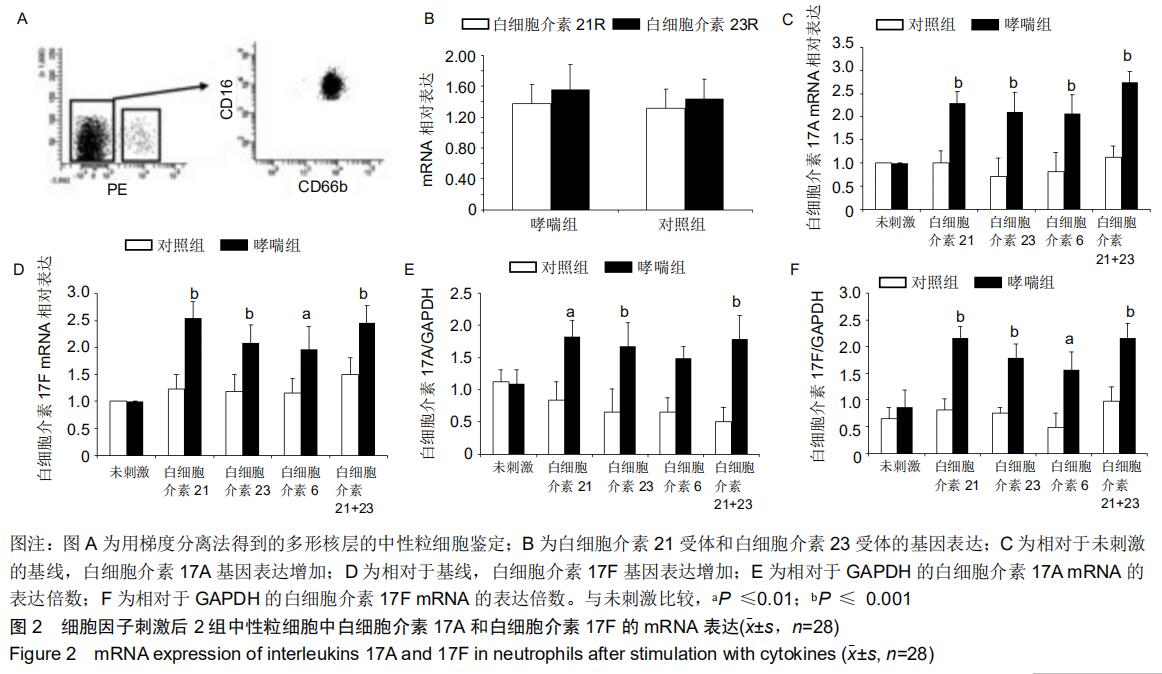
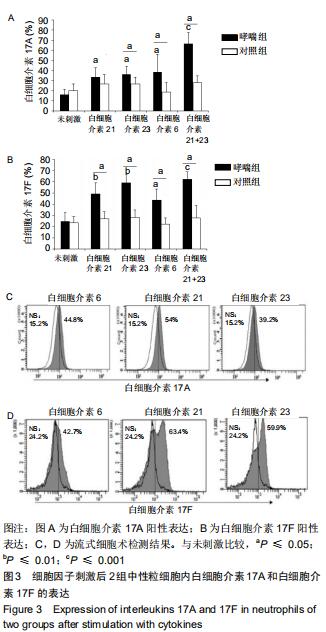
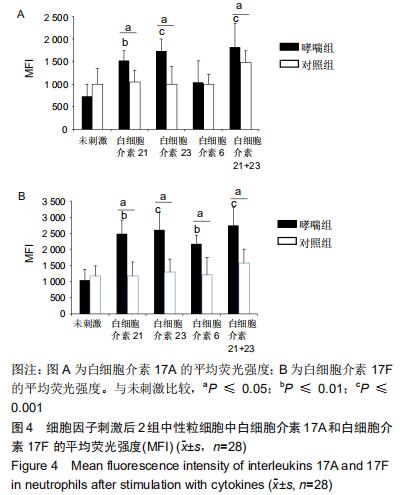
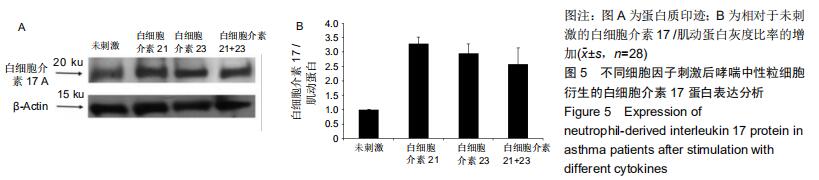
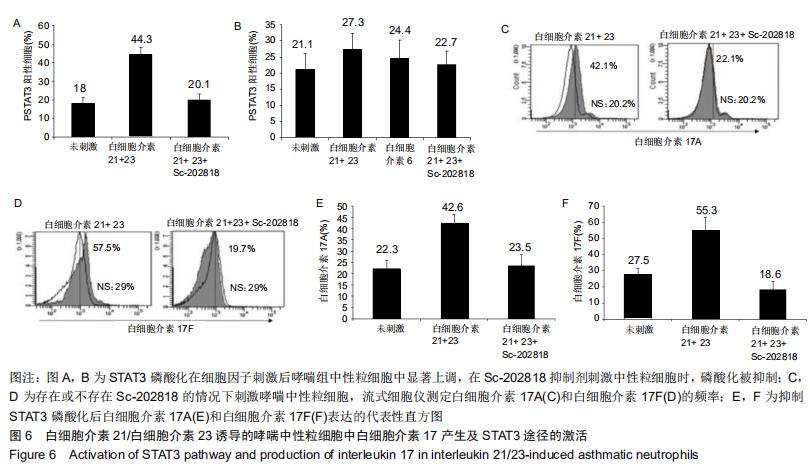
|
[1] MOLET S, HAMID Q, DAVOINE F, et al. IL-17 is increased in asthmatic airways and induces human bronchial fibroblasts to produce cytokines.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108(3): 430-438.
[2] GREEN RH, BRIGHTLING CE, BRADDING P. The reclassification of asthma based on subphenotypes.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;7(1):43-50.
[3] WANG YH, WILLS-KARP M. The potential role of interleukin-17 in severe asthma.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011;11(5):388-394.
[4] WILSON RH, WHITEHEAD GS, NAKANO H, et al. Allergic sensitization through the airway primes Th17-dependent neutrophilia and airway hyperresponsiveness. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180(8):720-730.
[5] HALWANI R, AL-ABRI J, BELAND M, et al. CC and CXC chemokines induce airway smooth muscle proliferation and survival.J Immunol. 2011;186(7):4156-63.
[6] KORN T, BETTELLI E, OUKKA M, et al. IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:485-517.
[7] SADIK CD, KIM ND, LUSTER AD. Neutrophils cascading their way to inflammation.Trends Immunol. 2011;32(10): 452-460.
[8] OTA K, KAWAGUCHI M, MATSUKURA S, et al. Potential involvement of IL-17F in asthma.J Immunol Res. 2014; 2014: 602846.
[9] MORISHIMA N, MIZOGUCHI I, TAKEDA K, et al. TGF-β is necessary for induction of IL-23R and Th17 differentiation by IL-6 and IL-23.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009; 386(1): 105-110.
[10] HABIB T, SENADHEERA S, WEINBERG K, et al. The common γ chain (γc) is a required signaling component of the IL-21 receptor and supports IL-21-induced cell proliferation via JAK3. Biochemistry.2002;41(27): 8725-8731.
[11] ASAO H, OKUYAMA C, KUMAKI S, et al. Cutting edge: the common γ-chain is an indispensable subunit of the IL-21 receptor complex.J Immunol. 2001;167(1):1-5.
[12] BETTELLI E, KORN T, KUCHROO VK. Th17: the third member of the effector T cell trilogy.Curr Opin Immunol. 2007;19(6): 652-657.
[13] MUKHERJEE S, ALLEN RM, LUKACS NW, et al. STAT3 mediated IL-17 production by post-septic T cells exacerbates viral immunopathology of the lung.Shock (Augusta, Ga.). 2012;38(5):515.
[14] YANG XP, GHORESCHI K, STEWARD-THARP SM, et al. Opposing regulation of the locus encoding IL-17 through direct, reciprocal actions of STAT3 and STAT5. Nat Immunol. 2011;12(3): 247.
[15] MCGOVERN JL, NOTLEY CA. Production of IL-17: what’s STAT got to do with it?.Jak-stat.2012;1(2):80-82.
[16] RINCON M, IRVIN CG. Role of IL-6 in asthma and other inflammatory pulmonary diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(9): 1281-1290.
[17] BOONPIYATHAD S, PORNSURIYASAK P, BURANAPRADITKUN S, et al. Interleukin-2 levels in exhaled breath condensates, asthma severity, and asthma control in nonallergic asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2013;34(5):e35-41.
[18] PUEL A, DÖFFINGER R, NATIVIDAD A, et al. Autoantibodies against IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 in patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis and autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I.J Exp Med. 2010;207(2):291-297.
[19] MA CS, CHEW GYJ, SIMPSON N, et al. Deficiency of Th17 cells in hyper IgE syndrome due to mutations in STAT3.J Exp Med. 2008;205(7):1551-1557.
[20] SMEEKENS SP, PLANTINGA TS, VAN DE VEERDONK FL, et al. STAT1 hyperphosphorylation and defective IL12R/IL23R signaling underlie defective immunity in autosomal dominant chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. PloS one.2011;6(12): e29248.
[21] HOSHINO A, NAGAO T, NAGI-MIURA N, et al. MPO-ANCA induces IL-17 production by activated neutrophils in vitro via its Fc region-and complement-dependent manner.J Autoimmun. 2008; 31(1):79-89.
[22] LI L, HUANG L, VERGIS AL, et al. IL-17 produced by neutrophils regulates IFN-γ–mediated neutrophil migration in mouse kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury.J Clin Invest. 2010; 120(1):331-342.
[23] WERNER JL, GESSNER MA, LILLY LM, et al. Neutrophils produce IL-17A in a Dectin-1 and IL-23 dependent manner during invasive fungal infection.Infect Immun. 2011;79(10): 3966-3977.
[24] KATAYAMA M, OHMURA K, YUKAWA N, et al. Neutrophils are essential as a source of IL-17 in the effector phase of arthritis. PLoS One.2013;8(5):e62231.
[25] CLARK RA. Activation of the neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase. J Infect Dis.1999;179(Suppl 2):S309-S317.
[26] 陈和敏,申婷,游晶,等.Th17细胞的分化、调节及其主要细胞因子和功能[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(1):191-194.
[27] HUPPERT J, CLOSHEN D, CROXFORD A, et al. Cellular mechanisms of IL-17-induced blood-brain barrier disruption. FASEB J. 2010;24(4):1023-1034.
[28] 张南.孟鲁司特对支气管哮喘大鼠Th17细胞调节作用的研究[D].新乡:新乡医学院,2014.
[29] GRAYSON MH, FELDMAN S, PRINCE BT, 等.2017年哮喘研究进展:发病机制、生物制剂和遗传学[J].中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志,2018,12(6):673-684.
[30] 张杨,梁涛,许依婷,等.哮喘患者外周血单个核细胞白细胞介素23/Th-17轴及相关因子mRNA的表达与临床意义[J].临床血液学杂志(输血与检验),2016,29(2):263-266.
|