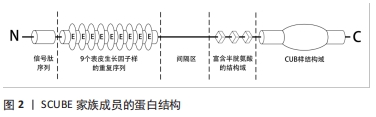
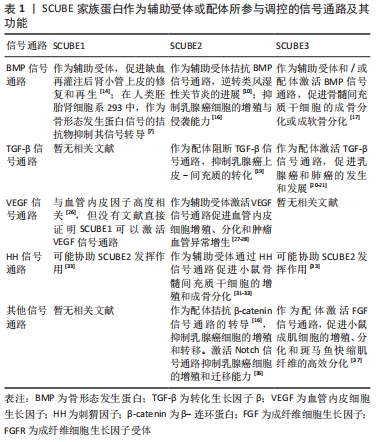
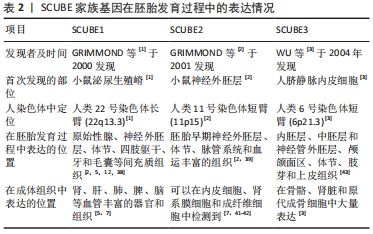
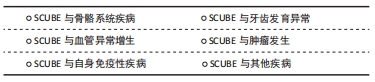
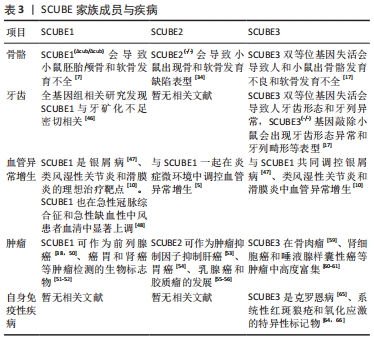
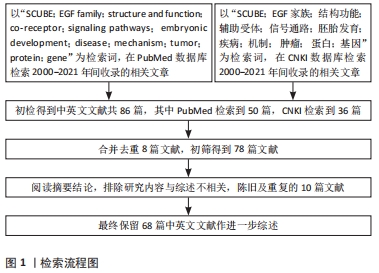
[1] GRIMMOND S, LARDER R, VAN HATEREN N, et al. Cloning, mapping, and expression analysis of a gene encoding a novel mammalian EGF-related protein (SCUBE1). Genomics. 2000;70(1):74-81.
[2] GRIMMOND S, LARDER R, VAN HATEREN N, et al. Expression of a novel mammalian epidermal growth factor-related gene during mouse neural development. Mech Dev. 2001;102(1-2):209-211.
[3] WU BT, SU YH, TSAI MT, et al. A novel secreted, cell-surface glycoprotein containing multiple epidermal growth factor-like repeats and one CUB domain is highly expressed in primary osteoblasts and bones. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(36):37485-37490.
[4] SABBAH DA, HAJJO R, SWEIDAN K. Review on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Structure, Signaling Pathways, Interactions, and Recent Updates of EGFR Inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(10):815-834.
[5] YANG RB, NG CK, WASSERMAN SM, et al. Identification of a novel family of cell-surface proteins expressed in human vascular endothelium. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(48):46364-46373.
[6] ZENG F, HARRIS RC. Epidermal growth factor, from gene organization to bedside. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014;28:2-11.
[7] TU CF, YAN YT, WU SY, et al. Domain and functional analysis of a novel platelet-endothelial cell surface protein, SCUBE1. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283(18):12478-12488.
[8] TU CF, SU YH, HUANG YN, et al. Localization and characterization of a novel secreted protein SCUBE1 in human platelets. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;71(3):486-495.
[9] FUCHS H, SABRAUTZKI S, PREZMECK GK, et al. The First Scube3 Mutant Mouse Line with Pleiotropic Phenotypic Alterations. G3 (Bethesda). 2016;6(12):4035-4046.
[10] YANG M, GUO M, HU Y, et al. Scube regulates synovial angiogenesis-related signaling. Med Hypotheses. 2013;81(5):948-953.
[11] TSAI MT, CHENG CJ, LIN YC, et al. Isolation and characterization of a secreted, cell-surface glycoprotein SCUBE2 from humans. Biochem J. 2009;422(1):119-128.
[12] XAVIER GM, SHARPE PT, COBOURNE MT. Scube1 is expressed during facial development in the mouse. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2009; 312B(5):518-524.
[13] GILLMAN CE, JAYASURIYA AC. FDA-approved bone grafts and bone graft substitute devices in bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;130:112466.
[14] LIAO WJ, LIN H, CHENG CF, et al. SCUBE1-enhanced bone morphogenetic protein signaling protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865(2): 329-338.
[15] TSAO KC, TU CF, LEE SJ, et al. Zebrafish scube1 (signal peptide-CUB (complement protein C1r/C1s, Uegf, and Bmp1)-EGF (epidermal growth factor) domain-containing protein 1) is involved in primitive hematopoiesis. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(7):5017-5026.
[16] LIN YC, CHEN CC, CHENG CJ, et al. Domain and functional analysis of a novel breast tumor suppressor protein, SCUBE2. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(30):27039-27047.
[17] LIN YC, NICETA M, MUTO V, et al. SCUBE3 loss-of-function causes a recognizable recessive developmental disorder due to defective bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Am J Hum Genet. 2021;108(1):115-133.
[18] ZOU ML, CHEN ZH, TENG YY, et al. The Smad Dependent TGF-beta and BMP Signaling Pathway in Bone Remodeling and Therapies. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:593310.
[19] LIN YC, LEE YC, LI LH, et al. Tumor suppressor SCUBE2 inhibits breast-cancer cell migration and invasion through the reversal of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Sci. 2014;127(Pt 1):85-100.
[20] YANG X, HU J, SHI C, et al. Activation of TGF-beta1 Pathway by SCUBE3 Regulates TWIST1 Expression and Promotes Breast Cancer Progression. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020;35(2):120-128.
[21] WU YY, PECK K, CHANG YL, et al. SCUBE3 is an endogenous TGF-beta receptor ligand and regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. Oncogene. 2011;30(34):3682-3693.
[22] ZHAO C, QIN Q, WANG Q, et al. SCUBE3 overexpression predicts poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Biosci Trends. 2013;7(6):264-269.
[23] YANG HY, CHENG CF, DJOKO B, et al. Transgenic overexpression of the secreted, extracellular EGF-CUB domain-containing protein SCUBE3 induces cardiac hypertrophy in mice. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;75(1):139-147.
[24] KAUFMAN NEM, DHINGRA S, JOIS SD, et al. Molecular Targeting of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor (VEGFR). Molecules. 2021;26(4):1076.
[25] TSAO KC, LIN YC, CHEN YT, et al. Zebrafish scube1 and scube2 cooperate in promoting Vegfa signaling during embryonic vascularization. Cardiovasc Res. 2021:cvab125. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab125.
[26] FAVRE CJ, MANCUSO M, MAAS K, et al. Expression of genes involved in vascular development and angiogenesis in endothelial cells of adult lung. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;285(5):H1917-H1938.
[27] LIN YC, CHAO TY, YEH CT, et al. Endothelial SCUBE2 Interacts With VEGFR2 and Regulates VEGF-Induced Angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017;37(1):144-155.
[28] LIN YC, LIU CY, KANNAGI R, et al. Inhibition of Endothelial SCUBE2 (Signal Peptide-CUB-EGF Domain-Containing Protein 2), a Novel VEGFR2 (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2) Coreceptor, Suppresses Tumor Angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018; 38(5):1202-1215.
[29] SKODA AM, SIMOVIC D, KARIN V, et al. The role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: A comprehensive review. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2018;18(1):8-20.
[30] LEE RT, ZHAO Z, INGHAM PW. Hedgehog signalling. Development. 2016;143(3):367-372.
[31] WOODS IG, TALBOT WS. The you gene encodes an EGF-CUB protein essential for Hedgehog signaling in zebrafish. PLoS Biol. 2005;3(3):e66.
[32] JAKOBS P, EXNER S, SCHURMANN S, et al. Scube2 enhances proteolytic Shh processing from the surface of Shh-producing cells. J Cell Sci. 2014; 127(Pt 8):1726-1737.
[33] JOHNSON JL, HALL TE, DYSON JM, et al. Scube activity is necessary for Hedgehog signal transduction in vivo. Dev Biol. 2012;368(2):193-202.
[34] LIN YC, ROFFLER SR, YAN YT, et al. Disruption of Scube2 Impairs Endochondral Bone Formation. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(7): 1255-1267.
[35] CREANGA A, GLENN TD, MANN RK, et al. Scube/You activity mediates release of dually lipid-modified Hedgehog signal in soluble form. Genes Dev. 2012;26(12):1312-1325.
[36] CHEN JH, KUO KT, BAMODU OA, et al. Upregulated SCUBE2 expression in breast cancer stem cells enhances triple negative breast cancer aggression through modulation of notch signaling and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Exp Cell Res. 2018;370(2):444-453.
[37] TU CF, TSAO KC, LEE SJ, et al. SCUBE3 (signal peptide-CUB-EGF domain-containing protein 3) modulates fibroblast growth factor signaling during fast muscle development. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(27):18928-18942.
[38] VANPOUCKE G, ORR B, GRACE OC, et al. Transcriptional profiling of inductive mesenchyme to identify molecules involved in prostate development and disease. Genome Biol. 2007;8(10):R213.
[39] HOLLWAY GE, MAULE J, GAUTIER P, et al. Scube2 mediates Hedgehog signalling in the zebrafish embryo. Dev Biol. 2006;294(1):104-118.
[40] XAVIER GM, ECONOMOU A, SENNA GUIMARÃES AL, et al. Characterization of a mouse Scube3 reporter line. Genesis. 2010; 48(12):684-692.
[41] CHENG CJ, LIN YC, TSAI MT, et al. SCUBE2 suppresses breast tumor cell proliferation and confers a favorable prognosis in invasive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69(8):3634-3641.
[42] SONG Q, LI C, FENG X, et al. Decreased expression of SCUBE2 is associated with progression and prognosis in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2015;33(4):1956-1964.
[43] HAWORTH K, SMITH F, ZOUPA M, et al. Expression of the Scube3 epidermal growth factor-related gene during early embryonic development in the mouse. Gene Expr Patterns. 2007;7(5):630-634.
[44] WANG L, ZHANG L, YAN H, et al. Genome-wide association studies identify the loci for 5 exterior traits in a Large White × Minzhu pig population. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e103766.
[45] XAVIER GM, PANOUSOPOULOS L, COBOURNE MT. Scube3 is expressed in multiple tissues during development but is dispensable for embryonic survival in the mouse. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55274.
[46] KUHNISCH J, THIERING E, HEITMULLER D, et al. Genome-wide association study (GWAS) for molar-incisor hypomineralization (MIH). Clin Oral Investig. 2014;18(2):677-682.
[47] CAPKIN AA, DEMIR S, MENTESE A, et al. Can signal peptide-CUB-EGF domain-containing protein (SCUBE) levels be a marker of angiogenesis in patients with psoriasis? Arch Dermatol Res. 2017;309(3):203-207.
[48] DAI DF, THAJEB P, TU CF, et al. Plasma concentration of SCUBE1, a novel platelet protein, is elevated in patients with acute coronary syndrome and ischemic stroke. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51(22):2173-2180.
[49] ZHUANG J, DEANE JA, YANG RB, et al. SCUBE1, a novel developmental gene involved in renal regeneration and repair. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25(5):1421-1428.
[50] ORR B, GRACE OC, BROWN P, et al. Reduction of pro-tumorigenic activity of human prostate cancer-associated fibroblasts using Dlk1 or SCUBE1. Dis Model Mech. 2013;6(2):530-536.
[51] MENTESE A, FIDAN E, SUMER AU, et al. Is SCUBE 1 a new biomarker for gastric cancer? Cancer Biomark. 2012;11(5):191-195.
[52] KARAGUZEL E, MENTESE A, KAZAZ IO, et al. SCUBE1: a promising biomarker in renal cell cancer. Int Braz J Urol. 2017;43(4):638-643.
[53] ZHEN L, NING G, WU L, et al. Prognostic value of aberrantly expressed methylation genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(10):BSR20192593.
[54] WANG X, ZHONG RY, XIANG XJ. Reduced expression of SCUBE2 predicts poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018;11(2):972-980.
[55] FEI H, CHEN S, XU C. RNA-sequencing and microarray data mining revealing: the aberrantly expressed mRNAs were related with a poor outcome in the triple negative breast cancer patients. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(6):363.
[56] GUO E, LIU H, LIU X. Overexpression of SCUBE2 Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Glioma Cells. Oncol Res. 2017;25(3):437-444.
[57] SHENG J, SHI W, GUO H, et al. The Inhibitory Effect of (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on Breast Cancer Progression via Reducing SCUBE2 Methylation and DNMT Activity. Molecules. 2019; 24(16):2899.
[58] YANG B, MIAO S, LI Y. SCUBE2 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of human non-small cell lung cancer cells through regulation of the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Gene. 2018;672:143-149.
[59] LIANG W, YANG C, PENG J, et al. The Expression of HSPD1, SCUBE3, CXCL14 and Its Relations with the Prognosis in Osteosarcoma. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015;73(3):763-768.
[60] JOOSTEN SC, ODEH SNO, KOCH A, et al. Development of a prognostic risk model for clear cell renal cell carcinoma by systematic evaluation of DNA methylation markers. Clin Epigenetics. 2021;13(1):103.
[61] HAN N, LU H, ZHANG Z, et al. Comprehensive and in-depth analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression profile in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Gene. 2018;678:349-360.
[62] XUE YY, LU YY, SUN GQ, et al. CN-3 induces mitochondrial apoptosis in glioma via Ros-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway. Pharmazie. 2021;76(5): 208-214.
[63] 骆傲然.SCUBE3通过TGF β信号通路促进肝癌细胞增殖的分子机制研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2019.
[64] QI YY, ZHAO YF, ZHAI YL, et al. SCUBE3 Is Likely a Susceptibility Gene for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus for Chinese Populations. J Immunol Res. 2020;2020:8897936.
[65] CARVALHO AY, BISHOP KS, HAN DY, et al. The role of Vitamin D level and related single nucleotide polymorphisms in Crohn’s disease. Nutrients. 2013;5(10):3898-3909.
[66] LIU R, LIU J, ZHAO G, et al. Relevance of the intestinal health-related pathways to broiler residual feed intake revealed by duodenal transcriptome profiling. Poult Sci. 2019;98(3):1102-1110.
[67] KAWAKAMI A, NOJIMA Y, TOYODA A, et al. The zebrafish-secreted matrix protein you/scube2 is implicated in long-range regulation of hedgehog signaling. Curr Biol. 2005;15(5):480-488.
[68] ULUSOY S, OZKAN G, MENTESE A, et al. Signal peptide-CUB-EGF domain-containing protein 1 (SCUBE1) level in hemodialysis patients and parameters affecting that level. Clin Biochem. 2012;45(16-17): 1444-1449.
|