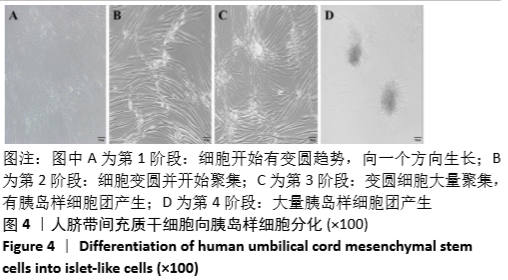
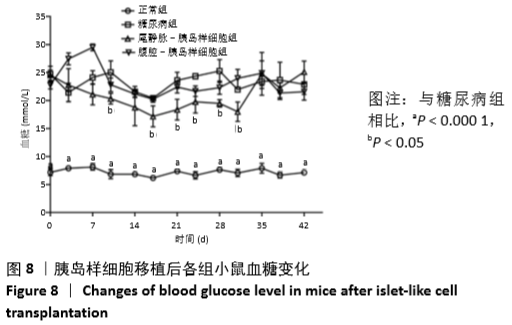
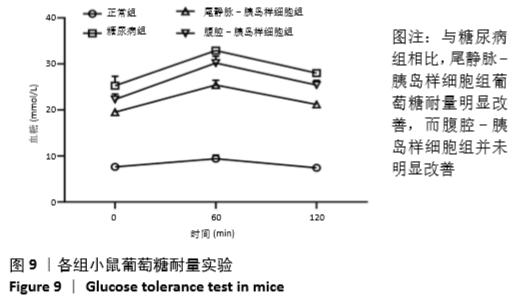
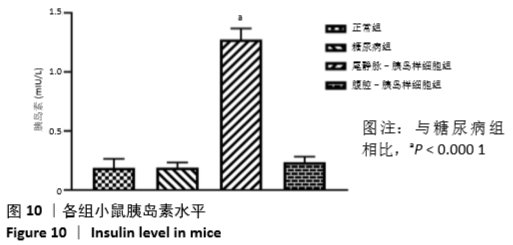
[1] VERES A, FAUST AL, BUSHNELL HL, et al. Charting cellular identity during human in vitro β-cell differentiation. Nature. 2019;569(7756): 368-373.
[2] RUSS HA, PARENT AV, RINGLER JJ, et al. Controlled induction of human pancreatic progenitors produces functional beta-like cells in vitro. EMBO J. 2015;34(13):1759-1772.
[3] AMERICAN DIABETES ASSOCIATION. Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2012. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(4):1033-1046.
[4] FRYER BH, REZANIA A, ZIMMERMAN MC. Generating β-cells in vitro: progress towards a Holy Grail. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2013;20(2):112-117.
[5] STEPHENS CH, ORR KS, ACTON AJ, et al. In situ type I oligomeric collagen macroencapsulation promotes islet longevity and function in vitro and in vivo. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2018;315(4): E650-E661.
[6] LENNON DP, EDMISON JM, CAPLAN AI. Cultivation of rat marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in reduced oxygen tension: effects on in vitro and in vivo osteochondrogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2001;187(3):345-355.
[7] PITTENGER MF, MACKAY AM, BECK SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411): 143-147.
[8] HAKUNO D, FUKUDA K, MAKINO S, et al. Bone marrow-derived regenerated cardiomyocytes (CMG Cells) express functional adrenergic and muscarinic receptors. Circulation. 2002;105(3): 380-386.
[9] JIANG J, AU M, LU K, et al. Generation of insulin-producing islet-like clusters from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2007;25(8): 1940-1953.
[10] WANG H, QIU X, NI P, et al. Immunological characteristics of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and the therapeutic effects of their transplantion on hyperglycemia in diabetic rats. Int J Mol Med. 2014;33(2):263-270.
[11] YU S, CHENG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Treatment with adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells exerts anti-diabetic effects, improves long-term complications, and attenuates inflammation in type 2 diabetic rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):333.
[12] TSAI PJ, WANG HS, LIN GJ, et al. Undifferentiated Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Induces Insulin-Producing Cell Differentiation and Suppression of T-Cell-Mediated Autoimmunity in Nonobese Diabetic Mice. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(8):1555-1570.
[13] HU J, WANG Y, WANG F, et al. Effect and mechanisms of human Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells on type 1 diabetes in NOD model. Endocrine. 2015;48(1):124-134.
[14] CHAO KC, CHAO KF, FU YS, et al. Islet-like clusters derived from mesenchymal stem cells in Wharton’s Jelly of the human umbilical cord for transplantation to control type 1 diabetes. PLoS One. 2008; 3(1):e1451.
[15] 山霞,崔晓兰,时瀚,等.人脐带间充质干细胞诱导分化不同阶段的胰岛样细胞移植治疗糖尿病[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(29):4703-4708.
[16] YU YB, BIAN JM, GU DH. Transplantation of insulin-producing cells to treat diabetic rats after 90% pancreatectomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(21):6582-6590.
[17] PRABAKAR KR, DOMÍNGUEZ-BENDALA J, MOLANO RD, et al. Generation of glucose-responsive, insulin-producing cells from human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(6):1321-1339.
[18] 李兰兰,李宁,杨晓菲,等.人脐带间充质干细胞分化为胰岛素分泌细胞的免疫原性变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(13): 2045-2050.
[19] EL-TANTAWY WH, HALEEM EN. Therapeutic effects of stem cell on hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and oxidative stress in alloxan-treated rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;391(1-2):193-200.
[20] LI B, CHENG Y, YU S, et al. Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019: 8628027.
[21] DAVIES JE, WALKER JT, KEATING A. Concise Review: Wharton’s Jelly: The Rich, but Enigmatic, Source of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(7):1620-1630.
[22] 杨文英.中国糖尿病的流行特点及变化趋势[J].中国科学:生命科学, 2018, 48(8):812-819.
[23] TAN K, ZHENG K, LI D, et al. Impact of adipose tissue or umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells on the immunogenicity of human cord blood derived endothelial progenitor cells. PLoS One. 2017;12(5): e0178624.
[24] DING DC, CHANG YH, SHYU WC, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: a new era for stem cell therapy. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(3):339-347.
[25] CORSELLO T, AMICO G, CORRAO S, et al. Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Human Umbilical Cord: a Close-up on Immunomodulatory Molecules Featured In Situ and In Vitro. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019;15(6):900-918.
[26] BARCZEWSKA M, GRUDNIAK M, MAKSYMOWICZ S, et al. Safety of intrathecal injection of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis therapy. Neural Regen Res. 2019; 14(2):313-318.
[27] ROUSHANDEH AM, BAHADORI M, ROUDKENAR MH. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-based Therapy as a New Horizon for Kidney Injuries. Arch Med Res. 2017;48(2):133-146.
[28] LEE HJ, KANG KS, KANG SY, et al. Immunologic properties of differentiated and undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord blood. J Vet Sci. 2016;17(3):289-297.
[29] 杨大威,林和敏,刘广鹏.成骨分化的人脐带血间充质干细胞免疫原性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(6):752-757.
[30] 刘志刚,张万华,刘霆.腹膜腔细胞的免疫特性及功能研究进展[J].重庆医学,2019,48(14):2467-2470.
[31] 郭波,刘佳,崔晓兰,等.人脐带间充质干细胞联合免疫干预治疗1型糖尿病小鼠的实验研究[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(13): 2016-2021.
[32] MACLEAN FL, IMS GM, HORNE MK, et al. A Programmed Anti-Inflammatory Nanoscaffold (PAIN) as a 3D Tool to Understand the Brain Injury Response. Adv Mater. 2018;30(50):e1805209. |