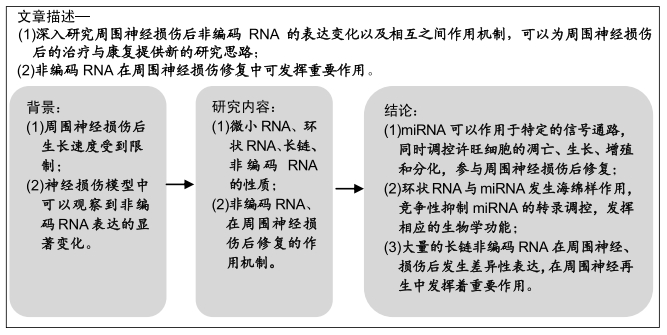
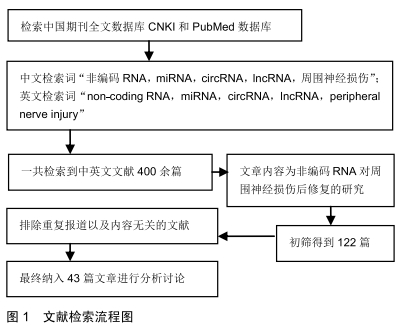
[1] GU X, DING F, YANG Y, et al. Construction of tissue engineered nerve grafts and their application in peripheral nerve regeneration. Prog Neurobiol. 2011;93(2):204-230.
[2] TIAN L, PRABHAKARAN MP, RAMAKRISHNA S. Strategies for regeneration of components of nervous system: scaffolds, cells and biomolecules. Regen Biomater. 2015;2(1):31-45.
[3] GIORGIO T, ANDREW H, MIKAEL W. The nerve injury and the dying neurons: diagnosis and prevention.J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2011;36(9):730-734.
[4] ALLODI I, UDINA E, NAVARRO X. Specificity of peripheral nerve regeneration: interactions at the axon level. Prog Neurobiol. 2012; 98(1):16-37.
[5] ENGLISH AW, WILHELM JC, SABATIER MJ. Enhancing recovery from peripheral nerve injury using treadmill training. Ann Anat. 2011;193(4):354-361.
[6] DEUMENS R, BOZKURT A, MEEK MF, et al. Repairing injured peripheral nerves: Bridging the gap.Prog Neurobiol. 2010;92(3): 245-276.
[7] HOUSCHYAR KS, MOMENI A, PYLES MN, et al. The Role of Current Techniques and Concepts in Peripheral Nerve Repair. Plast Surg Int. 2016;2016:4175293.
[8] ZHIPENG L, A GREGORY M. Vicinal: a method for the determination of ncRNA ends using chimeric reads from RNA-seq experiments.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(9):e79.
[9] BHALALA OG, SRIKANTH M, KESSLER JA. The emerging roles of microRNAs in CNS injuries. Nature Reviews Neurology, 2013; 9(6): 328-339.
[10] BARTEL DP, CHEN CZ. Micromanagers of gene expression: the potentially widespread influence of metazoan microRNAs. Nature Reviews Genetics.2004; 5(5): 396-400.
[11] ZHOU S, ZHANG S, WANG Y, et al. MiR-21 and miR-222 inhibit apoptosis of adult dorsal root ganglion neurons by repressing TIMP3 following sciatic nerve injury. Neuroscience Letters.2015;586(14):43-49.
[12] MENDOZA-VIVEROS L,CHIANG CK,JLK O,et al.miR-132/212 Modulates Seasonal Adaptation and Dendritic Morphology of the Central Circadian Clock. Cell Reports.2017; 19(3): 505-520.
[13] HANCOCK ML, NICOLAS P, JIE Q, et al. MicroRNA-132 is enriched in developing axons, locally regulates Rasa1 mRNA, and promotes axon extension.J Neurosci. 2014;34(1):66-78.
[14] ZHANG HY, ZHENG SJ, ZHAO JH, et al. MicroRNAs 144, 145, and 214 are down-regulated in primary neurons responding to sciatic nerve transection.Brain Res. 2011;1383:62-70.
[15] CHRISTIE KJ, WEBBER CA, MARTINEZ JA, et al. PTEN inhibition to facilitate intrinsic regenerative outgrowth of adult peripheral axons.J Neurosci. 2010;30(27):9306-9315.
[16] BOERBOOM A, DION V, CHARIOT A, et al. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Schwann Cell Plasticity.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:38.
[17] ANDREU V, LI-WEI C, TIMOTHY F, et al. MicroRNAs modulate Schwann cell response to nerve injury by reinforcing transcriptional silencing of dedifferentiation-related genes.J Neurosci. 2011;31(48):17358-17369.
[18] BIN Y, SONGLIN Z, YONGJUN W, et al. miR-221 and miR-222 promote Schwann cell proliferation and migration by targeting LASS2 after sciatic nerve injury.J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 11): 2675-2683.
[19] YAO C, SHI X, ZHANG Z, et al. Hypoxia-Induced Upregulation of miR-132 Promotes Schwann Cell Migration After Sciatic Nerve Injury by Targeting PRKAG3. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(8):5129-39.
[20] KOURI FM, HURLEY LA, DANIEL WL, et al. miR-182 integrates apoptosis, growth, and differentiation programs in glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 2015 ;29(7):732-745.
[21] SONGLIN Z, RONG G, WEN H, et al. MiR-9 inhibits Schwann cell migration by targeting Cthrc1 following sciatic nerve injury. J Cell Sci. 2014;127(Pt 5):967-976.
[22] LI WY, ZHANG WT, CHENG YX, et al. Inhibition of KLF7-Targeting Micro RNA 146b Promotes Sciatic Nerve Regeneration. Neurosci Bull. 2018;34(3):419-437.
[23] QIAN T, WANG X, WANG Y, et al. Novel miR-sc4 regulates the proliferation and migration of Schwann cells by targeting Cdk5r1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018;447(1-2):209-215.
[24] LI S, WANG X, GU Y, et al. Corrigendum to "let-7 microRNAs regenerate peripheral nerve regeneration by targeting nerve growth factor".Mol Ther. 2015;23(4):790.
[25] 程涵蓉,何少茹,吴本清.环状RNA研究的新进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21 (36): 5898-5904.
[26] VENØ MT, HANSEN TB, VENØ ST, et al. Spatio-temporal regulation of circular RNA expression during porcine embryonic brain development.Genome Biol. 2015;16:245.
[27] YAO C, YU B.Role of Long Noncoding RNAs and Circular RNAs in Nerve Regeneration.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019;12:165.
[28] ZHOU ZB, NIU YL, HUANG GX, et al. Silencing of circRNA.2837 Plays a Protective Role in Sciatic Nerve Injury by Sponging the miR-34 Family via Regulating Neuronal Autophagy. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;12:718-729.
[29] MERCER TR, DINGER ME, SUNKIN SM, et al. Specific expssion of long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(2):716-721.
[30] MARCHESE FP, MAITE H. Long non-coding RNAs and chromatin modifiers: their place in the epigenetic code. Epigenetics.2014; 9(1): 21-26.
[31] ROBERTS TC, MORRIS KV, WOOD MJA. The role of long non-coding RNAs in neurodevelopment, brain function and neurological disease.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014; 369(1652). pii: 20130507.
[32] YAO C, WANG J, ZHANG H, et al. Long non-coding RNA uc.217 regulates neurite outgrowth in dorsal root ganglion neurons following peripheral nerve injury.Eur J Neurosci. 2015;42(1): 1718-1725.
[33] MICHAEL C, INNA B, GRIFFIN RS, et al. Multiple chronic pain states are associated with a common amino acid-changing allele in KCNS1. Brain. 2010;133(9):2519-2527.
[34] BIN Y, SONGLIN Z, SHENG Y, et al. The regulatory roles of non-coding RNAs in nerve injury and regeneration.Prog Neurobiol. 2015;134:122-139.
[35] LIU X, YU X, HE Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 promotes the proliferation and migration of Schwann cells by regulating the miR-34a/Satb1 axis. J Cell Physiol. 2019 Feb 12.
[36] YAO C, WANG Y, ZHANG H, et al. lncRNA TNXA-PS1 Modulates Schwann Cells by Functioning As a Competing Endogenous RNA Following Nerve Injury. J Neurosci. 2018;38(29):6574-6585.
[37] WANG H, WU J, ZHANG X, et al. Microarray analysis of the expression profile of lncRNAs reveals the key role of lncRNA BC088327 as an agonist to heregulin‑1β‑induced cell proliferation in peripheral nerve injury. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(6): 3477-3484.
[38] FONTANA X, HRISTOVA M, COSTA CD, et al. c-Jun in Schwann cells promotes axonal regeneration and motoneuron survival via paracrine signaling. J Cell Biol. 2012;198(1):127-141.
[39] CHRISTINE W, DOUGLAS Z. The nerve regenerative microenvironment: early behavior and partnership of axons and Schwann cells. Experimental Neurology.2010; 223(1): 51-59.
[40] GLENN TD, TALBOT WS. Signals regulating myelination in peripheral nerves and the Schwann cell response to injury. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013;23(6):1041-1048.
[41] ALLODI I, MECOLLARI V, GONZÁLEZ‐PÉREZ F, et al. Schwann cells transduced with a lentiviral vector encoding Fgf-2 promote motor neuron regeneration following sciatic nerve injury. Glia.2015; 62(10): 1736-1746.
[42] ATANASOSKI S, BOENTERT M, VENTURA LD, et al. Postnatal Schwann cell proliferation but not myelination is strictly and uniquely dependent on cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (cdk4).Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008;37(3):519-527.
[43] PAN B, SHI ZJ, YAN JY, et al. Long non-coding RNA NONMMUG014387 promotes Schwann cell proliferation after peripheral nerve injury.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(12): 2084-2091.
|