中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (17): 2720-2725.doi: 10.12307/2022.541
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
sirtinol与地塞米松对哮喘模型小鼠体内沉默信息调节蛋白1和白细胞介素5水平的影响
罗秋锐1, 宋小琴2,王荣丽1
- 1西南医科大学附属医院呼吸与危重症医学科,四川省泸州市 646000;2重庆市渝北区人民医院呼吸内科,重庆市 401120
Effects of sirtinol versus dexamethasone on the levels of recombinant sirtuin 1 and interleukin-5 in asthmatic mice
Luo Qiurui1, Song Xiaoqin2, Wang Rongli1
- 1Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Respiratory, Chongqing Yubei District People’s Hospital, Chongqing 401120, China
摘要:
文题释义:
沉默信息调节蛋白1:是哺乳动物中第一个被发现的Sirtuins家族成员,目前研究最为深入,在代谢、炎症、细胞增殖、分化、凋亡以及基因转录的调控等方面发挥着重要的作用。
白细胞介素5:是哮喘的主要调节因子,对哮喘的发展进程起到关键的作用,能促进嗜酸性粒细胞募集、趋化、活化、增殖等,还能使嗜酸性粒细胞脱颗粒,释放具有细胞毒性的嗜酸性粒细胞阳离子,从而诱导嗜酸性粒细胞释放血小板活化因子和白三烯等炎症递质。
背景:哮喘是一种由多种炎性细胞介导的呼吸道慢性炎症性疾病,沉默信息调节蛋白1(recombinant sirtuin 1,SIRT1)与哮喘的发生及气道高反应有着密切的联系。
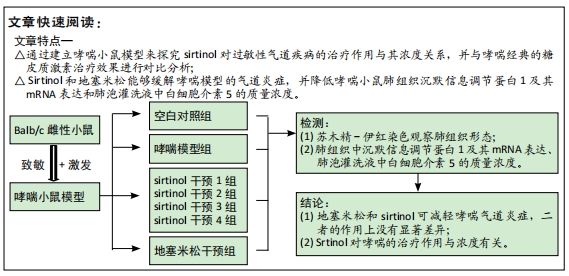
目的:比较不同浓度sirtinol(SIRT1的特异性抑制剂)与地塞米松对哮喘小鼠体内SIRT1基因及白细胞介素5表达水平的影响,为SIRT1在哮喘发病机制和相关治疗中的作用提供理论依据。
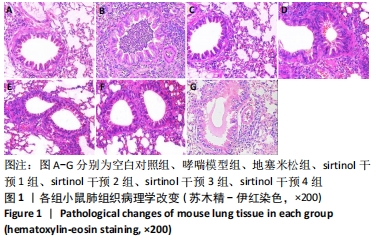
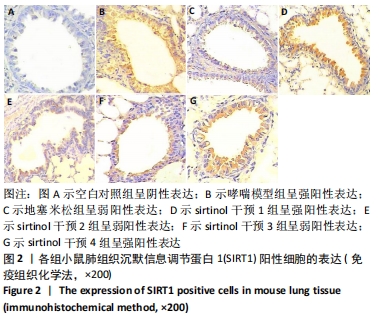
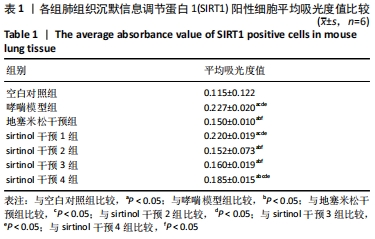
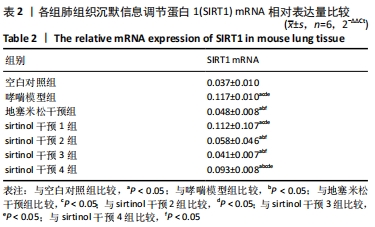
方法:将42只Balb/c雌性小鼠随机分为7组。哮喘模型组、地塞米松干预组、sirtinol干预1,2,3,4组小鼠于第1,8,15天腹腔注射0.2 mL抗原混悬液(鸡卵清蛋白100 μg+氢氧化铝2 mg+生理盐水0.2 mL)致敏,第16天开始鼻腔滴入40 μL 2%鸡卵清蛋白溶液(即鸡卵清蛋白2 g+生理盐水100 mL)连续7 d激发气道高反应制备小鼠哮喘模型,空白对照组以等量生理盐水替代。地塞米松干预组在激发前30 min腹腔注射地塞米松溶液0.2 mL(3 mg/kg),sirtinol干预1,2,3,4组在首次激发前1 h和末次激发后3 h分别腹腔注射0.12 mL sirtinol溶液(sirtinol溶液含量分别为0,0.05,0.5,3.0 mg/kg),其中sirtinol干预1组腹腔注射0.125%的二甲亚砜溶液0.12 mL。于末次激发24 h后麻醉处死小鼠,苏木精-伊红染色观察肺组织形态,Western blotting检测小鼠肺组织中SIRT1的表达,实时荧光定量PCR法检测小鼠肺组织中SIRT1和内参基因(β-actin)的mRNA含量,ELISA法检测肺泡灌洗液中白细胞介素5的质量浓度。
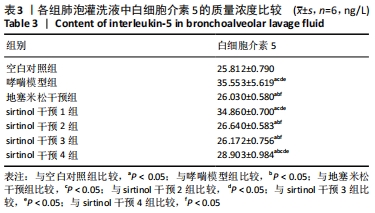
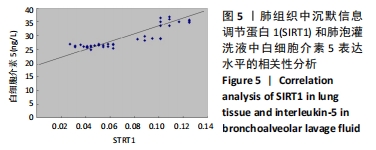
结果与结论:①与哮喘模型组相比,地塞米松干预组炎症减轻,sirtinol干预1组炎症减轻不明显,sirtinol干预2,3,4组炎症减轻程度逐渐降低;②与哮喘模型组相比,地塞米松干预组和sirtinol干预1,2,3,4组的SIRT1的表达下降,其中sirtinol干预2组最弱;③肺组织SIRT1 mRNA在哮喘模型组表达量最高,空白对照组中最低,哮喘模型组比地塞米松干预组、sirtinol干预2,3组的表达量高(P < 0.05),地塞米松干预组、sirtinol干预2,3组组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④空白对照组肺泡灌洗液中白细胞介素5水平最低,哮喘模型组白细胞介素5水平最高,sirtinol干预4组白细胞介素5表达量明显高于sirtinol干预2,3组及地塞米松干预组(P < 0.05),而地塞米松干预组与sirtinol干预2,3组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑤地塞米松和sirtinol均可降低哮喘小鼠体内SIRT1和白细胞介素5的表达水平,减轻气道炎症,二者的作用上没有显著差异,但后者作用与浓度有关。
缩略语:沉默信息调节蛋白1:recombinant sirtuin 1,SIRT1
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5185-6886 (罗秋锐)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: