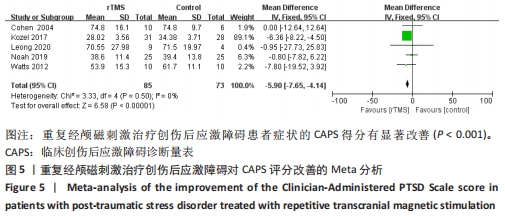
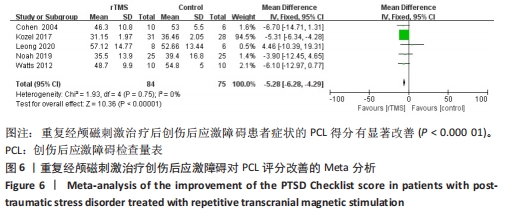
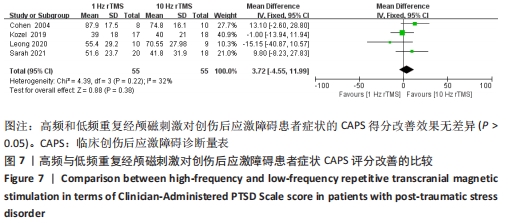
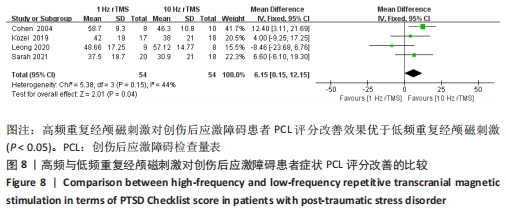
[1] American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013:271-272.
[2] BENJET C, BROMET E, KARAM EG, et al. The epidemiology of traumatic event exposure worldwide: results from the World Mental Health Survey Consortium. Psychol Med. 2016;46(2):327-343.
[3] KOENEN KC, RATANATHARATHORN A, NG L, et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder in the World Mental Health Surveys. Psychol Med. 2017;47:2260-2274.
[4] HUANG Y, WANG Y, WANG H, et al. Prevalence of mental disorders in China: a cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry. 2019;6:211-224.
[5] BERLIM MT, VAN DEN EYNDE F, TOVAR-PERDOMO S, et al. Response, remission and drop-out rates following high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for treating major depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind and sham-controlled trials. Psychol Med. 2014;44(2):225-239.
[6] SLOTEMA CW, ALEMAN A, DASKALAKIS ZJ, et al. Meta-analysis of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the treatment of auditory verbal hallucinations: Update and effects after one month. Schizophr Res. 2012;142(1-3):40-45.
[7] MCCANN UD, KIMBRELL TA, MORGAN CM, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55(3):276-279.
[8] LEFAUCHEUR JP, ALEMAN A, BAEKEN C , et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): An update (2014–2018). Clin Neurophysiol. 2020;131(2):474-528.
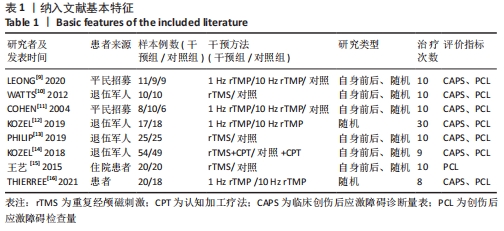
[9] LEONG K, CHAN P, ONG L, et al. A Randomized Sham-controlled Trial of 1-Hz and 10-Hz Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) of the Right Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Civilian Post-traumatic Stress Disorder. Can J Psychiatry. 2020;65(11):770-778.
[10] WATTS BV, LANDON B, GROFT A, et al. A sham controlled study of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for posttraumatic stress disorder. Brain Stimul. 2012;5(1):38-43.
[11] COHEN H, KAPLAN Z, KOTLER M, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in posttraumatic stress disorder: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161(3):515-524.
[12] KOZEL FA, VAN TREES K, LARSON V, et al. One hertz versus ten hertz repetitive TMS treatment of PTSD: A randomized clinical trial. Psychiatry Res. 2019;273:153-162.
[13] PHILIP NS, BARREDO J, AIKEN E, et al. Theta-Burst Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(11):939-948.
[14] KOZEL FA, MOTES MA, DIDEHBANI N, et al. Repetitive TMS to augment cognitive processing therapy in combat veterans of recent conflicts with PTSD: A randomized clinical trial. J Affect Disord. 2018;229:506-514.
[15] 王艺,彭李,周贤丽,等. rTMS对创伤后康复期PTSD患者核心症状、正负性情绪和心理弹性的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2015,37(15):1571-1575.
[16] THIERRÉE S, RAULIN-BRIOT M, LEGRAND M, et al. Combining Trauma Script Exposure With r TMS to Reduce Symptoms of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: Randomized Controlled Trial. Neuromodulation. 2021. doi: 10.1111/ner.13505.
[17] MCGIRR A, FREDERIQUE V, TOVAR-PERDOMO S, et al. Effectiveness and acceptability of accelerated repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for treatment-resistant major depressive disorder: An open label trial. J Affect Disord. 2015;173:216-220.
[18] PIGOT M, LOO C, SACHDEV P. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation as treatment for anxiety disorders. Expert Rev Neurother. 2008; 8(10):1449-1455.
[19] NARDONE R, SEBASTIANELLI L, VERSACE V, et al. Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in subjects with sleep disorders. Sleep Med. 2020;71:113-121.
[20] 任萌,单春雷.重复性经颅磁刺激对脑卒中后抑郁的作用及其机制的研究进展[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2020,42(4):5.
[21] 徐丹,田峻,陈晨,等.低频重复经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中后失眠的疗效[J].中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志,2021,28(1):4.
[22] TAZOE T, PEREZ MA. Effects of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Recovery of Function After Spinal Cord Injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;96(4):145-155.
[23] O’CONNELL NE, MARSTON L, SPENCER S, et al. Non-invasive brain stimulation techniques for chronic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018; 4(4):CD008208.
[24] DAN JS, SEEDAT S, IVERSEN A, et al. Post-traumatic stress disorder: medicine and politics. Lancet. 2007;369(9556):139-144.
[25] BRUNELLO N, DAVIDSON J, DEAHL M, et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder: diagnosis and epidemiology, comorbidity and social consequences, biology and treatment. Neuropsychobiology. 2001;43(3):150-162.
[26] Ipser JC, Stein DJ. Evidence-based pharmacotherapy of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology(6):825.
[27] YAN T, XIE Q, ZHENG Z, et al. Different frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Psychiatr Res. 2017;89:125-135.
[28] GRISARU N, AMIR M, COHEN H, et al. Effect of transcranial magnetic stimulation in posttraumatic stress disorder: a preliminary study. Biol Psychiatry. 1998;44(1):52-55.
[29] BERLIM MT, VAN DEN EYNDE F. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex for treating posttraumatic stress disorder: an exploratory meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind and sham-controlled trials. Can J Psychiatry. 2014; 59(9):487-496.
|