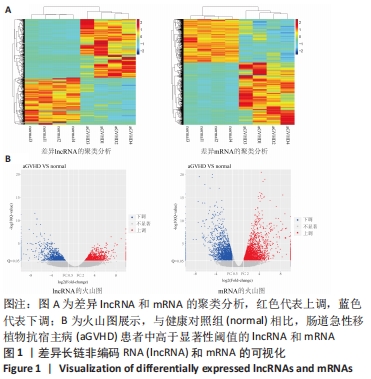
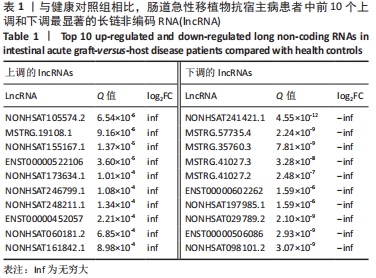
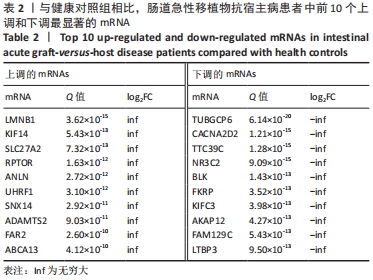
[1] BLAZAR BR, MURPHY WJ, ABEDI M. Advances in graft-versus-host disease biology and therapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12(6):443-458.
[2] MARKEY KA, MACDONALD KP, HILL GR. The biology of graft-versus-host disease: experimental systems instructing clinical practice. Blood. 2014;124(3):354-362.
[3] SHLOMCHIK WD. Graft-versus-host disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007; 7(5):340-352.
[4] FERRARA JL, LEVINE JE, REDDY P, et al. Graft-versus-host disease. Lancet. 2009;373(9674):1550-1561.
[5] FANG H, BONORA G, LEWANDOWSKI JP, et al. Trans- and cis-acting effects of Firre on epigenetic features of the inactive X chromosome. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):6053.
[6] NIE J, ZHAO Q. Lnc-ITSN1-2, Derived From RNA Sequencing, Correlates With Increased Disease Risk, Activity and Promotes CD4+ T Cell Activation, Proliferation and Th1/Th17 Cell Differentiation by Serving as a ceRNA for IL-23R via Sponging miR-125a in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front Immunol. 2020;11:852.
[7] RANZANI V, ROSSETTI G, PANZERI I, et al. The long intergenic noncoding RNA landscape of human lymphocytes highlights the regulation of T cell differentiation by linc-MAF-4. Nat Immunol. 2015;16(3):318-325.
[8] XIA M, LIU J, LIU S, et al. Ash1l and lnc-Smad3 coordinate Smad3 locus accessibility to modulate iTreg polarization and T cell autoimmunity. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15818.
[9] TANAKA J, IMAMURA M, KASAI M, et al. Cytokine gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells during graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol. 1993; 85(3):558-565.
[10] SCHMALTZ C, ALPDOGAN O, HORNDASCH KJ, et al. Differential use of Fas ligand and perforin cytotoxic pathways by donor T cells in graft-versus-host disease and graft-versus-leukemia effect. Blood. 2001; 97(9):2886-2895.
[11] CHANDRASEKAR B, VEMULA K, SURABHI RM, et al. Activation of intrinsic and extrinsic proapoptotic signaling pathways in interleukin-18-mediated human cardiac endothelial cell death. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279(19):20221-20233.
[12] LUO M, YERUVA S, LIU Y, et al. IL-1beta-Induced Downregulation of the Multifunctional PDZ Adaptor PDZK1 Is Attenuated by ERK Inhibition, RXRalpha, or PPARalpha Stimulation in Enterocytes. Front Physiol. 2017;8:61.
[13] SABZEVARY-GHAHFAROKHI M, SOLTANI A, LUZZA F, et al. The protective effects of resveratrol on ulcerative colitis via changing the profile of Nrf2 and IL-1β protein. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(9):6941-6947.
[14] PARK MJ, MOON SJ, LEE SH, et al. Blocking activator protein 1 activity in donor cells reduces severity of acute graft-versus-host disease through reciprocal regulation of IL-17-producing T cells/regulatory T cells. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20(8):1112-1120.
[15] MORIYAMA I, ISHIHARA S, RUMI MA, et al. Decoy oligodeoxynucleotide targeting activator protein-1 (AP-1) attenuates intestinal inflammation in murine experimental colitis. Lab Invest. 2008;88(6):652-663.
[16] DING L, NING HM, LI PL, et al. Tumor necrosis factor α in aGVHD patients contributed to the impairment of recipient bone marrow MSC stemness and deficiency of their hematopoiesis-promotion capacity. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):119.
[17] LIN Y, HU X, CHENG H, et al. Graft-versus-host disease causes broad suppression of hematopoietic primitive cells and blocks megakaryocyte differentiation in a murine model. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014; 20(9):1290-1300.
[18] DING Q, WANG Y, ZHANG AL, et al. ZEB2 Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammation by the NF-κB Pathway in HK-2 Cells. Inflammation. 2018; 41(2):722-731.
[19] BUSS H, HANDSCHICK K, JURRMANN N, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 phosphorylates NF-κB P65 at serine 536 and contributes to the regulation of inflammatory gene expression. PLoS One. 2012;7(12): e51847.
[20] CHEN L, CHEN Z, BAKER K, et al. The short isoform of the CEACAM1 receptor in intestinal T cells regulates mucosal immunity and homeostasis via Tfh cell induction. Immunity. 2012;37(5):930-946.
[21] HORST AK, WEGSCHEID C, SCHAEFERS C, et al. Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 controls IL-2-dependent regulatory T-cell induction in immune-mediated hepatitis in mice. Hepatology. 2018;68(1):200-214.
[22] IIJIMA H, NEURATH MF, NAGAISHI T, et al. Specific regulation of T helper cell 1-mediated murine colitis by CEACAM1. J Exp Med. 2004; 199(4):471-482.
[23] STENGEL ST, FAZIO A, LIPINSKI S, et al. Activating Transcription Factor 6 Mediates Inflammatory Signals in Intestinal Epithelial Cells Upon Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(4): 1357-1374.e10.
[24] XU YJ, CHEN FP, CHEN Y, et al. A Possible Reason to Induce Acute Graft-vs.-Host Disease After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Lack of Sirtuin-1 in CD4+ T Cells. Front Immunol. 2018;9:3078.
[25] WAICKMAN AT, POWELL JD. Mammalian target of rapamycin integrates diverse inputs to guide the outcome of antigen recognition in T cells. J Immunol. 2012;188(10):4721-4729.
[26] WU LX, LA ROSE J, CHEN L, et al. CD28 regulates the translation of Bcl-xL via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. J Immunol. 2005;174(1):180-194.
[27] DELGOFFE GM, POLLIZZI KN, WAICKMAN AT, et al. The kinase mTOR regulates the differentiation of helper T cells through the selective activation of signaling by mTORC1 and mTORC2. Nat Immunol. 2011; 12(4):295-303.
[28] LEE K, GUDAPATI P, DRAGOVIC S, et al. Mammalian target of rapamycin protein complex 2 regulates differentiation of Th1 and Th2 cell subsets via distinct signaling pathways. Immunity. 2010;32(6):743-753.
[29] SHAO J, EVERS BM, SHENG H. Roles of phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin/p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase in K-Ras-mediated transformation of intestinal epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64(1):229-235.
[30] WANG Q, ZHOU Y, JACKSON LN, et al. Nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) signaling regulates PTEN expression and intestinal cell differentiation. Mol Biol Cell. 2011;22(3):412-420.
[31] ZHOU Y, WANG Q, GUO Z, et al. Nuclear factor of activated T-cell c3 inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling through induction of regulated in development and DNA damage response 1 in human intestinal cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2012;23(15):2963-2972.
[32] WANG Q, ZHOU Y, RYCHAHOU P, et al. NFAT5 represses canonical Wnt signaling via inhibition of β-catenin acetylation and participates in regulating intestinal cell differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4(6):e671.
[33] ZHANG Y, SANDY AR, WANG J, et al. Notch signaling is a critical regulator of allogeneic CD4+ T-cell responses mediating graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2011;117(1):299-308.
[34] TRAN IT, SANDY AR, CARULLI AJ, et al. Blockade of individual Notch ligands and receptors controls graft-versus-host disease. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(4):1590-1604.
[35] LUO X, XU L, LI Y, et al. Notch pathway plays a novel and critical role in regulating responses of T and antigen-presenting cells in aGVHD. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2017;33(2):169-181.
[36] KOBIA FM, PREUSSE K, DAI Q, et al. Notch dimerization and gene dosage are important for normal heart development, intestinal stem cell maintenance, and splenic marginal zone B-cell homeostasis during mite infestation. PLoS Biol. 2020;18(10):e3000850.
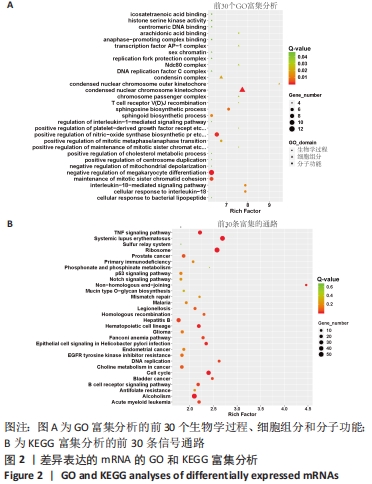
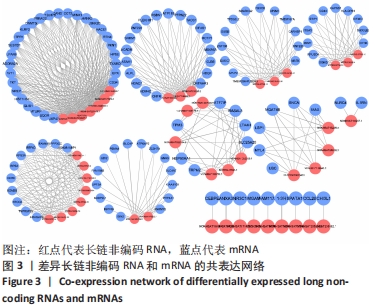
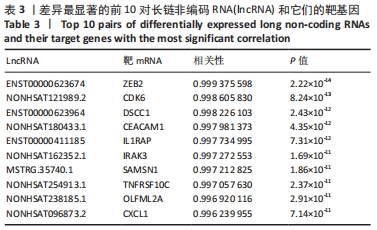
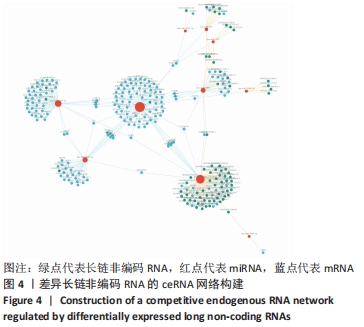
|