中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (25): 3937-3943.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1767
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 下一篇
骨髓间充质干细胞分泌半乳凝素1可抑制哮喘小鼠的气道炎症
戈霞晖1,张国瑞2,管雯斌3,白 冲4
- 1上海中医药大学附属第七人民医院呼吸科,上海市 200137;上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院,2呼吸科,3病理科,上海市 200092;4上海长海医院呼吸与危重症医学科,上海市 200433
Galectin-1 secreted by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells may suppress airway inflammation in an asthmatic mouse
Ge Xiahui1, Zhang Guorui2, Guan Wenbin3, Bai Chong4
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用:间充质干细胞是属于中胚层的一类成体干细胞,对多种炎性细胞有免疫抑制作用。间充质干细胞能抑制自体及异体的T淋巴细胞增生,通过加入中和抗体发现间充质干细胞是通过分泌转化生长因子和肝细胞生长因子来抑制T淋巴细胞增生。另外间充质干细胞还能抑制单核细胞向树突状细胞的分化,下调成熟树突状细胞表面MHCⅡ类分子及共刺激分子CD40和CD86表达,使其保持半成熟状态的抑制表型。因此,间充质干细胞能通过分泌半乳凝素1、转化生长因子β1和肝细胞生长因子等多种免疫调节因子抑制多种免疫细胞功能。
半乳凝素1:是一种有免疫抑制作用的凝集素家族成员,其结构上含有约135个氨基酸的糖类识别区,能与糖蛋白和糖脂上的寡聚糖配体结合,参与细胞黏附、迁移、增殖和免疫调节等多种生物学功能。大量研究表明,半乳凝素1可通过抑制生长、诱导凋亡及下调促炎因子的表达等方式,抑制T细胞的活性。半乳凝素1在哮喘发病中起免疫保护作用,半乳凝素1的缺失可引起小鼠体内嗜酸性粒细胞数量增加及易于发生气道高反应。
背景:课题组前期研究表明移植骨髓间充质干细胞能减轻哮喘气道炎症程度且能调节哮喘炎症因子水平,进一步体外研究提示骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的半乳凝素1能影响树突状细胞的免疫功能,而骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的半乳凝素1对哮喘的作用尚不明确。
目的:观察骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的半乳凝素1对哮喘小鼠气道炎症的影响。
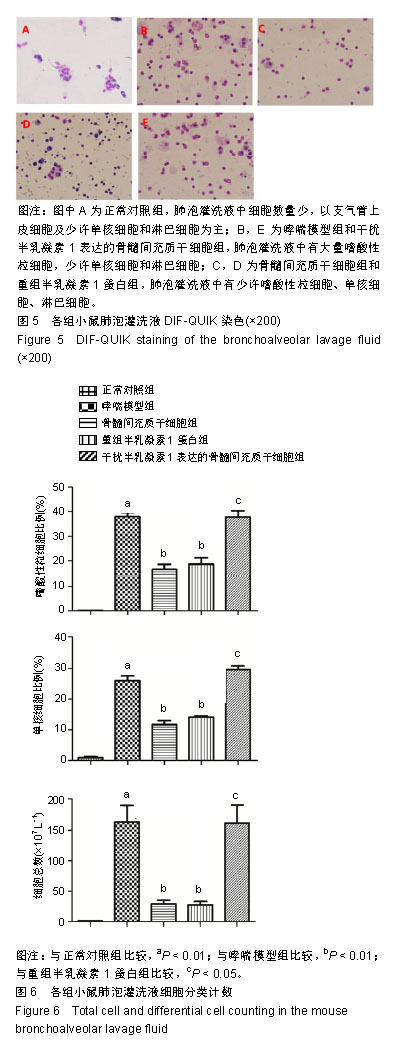
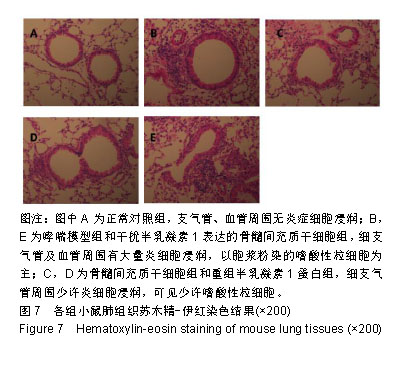
方法:构建小鼠pLVX-gal-1-shRNA并感染骨髓间充质干细胞。取40只雌性BALB/c小鼠,随机分为正常对照组、哮喘模型组、骨髓间充质干细胞组、重组半乳凝素1蛋白组、干扰半乳凝素1表达的骨髓间充质干细胞组,对比各组小鼠肺泡灌洗液中炎症细胞总数及分类的差异,采用苏木精-伊红染色观察各组小鼠气道炎症变化。
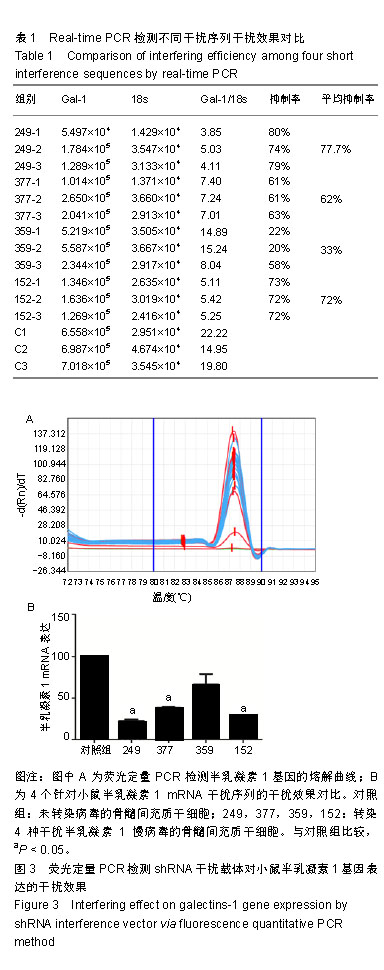
结果与结论:①针对小鼠半乳凝素1基因设计了4条RNA干扰序列,通过Real-time PCR验证249干扰位点的干扰序列对半乳凝素1基因干扰效果最佳,并以此进行后续的体内实验;②与正常对照组相比,哮喘模型组肺泡和气道周围有大量的炎症细胞聚集,以嗜酸性粒细胞为主;骨髓间充质干细胞组或重组半乳凝素1蛋白组气道及肺泡灌洗液中炎症细胞显著减少,而半乳凝素1基因干扰的骨髓间充质干细胞输注对哮喘小鼠气道及肺泡灌洗液炎症细胞聚集无明显影响;③结果表明骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的半乳凝素1对哮喘小鼠气道炎症有明显的抑制作用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
ORCID:0000-0003-4697-7979(戈霞晖)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)