关,而有氧运动可以直接刺激下丘脑分泌促甲状腺激素,即表明运动可以提高促甲状腺激素的表达水平,并在一定程度上可以提高成骨细胞介导的骨形成能力,提高骨密度[63-64]。此外,运动诱导未羧化形式骨钙素促进成骨细胞的分化;研究发现,运动可激活骨髓间充质干细胞活性,诱导Runx2、Osx等基因表达上调,抑制过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ、CCATT 增强结合蛋白α(CCAAT enhancer binding protein α,C/EBPα)等表达,并通过PI3K/Akt、MAPK、Wnt/β-catenin等信号通路促进骨钙素活性的增强[65];与此同时,运动还可介导未羧化形式骨钙素间接刺激胰岛素分泌,并形成未羧化形式骨钙素与胰岛素之间的反馈回路,而胰岛素在抑制Twist2表达的同时促进成骨细胞的分化,保证了骨形成代谢的平衡[38]。
2.2.2 下丘脑介导运动对破骨细胞的影响 运动维持骨代谢的平衡不仅可以提高成骨细胞介导的骨形成能力,同时还表现在抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收能力。甲状旁腺激素作为调控骨骼发育和成熟的重要因子之一,其对骨代谢具有双向调控作用。研究发现,甲状旁腺激素不仅可以增加成骨细胞的数量,提高成骨细胞的分化水平,而且还可以促进破骨细胞的吸收[56]。研究证实,长期运动刺激会使下丘脑持续释放甲状旁腺激素,促进骨吸收;而中等强度的运动干预后甲状旁腺激素的分泌水平有所下降,成骨细胞的活性提升,骨密度随之提高,而机体内的变化与运动的方式和强度有着密切联系。下丘脑也受到不同运动项目和方式的影响,具体表现在运动刺激下丘脑并改变甲状旁腺激素的分泌水平,进而影响骨形成和骨吸收之间的平衡,即甲状旁腺激素的分泌水平与骨量呈负相关。此外,杨念恩等[44,66]研究发现下坡跑运动较平坡跑台运动小鼠血清内甲状旁腺激素含量明显升高,血清中骨钙素含量显著降低,成骨细胞的成骨能力提高;与此同时,上述运动也可使降钙素含量提升,并激活成骨细胞,诱导碱性磷酸酶的表达,进而抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收,说明跑台运动可较好地通过提高内源性甲状旁腺激素和降钙素的分泌水平来影响骨代谢。而对于运动如何调控降钙素来影响骨代谢的研究中,GRIMSTON等[67]发现正常的受试者在运动后降钙素含量明显下降,进而抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收能力,维持骨量平衡。
除此之外,运动刺激对下丘脑中神经肽Y的活性也发挥了重要作用。机体内神经肽Y过度表达会抑制成骨细胞的活性,同时神经肽Y受体Y1R、Y2R也存在相似的抑制骨形成能力,随之也可以参与调节破骨细胞的骨吸收。神经肽Y与下丘脑中Y2R结合,使OPG/RANKL比值发生变化,并调节成骨细胞和破骨细胞的代谢水平,而Y1R、Y2R可以通过下丘脑-垂体-靶腺轴来实现对骨组织细胞生长发育的控制;此外,神经肽Y还可以通过调控机体中枢和外周系统中RANKL的表达,加速骨保护素和RANKL的结合,阻止RANK与RANKL的结合,进而影响破骨细胞的骨吸收能力[68]。
2.2.3 下丘脑介导运动对软骨细胞的影响 适当运动刺激下,下丘脑会发射信号并促进激素分泌,刺激成骨细胞的骨形成和抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收,并进一步改善两者之间的平衡,进而促进骨组织细胞的正常代谢;此外,运动更有助于软骨细胞的矿化和骨基质的沉淀。有研究观察到体内甲状旁腺激素的浓度会受到运动的影响,发现运动时血清中甲状旁腺激素含量急剧上升,而运动结束后一段时间又恢复到正常水平。但却又发现甲状旁腺激素对骨骼的发育有双向调节作用,即表现为低剂量的甲状旁腺激素可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞的转化;持续较高水平的甲状旁腺激素则会抑制软骨细胞的生成[69-70]。除此之外,运动可以改变下丘脑-垂体-性腺轴的活性,刺激性激素的分泌,进而提高骨密度[71]。此外,还发现在运动时软骨细胞受到压力刺激,激活OPG/RANKL/RANK信号通路,使得骨细胞中的RANKL表达上调以及骨保护素表达下调,并有效地阻止RANKL与RANK的结合,OPG/RANKL比值下降,进而表明骨吸收受到抑制,防止了骨量的丢失,进一步促进了骨基质在软骨细胞上的沉淀和堆积[51]。除此之外,继发性骨质疏松是2型糖尿病患者常见的并发症之一,作者在之前的研究中发现,高脂高糖环境下会导致破骨细胞活性提升迅速,骨量丢失严重,使得机体骨密度下降,骨骼强度下降。而运动可以刺激胰腺分泌胰岛素,并直接作用于成骨细胞,使得骨形成能力提升,进而促进骨量沉淀、堆积和软骨细胞的发育和成熟;在此过程中,软骨细胞内Wnt/β-catenin信号途径受到运动刺激,Wnt信号激活成骨细胞活性;此外运动还可上调Wnt1、Wnt3a和β-catenin的活性,激活Runx2,促进骨桥蛋白和骨钙素的表达进而提高成骨细胞的成骨能力,促使骨密度明显提升[72-73]。
综上所述,运动介导下丘脑调控相关分子和激素的分泌水平,应对各生理活动和病理状况的发生,维持成骨细胞和破骨细胞的代谢平衡,进而影响骨代谢水平,改善骨质疏松,保证机体的生长发育。

| [1] WEE NK, KULKARNI RN, HORSNELL H, et al. The brain in bone and fuel metabolism. Bone. 2016;82:56-63. [2] SUN P, HE L, JIA K, et al. Regulation of body length and bone mass by Gpr126/Adgrg6. Sci Adv. 2020;6(12):eaaz0368. [3] 刘媛.骨源性LCN2在不同方式运动调控骨—下丘脑轴中的作用和机制[D].上海:华东师范大学,2019. [4] MASI L. Crosstalk between the brain and bone. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2012;9(1):13-16. [5] 徐帅,陈祥和,李世昌.下丘脑介导能量代谢与骨骼反调节及其运动干预机制研究进展[J].中国体育科技,2021,57(2):74-81. [6] IDELEVICH A, BARON R. Brain to bone: What is the contribution of the brain to skeletal homeostasis? Bone. 2018;115:31-42. [7] 于小奎,朱兵.神经肽Y对骨代谢调节的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2013,19(12):1323-1326. [8] LEE NJ, QI Y, ENRIQUEZ RF, et al. Lack of NPY in neurotensin neurons leads to a lean phenotype. Neuropeptides. 2020;80:101994. [9] BALDOCK PA, ALLISON SJ, LUNDBERG P, et al. Novel role of Y1 receptors in the coordinated regulation of bone and energy homeostasis. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282(26):19092-19102. [10] SOUSA DM, CONCEIÇÃO F, SILVA DI, et al. Ablation of Y1 receptor impairs osteoclast bone-resorbing activity. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33470. [11] YAO D, HUANG L, KE J, et al. Bone metabolism regulation: Implications for the treatment of bone diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110494. [12] SHI YC, BALDOCK PA. Central and peripheral mechanisms of the NPY system in the regulation of bone and adipose tissue. Bone. 2012;50(2):430-436. [13] CATAK Z, AYDIN S, SAHIN I, et al. Regulatory neuropeptides (ghrelin, obestatin and nesfatin-1) levels in serum and reproductive tissues of female and male rats with fructose-induced metabolic syndrome. Neuropeptides. 2014;48(3):167-177. [14] ELEFTERIOU F. Regulation of bone remodeling by the central and peripheral nervous system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008;473(2):231-236. [15] SELDEEN KL, HALLEY PG, VOLMAR CH, et al. Neuropeptide Y Y2 antagonist treated ovariectomized mice exhibit greater bone mineral density. Neuropeptides. 2018; 67:45-55. [16] 徐帅,李世昌,孙朋.神经肽Y介导的骨代谢及运动干预调控研究[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2018,11(2):193-199. [17] LUNDBERG P, ALLISON SJ, LEE NJ, et al. Greater bone formation of Y2 knockout mice is associated with increased osteoprogenitor numbers and altered Y1 receptor expression. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(26):19082-19091. [18] BALDOCK PA, SAINSBURY A, COUZENS M, et al. Hypothalamic Y2 receptors regulate bone formation. J Clin Invest. 2002;109(7):915-921. [19] QI Y, FU M, HERZOG H. Y2 receptor signalling in NPY neurons controls bone formation and fasting induced feeding but not spontaneous feeding. Neuropeptides. 2016;55:91-97. [20] UPADHYAY J, FARR OM, MANTZOROS CS. The role of leptin in regulating bone metabolism. Metabolism. 2015;64(1):105-113. [21] SHAO P, WANG Y, ZHANG M, et al. The interference of DEHP in precocious puberty of females mediated by the hypothalamic IGF-1/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019;181:362-369. [22] FERNÁNDEZ-GALAZ MC, FERNÁNDEZ-AGULLÓ T, CARRASCOSA JM, et al. Leptin accumulation in hypothalamic and dorsal raphe neurons is inversely correlated with brain serotonin content. Brain Res. 2010;1329:194-202. [23] MANTZOROS CS, MAGKOS F, BRINKOETTER M, et al. Leptin in human physiology and pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011;301(4):E567-E584. [24] LEE NJ, CLARKE IM, ENRIQUEZ RF, et al. Central RANK signalling in NPY neurons alters bone mass in male mice. Neuropeptides. 2018;68:75-83. [25] FRANCISCO V, PÉREZ T, PINO J, et al. Biomechanics, obesity, and osteoarthritis. The role of adipokines: When the levee breaks. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(2):594-604. [26] MENG XH, TAN LJ, XIAO HM, et al. Examining the causal role of leptin in bone mineral density: A Mendelian randomization study. Bone. 2019;125:25-29. [27] DIMITRI P, ROSEN C. The Central Nervous System and Bone Metabolism: An Evolving Story. Calcif Tissue Int. 2017;100(5):476-485. [28] SINGH S, SINGH S. JAK-STAT inhibitors: Immersing therapeutic approach for management of rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;86:106731. [29] CHOPIN F, BIVER E, FUNCK-BRENTANO T, et al. Prognostic interest of bone turnover markers in the management of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Joint Bone Spine. 2012;79(1):26-31. [30] SAHIN ERSOY G, GIRAY B, SUBAS S, et al. Interpregnancy interval as a risk factor for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Maturitas. 2015;82(2):236-240. [31] 董万涛,吕泽斌,宋敏,等.从脾肾论治骨质疏松的神经-内分泌-免疫网络平衡机制[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(11):1416-1419. [32] EL HADIDY EL HM, GHONAIM M, El Gawad SSh, et al. Impact of severity, duration, and etiology of hyperthyroidism on bone turnover markers and bone mineral density in men. BMC Endocr Disord. 2011;11:15. [33] MOSIALOU I, SHIKHEL S, LIU JM, et al. Corrigendum: MC4R-dependent suppression of appetite by bone-derived lipocalin 2. Nature. 2017;546(7658):440. [34] 董万涛,周灵通,宋敏,等.固本增骨方对去卵巢大鼠血清骨钙素和NEI网络组织中游离[Ca2+]i的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2018,34(1):121-127. [35] GUEDES JAC, ESTEVES JV, MORAIS MR, et al. Osteocalcin improves insulin resistance and inflammation in obese mice: Participation of white adipose tissue and bone. Bone. 2018;115:68-82. [36] KONDO A, TOKUDA H, KATO K, et al. Rho-kinase negatively regulates thyroid hormone-stimulated osteocalcin synthesis in osteoblasts. Biochimie. 2013;95(4): 719-724. [37] 苏俊平,张博,陈云霞,等.甲状腺功能亢进者治疗前后甲状腺激素和血清骨钙素的变化[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2017,39(3):303-305. [38] MIZOKAMI A, KAWAKUBO-YASUKOCHI T, HIRATA M. Osteocalcin and its endocrine functions. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017;132:1-8. [39] CHOU SH, MANTZOROS C. Bone metabolism in anorexia nervosa and hypothalamic amenorrhea. Metabolism. 2018;80:91-104. [40] YAO Q, LIANG H, HUANG B, et al. Beta-adrenergic signaling affect osteoclastogenesis via osteocytic MLO-Y4 cells’ RANKL production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;488(4):634-640. [41] MANGLANI K, VIJAYAN V, PATHAK C, et al. Development and characterization of supramolecular calcitonin assembly and assessment of its interactions with the bone remodelling process. Bone. 2019;122:123-135. [42] ENDO N, FUJINO K, DOI T, et al. Effect of elcatonin versus nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications for acute back pain in patients with osteoporotic vertebral fracture: a multiclinic randomized controlled trial. J Bone Miner Metab. 2017;35(4):375-384. [43] YAZDANI J, KHIAVI RK, GHAVIMI MA, et al. Calcitonin as an analgesic agent: review of mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2019;69(6): 594-604. [44] 杨念恩.不同方式运动对生长期小鼠骨合成代谢和Wnt信号通路的影响[D].上海:华东师范大学,2014. [45] 高飞,周武,谢卯,等.PFNA联合规范化抗骨质疏松药物治疗老年骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折[J].第二军医大学学报,2017,38(4):437-442. [46] 刘锡仪,刘浩宇.下丘脑弓状核在骨质疏松发病机制中的作用[J].广东医学院学报,2014,32(6):881-885. [47] 孙晓琪.雌二醇通过G蛋白偶联雌激素受体30(GPR30)/ERK1/2信号通路调节MC3T3-E1细胞线粒体自噬的分子机制研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2018. [48] 李微,张博,张雨薇,等.雌激素调节骨代谢作用的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(2):262-266. [49] 范金柱,杨柳,罗卓荆,等.雌激素对绝经后骨质疏松患者骨髓间充质干细胞Notch信号通路的影响[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2013,6(3):232-239. [50] 张萌萌.雌激素与雌激素受体骨代谢调节作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019, 25(5):704-708. [51] KLEIN-NULEND J, VAN OERS RF, BAKKER AD, et al. Bone cell mechanosensitivity, estrogen deficiency, and osteoporosis. J Biomech. 2015;48(5):855-865. [52] YUAN Y, CHEN X, ZHANG L, et al. The roles of exercise in bone remodeling and in prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2016;122(2): 122-130. [53] HUHMANN K. Menses Requires Energy: A Review of How Disordered Eating, Excessive Exercise, and High Stress Lead to Menstrual Irregularities. Clin Ther. 2020;42(3):401-407. [54] 秦晋泽,荣晓旭,朱国兴,等.广场舞对绝经期后骨质疏松患者的骨密度和骨转换指标影响的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(1):43-46,50. [55] GOLDBER GA. Postm enopausal obesity risk a reduced when aerobic exercise is added to weight loss. Women Health Weakly. 2002;19(2):20. [56] PEREIRA LJ, MACARI S, COIMBRA CC, et al. Aerobic and resistance training improve alveolar bone quality and interferes with bone-remodeling during orthodontic tooth movement in mice. Bone. 2020;138:115496. [57] 陈鑫林.运动对原发性骨质疏松的干预与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(8):1294-1299. [58] 徐瑞,严翊,谢敏豪.性激素反馈调节下丘脑ARC和AVPV中kisspeptin-GPR54信号通路的核团差异[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2018,34(8): 810-817. [59] 李良,徐建方,房国梁,等.有氧运动或抗阻运动诱导骨形态发生蛋白7调节大鼠能量代谢的研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(11):960-968. [60] 龚文辉,张素梅,储珏.有氧运动对饮食诱导的肥胖鼠下丘脑和褐色脂肪BMP7表达的影响[J].中国康复,2016,31(2):114-117. [61] CHEN C, BAI GC, JIN HL, et al. Local injection of bone morphogenetic protein 7 promotes neuronal regeneration and motor function recovery after acute spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(6):1054-1060. [62] REID IR. Short-term and long-term effects of osteoporosis therapies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015;11(7):418-428. [63] 王璐,陈媛媛,阮彩莲.有氧运动对焦虑大鼠血清促肾上腺皮质激素、三碘甲状腺原氨酸、甲状腺素及促甲状腺激素的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2015, 35(8):2174-2175. [64] 朱于青,孙琳.促甲状腺激素与骨代谢[J].中国医师杂志,2019,21(2):315-318. [65] PRIDEAUX M, KITASE Y, KIMBLE M, et al. Taurine, an osteocyte metabolite, protects against oxidative stress-induced cell death and decreases inhibitors of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Bone. 2020;137:115374. [66] 杨念恩,李世昌.降钙素在不同方式运动影响骨形成代谢过程中的机制研究[A]//中国体育科学学会运动生理与生物化学分会.第四届(2016)全国运动生理与生物化学学术会议论文集[C].无锡:第四届(2016)全国运动生理与生物化学学术会议,2016:69. [67] GRIMSTON SK, TANGUAY KE, GUNDBERG CM, et al. The calciotropic hormone response to changes in serum calcium during exercise in female long distance runners. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993;76(4):867-872. [68] POLITO R, MONDA V, NIGRO E, et al. The Important Role of Adiponectin and Orexin-A, Two Key Proteins Improving Healthy Status: Focus on Physical Activity. Front Physiol. 2020;11:356. [69] ZHANG Y, KUMAGAI K, SAITO T. Effect of parathyroid hormone on early chondrogenic differentiation from mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;9:68. [70] O’ BRIEN MH, DUTRA EH, LIMA A, et al. PTH [1-34] induced differentiation and mineralization of mandibular condylar cartilage. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3226. [71] 赵丹,施丹,史晓.围绝经期女性预防骨质疏松症研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2019,21(2):118-121. [72] LIU SS, ZHOU P, ZHANG Y. Abnormal expression of key genes and proteins in the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway of articular cartilage in a rat model of exercise-induced osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(3):1999-2006. [73] CHENG L, KHALAF AT, LIN T, et al. Exercise Promotes the Osteoinduction of HA/β-TCP Biomaterials via the Wnt Signaling Pathway. Metabolites. 2020;10(3):90. |
| [1] | 刘金玉, 张晗硕, 崔洪鹏, 潘灵之, 赵博然, 李 菲, 丁 宇. 脊柱微创治疗脊髓型颈椎病的有限元生物力学分析及精准化运动康复方案[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1359-1364. |
| [2] | 党 祎, 杜成砚, 姚红林, 袁能华, 曹 金, 熊 山, 张顶梅, 王 信. 激素型骨坏死与氧化应激[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [3] | 孙佳佳, 朱海迪, 卢 赟, 张 凯. 髋部骨折合并2型糖尿病和非2型糖尿病患者骨代谢标志物的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1156-1160. |
| [4] | 龙桂月, 李冬冬, 廖红兵. 磷酸钙骨水泥/聚乳酸羟基乙酸降解产物促进小鼠单核细胞破骨向分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1193-1198. |
| [5] | 黄林科, 韦林华, 蒋 捷, 刘 倩, 陈蔚蔚. 雌激素与跑台运动干预卵巢切除模型小鼠骨量和关节软骨的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [6] | 毕耕超, 张彦龙, 李秋月, 胡龙威, 张 愉. 不同高度和间距下跳深动作中膝关节力学和周围肌肉的激活特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1211-1218. |
| [7] | 阮 凌, 王光华, 吴荣平, 晋 战, 吕镇庆, 张 楠, 李寿邦. 运动强度与高脂饮食模型大鼠脂代谢紊乱和氧化应激的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1149-1155. |
| [8] | 张永强, 潘 凤, 孙 鹏, 谭明辉, 轩留明, 王勤章. Gja1基因重组慢病毒对糖尿病豚鼠膀胱病变模型中缝隙连接蛋白43蛋白及mRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1161-1165. |
| [9] | 贾圣琪, 罗文龙, 田丁元, 张新会, 崔 茜, 王 超, 裴汉军. 急性肾缺血再灌注损伤模型小鼠线粒体去乙酰化酶3的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1172-1178. |
| [10] | 赵 璐, 赵逸菲, 高 达, 刘艳芳, 付婷婷, 徐江雁. Zeste基因抑制子基因12在糖尿病肾脏病模型大鼠肾组织中的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1179-1186. |
| [11] | 张 艳, 何瑞波, 王庆博, 皮亦华, 陆春敏, 徐传仪, 马 刚, 彭 朋. 不同负荷量有氧运动对肥胖大鼠骨骼肌炎症反应和胰岛素信号途径的影响及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1237-1244. |
| [12] | 吴东哲, 高晓嶙, 李闯涛, 王 昊. 根据心肺最佳点构建反向传播神经网络最大摄氧量预测模型[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1224-1231. |
| [13] | 杨九杰, 李 治, 王树杰, 田 野, 赵 伟. 神经电生理监测硬脊膜切开减压治疗急性脊髓损伤过程中脊髓的功能变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [14] | 杨芷姗, 唐正龙. Hippo信号通路中的核心因子YAP/TAZ参与骨形成的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [15] | 王 继, 张 敏, 杨中亚, 张 龙. 体力活动干预2型糖尿病肌少症的研究现状[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
近年来,随着骨生物工程研究的发展,对骨代谢分子机制及相关代谢信号通路做了更为深层的研究,其中骨代谢的主要调控枢纽——下丘脑,成为运动医学领域的研究焦点。大量研究证实了骨代谢受内分泌系统的影响,且对骨内分泌系统的作用机制不断有新的发现,因此提出了下丘脑可通过“脑-骨”串联实现对骨代谢紊乱的调控[1]。下丘脑作为调节脏器活动、神经活动及内分泌活动等生理活动的高级中枢所在,其不仅在调节体温、摄食、内外渗透压平衡以及控制一些腺体激素分泌和情绪活动等方面发挥重要作用,且近年来发现下丘脑受损会导致青少年骨骼发育受到影响,阻碍人体正常生理活动的进行[2]。研究发现,骨代谢受下丘脑调控,因此提出“下丘脑-骨”轴的存在[3],发现骨代谢紊乱发生与神经肽Y、瘦素、骨钙素、降钙素以及雌激素等激素的分泌存在密切联系。此外,下丘脑-垂体-肾上腺轴、下丘脑-垂体-性腺轴及下丘脑-垂体-甲状腺轴的功能缺失也与骨代谢有关,而运动可通过介导下丘脑-垂体-靶腺轴刺激生长激素及胰岛素样生长因子1分泌,提高雌激素和睾酮的生成,促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞的分化,并激活成骨细胞的骨形成能力,抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收能力,维持骨代谢的动态平衡。对运动参与改善骨代谢的研究,大都聚焦于运动通过调节骨代谢信号通路及下游基因、蛋白等对成骨细胞、破骨细胞分化和活性的影响,鲜有研究揭示运动如何通过关键中枢——下丘脑来调控骨代谢紊乱的分子机制。文章将基于“脑-骨”串联就运动介导下丘脑调控骨代谢的作用机制进行着重探讨,进一步揭示身体发育、骨骼生长与下丘脑的联系,并为运动健骨及促进生长发育提供新的思路和理论依据。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 陆鹏程、金圣杰在2020年7月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 1983年1月至2020年12月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中文数据库:中国知网,万方;英文数据库:PubMed,Web of Science,ScienceDirect。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“运动”“骨代谢”“下丘脑”;英文检索词为“exercise”“bone metabolism”“hypothalamus”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
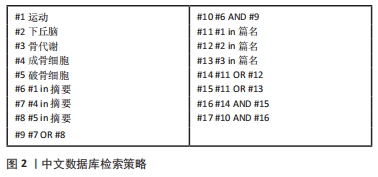
1.1.6 检索策略 见图1,2。

1.2 入组标准 ①下丘脑与骨代谢相关的研究;②运动介导下丘脑改善骨代谢的相关研究;③与研究目的和研究内容相关的文献。
1.3 排除标准 ①重复性研究;②与研究内容不相关的文献;③年代久远且非权威的文献。
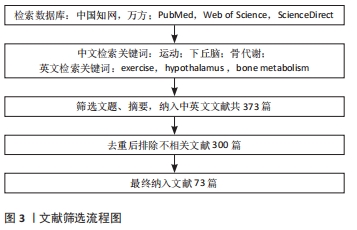
1.4 资料整合 共检索到373篇相关文献,其中排除300篇,实际纳入73篇,中文23篇,英文50篇。检索流程,见图3。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 近年来,医学、生物学和体育学相关研究已经为运动改善骨代谢的作用机制积累了大量素材,通过整理前期文献,逐渐明确了下丘脑在改善骨代谢过程中的重要地位,并在此基础上,串联运动、下丘脑和骨代谢3大研究领域的成果,深入探讨“脑-骨”串联的机制变化。
3.3 综述的局限性 文章对下丘脑调控骨代谢的机制进行探讨,并结合运动在其中的重要作用,总结了前人的研究,并提出未来展望,但对于各器官之间相互作用对骨代谢的影响并未作相应的介绍和研究,此为文章所欠缺之处,并且可作为未来研究的关注点。
3.4 综述的重要意义 运动医学领域也将对不同项目、不同强度及不同频率运动介导下丘脑改善骨代谢紊乱的研究进行更深入的实验论证,为未来运动科学健骨理念的推广提供更加科学的理论支持,为缓解和改善骨质疏松提供新的靶点。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 未来对运动介导下丘脑改善骨代谢的研究仍需做更深入的机制和相关分子的探讨,且相关器官和组织之间的相关关系可作为课题组的未来研究方向。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程

文题释义:
骨代谢:作为骨组织的正常生理性代谢,主要包括成骨细胞、破骨细胞和骨细胞的代谢,3者的功能活性和代谢平衡均直接影响骨质和骨量,病理性骨代谢常会形成动态平衡紊乱,进而导致出现骨质疏松。
“脑-骨”串联:人体各组织和器官中常存在着交互作用,进而影响机体的正常生理代谢,“脑-骨”之间存在的串联关系在运动改善骨代谢中发挥了重要作用。
该研究基于“脑-骨”串联对运动介导下丘脑改善骨代谢的机制进行综述,通过对器官间相互作用进而影响骨代谢的研究。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||