| [1] Barnes PJ. Immunology of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(3):183-192.
[2] Galli SJ, Tsai M, Piliponsky AM. The development of allergic inflammation. Nature. 2008;454(7203):445-454.
[3] Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood. 2002;99(10):3838-3843.
[4] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372.
[5] Sotiropoulou PA, Perez SA, Gritzapis AD, et al. Interactions between human mesenchymal stem cells and natural killer cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(1):74-85.
[6] Sun YQ, Deng MX, He J, et al. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent allergic airway inflammation in mice. Stem Cells. 2012;30(12):2692-2699.
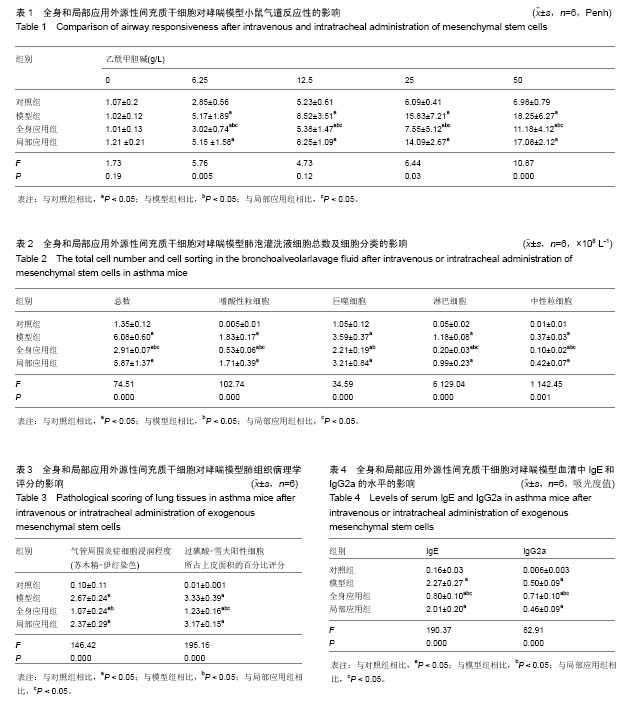
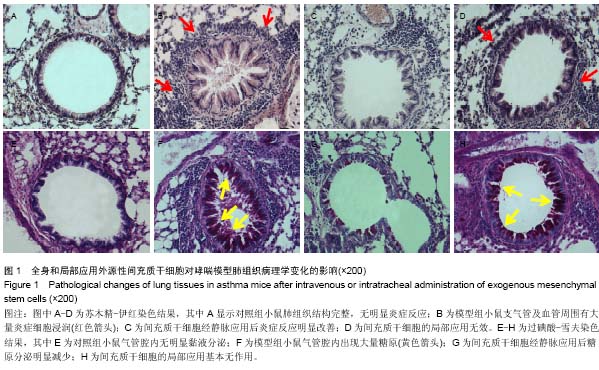
[7] 李斌恺,赖克方,洪燕华,等.支气管哮喘小鼠气道反应性无创检测方法的建立[J].国际呼吸杂志,2009,29(1):5-8.
[8] Baïz N, Annesi-Maesano I. Is the asthma epidemic still ascending? Clin Chest Med. 2012;33(3):419-429.
[9] Eder W, Ege MJ, von Mutius E. The asthma epidemic. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(21):2226-2235.
[10] Orihara K, Dil N, Anaparti V, et al. What's new in asthma pathophysiology and immunopathology? Expert Rev Respir Med. 2010;4(5):605-629.
[11] Fahy JV. Type 2 inflammation in asthma--present in most, absent in many. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15(1):57-65.
[12] Papaioannou AI, Kostikas K, Zervas E, et al. Control of asthma in real life: still a valuable goal? Eur Respir Rev. 2015; 24(136):361-369.
[13] In 't Anker PS, Scherjon SA, Kleijburg-van der Keur C, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells of fetal or maternal origin from human placenta. Stem Cells. 2004;22(7):1338-1345.
[14] Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.
[15] Nadri S, Soleimani M. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stromal cells from murine bone marrow and amniotic fluid. Cytotherapy. 2007;9(8):729-737.
[16] Keating A. Mesenchymal stromal cells: new directions. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(6):709-716.
[17] Kim N, Cho SG. New strategies for overcoming limitations of mesenchymal stem cell-based immune modulation. Int J Stem Cells. 2015;8(1):54-68.
[18] Prockop DJ. Concise review: two negative feedback loops place mesenchymal stem/stromal cells at the center of early regulators of inflammation. Stem Cells. 2013;31(10): 2042- 2046.
[19] Ahmad T, Mukherjee S, Pattnaik B, et al. Miro1 regulates intercellular mitochondrial transport & enhances mesenchymal stem cell rescue efficacy. EMBO J. 2014; 33(9):994-1010.
[20] Nemeth K, Keane-Myers A, Brown JM, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells use TGF-beta to suppress allergic responses in a mouse model of ragweed-induced asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(12):5652-5657.
[21] François M, Galipeau J. New insights on translational development of mesenchymal stromal cells for suppressor therapy. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(11):3535-3538.
[22] Weiss DJ. Stem cells, cell therapies, and bioengineering in lung biology and diseases. Comprehensive review of the recent literature 2010-2012. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013;10(5): S45-97.
[23] Bonfield TL, Koloze M, Lennon DP, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells suppress chronic airway inflammation in the murine ovalbumin asthma model. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010;299(6):L760-770.
[24] 韩灵,孙悦奇,付清玲,等.呼吸道变应性炎性反应小鼠模型的建立[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2013,48(3):224-228.
[25] Abreu SC, Antunes MA, de Castro JC, et al. Bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells vs. mesenchymal stromal cells in experimental allergic asthma. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2013;187(2):190-198.
[26] Lee RH, Pulin AA, Seo MJ, et al. Intravenous hMSCs improve myocardial infarction in mice because cells embolized in lung are activated to secrete the anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5(1):54-63.
[27] Islam MN, Das SR, Emin MT, et al. Mitochondrial transfer from bone-marrow-derived stromal cells to pulmonary alveoli protects against acute lung injury. Nat Med. 2012;18(5): 759-765.
[28] Galipeau J. The mesenchymal stromal cells dilemma--does a negative phase III trial of random donor mesenchymal stromal cells in steroid-resistant graft-versus-host disease represent a death knell or a bump in the road? Cytotherapy. 2013;15(1): 2-8.
[29] Kretlow JD, Jin YQ, Liu W, et al. Donor age and cell passage affects differentiation potential of murine bone marrow-derived stem cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2008;9:60.
[30] Weiss DJ, Bertoncello I, Borok Z, et al. Stem cells and cell therapies in lung biology and lung diseases. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2011;8(3):223-272.
[31] Kips JC, Anderson GP, Fredberg JJ, et al. Murine models of asthma. Eur Respir J. 2003;22(2):374-382.
[32] Gao P, Zhou Y, Xian L, et al. Functional effects of TGF-β1 on mesenchymal stem cell mobilization in cockroach allergen-induced asthma. J Immunol. 2014;192(10): 4560-4570.
[33] Cho KS, Park HK, Park HY, et al. IFATS collection: Immunomodulatory effects of adipose tissue-derived stem cells in an allergic rhinitis mouse model. Stem Cells. 2009; 27(1):259-265.
[34] Su WR, Zhang QZ, Shi SH, et al. Human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate contact hypersensitivity via prostaglandin E2-dependent mechanisms. Stem Cells. 2011;29(11):1849-1860.
[35] Lewkowich IP, Herman NS, Schleifer KW, et al. CD4+CD25+ T cells protect against experimentally induced asthma and alter pulmonary dendritic cell phenotype and function. J Exp Med. 2005;202(11):1549-1561.
[36] Pellerin L, Jenks JA, Bégin P, et al. Regulatory T cells and their roles in immune dysregulation and allergy. Immunol Res. 2014;58(2-3):358-368.
[37] Cho KS, Park MK, Kang SA, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells ameliorate allergic airway inflammation by inducing regulatory T cells in a mouse model of asthma. Mediators Inflamm. 2014; 2014:436476.
[38] 李建国,颛孙永勋,冉丕鑫,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对哮喘小鼠CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞及气道炎症的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(47):9302-9305.
[39] Ge X, Bai C, Yang J, et al. Intratracheal transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduced airway inflammation and up-regulated CD4?CD25? regulatory T cells in asthmatic mouse. Cell Biol Int. 2013; 37(7):675-686.
[40] Ge X, Bai C, Yang J, et al. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells on inhibiting airway remodeling and airway inflammation in chronic asthma. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(7):1595-1605.
[41] Kapoor S, Patel SA, Kartan S, et al. Tolerance-like mediated suppression by mesenchymal stem cells in patients with dust mite allergy-induced asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129(4):1094-1101.
|