| [1] Battaglia M, Atkinson MA. The Streetlight Effect in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes.2015;64(4):1081-1090.[2] Gülden E, Palm N, Herold KC. MAIT Cells: A Link between Gut Integrity and Type 1 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2017;26(6):813-815.[3] Atkinson MA, von Herrath M, Powers AC, et al. Current concepts on the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes-considerations for attempts to prevent and reverse the disease. Diabetes Care.2015;38(6):979-988.[4] Wang HS, Shyu JF, Shen WS,et al. Transplantation of insulin- producing cells derived from umbilical cord stromal mesenchymal stem cells to treat NOD mice. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(3):455-466.[5] Qu H, Liu X, Ni Y, et al. Laminin 411 acts as a potent inducer of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into insulin-producing cells. J Transl Med.2014;12:135.[6] 申义,王意忠,时瀚,等.人脐带间充质干细胞分化胰岛样细胞过程中胰岛素和巢蛋白的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(50):7500-7506.[7] Kuchroo P, Dave V, Vijayan A, et al. Paracrine factors secreted by umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce angiogenesis in vitro by a VEGF-independent pathway.Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(4): 437-450.[8] Shen C, Lie P, Miao T, et al. Conditioned medium from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells induces migration and angiogenesis. Mol Med Rep.2015;12(1):20-30.[9] Li T, Xia M, Gao Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: an overview of their potential in cell-based therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther.2015;15(9):1293-1306.[10] Ding D, Chang Y, Shyu W, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: a new era for stem cell therapy. Cell Transplant. 2015; 24(3):339-347.[11] Lu LL, Liu YJ, Yang SG, et al. Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with hematopoiesis- supportive function and other potentials. Haematologica.2006; 91(8):1017-1026.[12] Wilckens T, De Rijk R. Glucocorticoids and immune function: unknown dimensions and new frontiers. Immunol Today. 1997; 18(9):418-424.[13] Londono P, Komura A, Hara N, et al. Brief dexamethasone treatment during acute infection prevents virus-induced autoimmune diabetes. Clin Immunol.2010;135(3):401-411.[14] Harrison LC, Wentworth JM, Zhang Y, et al. Antigen-based vaccination and prevention of type 1 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep.2013; 13(5):616-623.[15] Harrison LC, Honeyman MC, Steele CE, et al. Pancreatic beta-cell function and immune responses to insulin after administration of intranasal insulin to humans at risk for type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(10):2348-2355.[16] 于文龙,高宏,余霄龙,等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗初发1型糖尿病[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(23):4363-4366.[17] 谭晓俊,王镇,李晓莹,等. 脐带间充质干细胞治疗1型糖尿病远期疗效观察三例报告[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2016,32(12):1030-1032.[18] Geng S, Zhang H, Zhou X, et al. Diabetes tolerogenic vaccines targeting antigen-specific inflammation. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(2): 522-530.[19] Campbell-Thompson ML, Atkinson MA, Butler AE, et al. The diagnosis of insulitis in human type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2013; 56(11):2541-2543.[20] Krogvold L, Skog O, Sundstrom G, et al. Function of Isolated Pancreatic Islets From Patients at Onset of Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin Secretion Can Be Restored After Some Days in a Nondiabetogenic Environment In Vitro: Results From the DiViD Study. Diabetes.2015; 64(7):2506-2512.[21] Marhfour I, Lopez XM, Lefkaditis D, et al. Expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress markers in the islets of patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia.2012;55(9):2417-2420.[22] Imai Y, Dobrian AD, Morris MA, et al. Lipids and immunoinflammatory pathways of beta cell destruction. Diabetologia.2016;59(4):673-678.[23] Grzesik WJ, Nadler JL, Machida Y, et al. Expression pattern of 12-lipoxygenase in human islets with type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(3):E387-E395.[24] Willcox A, Richardson SJ, Bone AJ, et al. Analysis of islet inflammation in human type 1 diabetes. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009; 155(2):173-181.[25] Visperas A, Vignali DA. Are Regulatory T Cells Defective in Type 1 Diabetes and Can We Fix Them?. J Immunol, 2016;197(10): 3762-3770.[26] D'Alessio FR, Tsushima K, Aggarwal NR, et al. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs resolve experimental lung injury in mice and are present in humans with acute lung injury. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(10): 2898-2913.[27] Liesz A, Suri-Payer E, Veltkamp C, et al. Regulatory T cells are key cerebroprotective immunomodulators in acute experimental stroke. Nat Med. 2009;15(2):192-199.[28] Chen X, Zhou B, Li M, et al. CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells suppress Mycobacterium tuberculosis immunity in patients with active disease. Clin Immunol.2007;123(1):50-59.[29] Qiao YC, Shen J, Hong XZ, et al. Changes of regulatory T cells, transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin-10 in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Immunol. 2016;170:61-69.[30] Ghonaim MM, El-Edel RH, Kamal ES, et al. T-Regulatory Cell Subsets in Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Relation to Control of the Disease. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2017; 17(3):238-245.[31] Lampeter EF, Signore A, Gale EA, et al. Lessons from the NOD mouse for the pathogenesis and immunotherapy of human type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1989;32(10): 703-708.[32] Lenzen S. Animal models of human type 1 diabetes for evaluating combination therapies and successful translation to the patient with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017;33(7). doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2915.[33] Geng S, Zhang H, Zhou X, et al. Diabetes tolerogenic vaccines targeting antigen-specific inflammation. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(2): 522-530.[34] Zipris D. Innate immunity in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2011;27(8): 824-829.[35] Hu J, Wang Y, Wang F, et al. Effect and mechanisms of human Wharton??s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells on type 1 diabetes in NOD model. Endocrine. 2015;48(1):124-134.[36] Wang D, Chen K, Du W T, et al. CD14+ monocytes promote the immunosuppressive effect of human umbilical cord matrix stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(15): 2414-2423.[37] Ribeiro A, Laranjeira P, Mendes S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord matrix, adipose tissue and bone marrow exhibit different capability to suppress peripheral blood B, natural killer and T cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(5):125.[38] Tang RJ, Shen SN, Zhao XY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-regulated Treg cells suppress colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:71.[39] Wang D, Huang S, Yuan X, et al. The regulation of the Treg/Th17 balance by mesenchymal stem cells in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Mol Immunol. 2017;14(5):423-431.[40] Montanucci P, Alunno A, Basta G, et al. Restoration of t cell substes of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus by microencapsulated human umbilical cord Wharton jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells: An in vitro study. Clin Immunol.2016;163:34-41.[41] 赵子粼,叶常青,罗建春,等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植对心力衰竭大鼠外周血CD_4~+CD_(25)~+Foxp_3~+Treg细胞表达的影响[J]. 山东医药, 2015,55(41):13-15.[42] El-Hossary N, Hassanein H, El Ghareeb AW, et al. Intravenous vs intraperitoneal transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton??s jelly in the treatment of streptozotocin- induced diabetic rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016; 21:102-111.[43] Sun X, Hao H, Han Q, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate insulin resistance by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammation in type 2 diabetes rats. Stem Cell Res Ther.2017;8(1):241. |
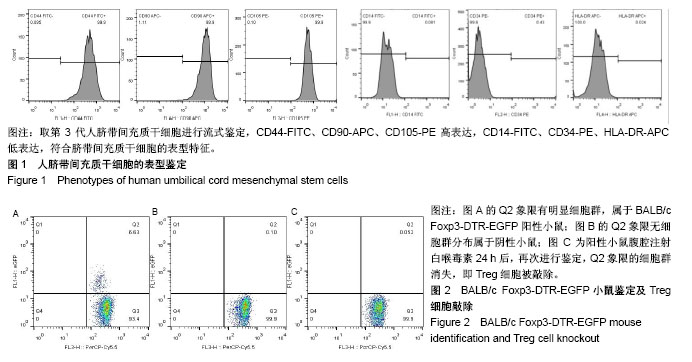
.jpg)
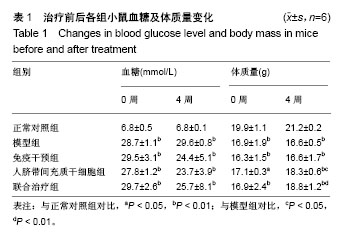
.jpg)
.jpg)