中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (2): 165-170.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1900
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 下一篇
补骨脂提取物干预骨质疏松模型大鼠骨密度及骨生物力学的变化
周倚墨1,张建宁1,单中书2
- 1青海红十字医院骨科,青海省西宁市 810000;2青海省人民医院骨科,青海省西宁市 810007
Effects of psoralen corylifolia extract on bone mineral density and bone biomechanics in osteoporosis rats
Zhou Yimo1, Zhang Jianning1, Shan Zhongshu2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Qinghai Red Cross Hospital, Xining 810000, Qinghai Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Qinghai People’s Hospital, Xining 810007, Qinghai Province, China
摘要:
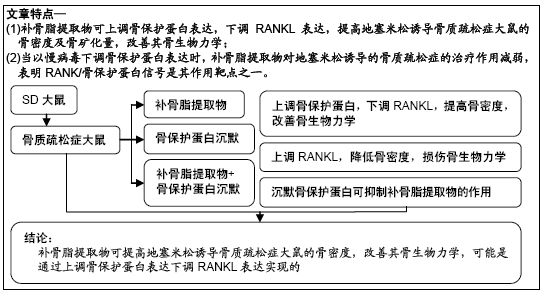
文题释义:
RANKL/OPG通路:核因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of NF-κB Ligand,RANKL)/骨保护蛋白在维持成骨与破骨的动态平衡,调节骨代谢功能方面发挥着重要作用。RANKL 可与破骨细胞前体细胞膜表面的核因子κB受体活化因子结合,促进破骨细胞分化和激活,抑制其凋亡,最终促进骨吸收;骨保护蛋白作为RANKL的天然抗体,可与RANKL直接结合,竞争性抑制核因子κB受体活化因子与其的结合,进而抑制破骨细胞分化、成熟,最终抑制骨吸收。生理状态下,体内RANKL与骨保护蛋白的表达保持一定的比例,若二者表达比例失衡,则会造成骨代谢紊乱,导致骨相关疾病发生。
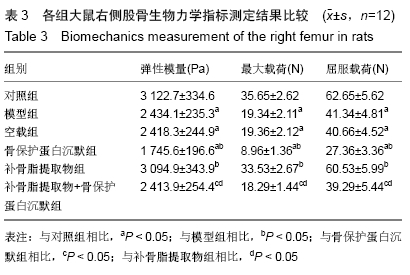
骨生物力学:是骨组织在外力作用下的力学生物学效应,对其进行检测可直接评价骨质量,是评价各种治疗骨丢失措施的最佳方案,其检测指标包括弹性模量、最大载荷、屈服载荷等。
背景:地塞米松作为一种糖皮质激素,长期应用会破坏成骨与破骨的动态平衡,降低骨密度,损伤骨生物力学,调控核因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of NF-κB ligand,RANKL)/骨保护蛋白通路可能影响地塞米松诱导的骨质疏松症大鼠骨密度及骨生物力学。
目的:探讨基于RANKL/骨保护蛋白通路研究补骨脂提取物对地塞米松诱导骨质疏松症大鼠骨密度及骨生物力学的影响。
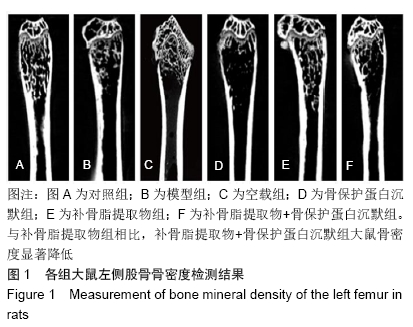
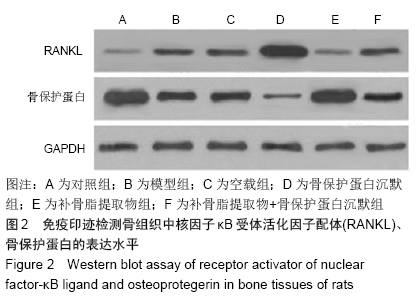
方法:SPF级Wistar大鼠肌肉注射地塞米松,建立骨质疏松大鼠模型。选择1×107 TU/mL浓度的慢病毒载体进行实验。将模型大鼠随机分为模型组、空载组(空慢病毒载体)、骨保护蛋白沉默组(含骨保护蛋白基因干扰片段的慢病毒载体)、补骨脂提取物组、补骨脂提取物+骨保护蛋白沉默组,每组12只,另取12只正常大鼠设为对照组。药物处理后,采用骨密度仪测定大鼠左侧股骨骨密度,采用力学实验测试机测定大鼠右侧股骨生物力学指标弹性模量、最大载荷、屈服载荷,测定大鼠股骨骨矿物盐含量,酶联免疫吸附法检测血清中RANKL、骨保护蛋白水平,蛋白免疫印迹法检测骨组织中RANKL、骨保护蛋白表达水平。实验方案经青海大学医学院动物实验伦理委员会批准(批准号为2017081501)
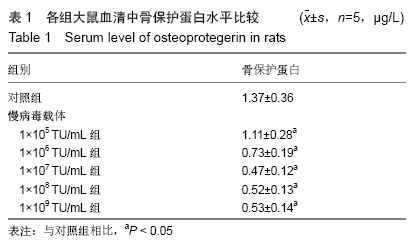
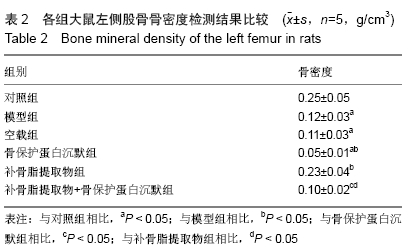
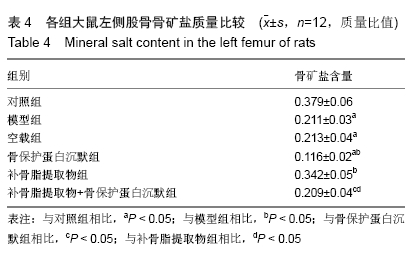
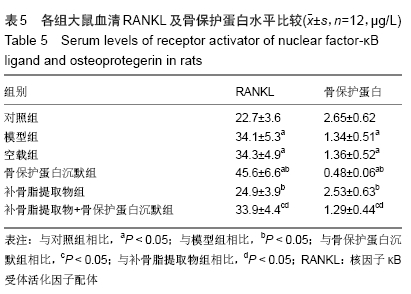
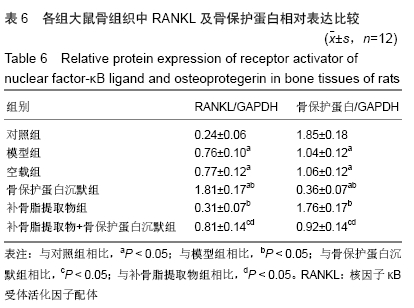
结果与结论:①大鼠骨密度、弹性模量、最大载荷、屈服载荷、骨矿物盐含量、血清中骨保护蛋白水平、骨组织中骨保护蛋白表达:模型组较对照组降低,骨保护蛋白沉默组较模型组降低,补骨脂提取物组较模型组升高,补骨脂提取物+骨保护蛋白沉默组较骨保护蛋白沉默组升高,较补骨脂提取物组降低(均P < 0.05);②大鼠血清中RANKL水平、骨组织中RANKL蛋白表达结果显示,模型组较对照组升高;骨保护蛋白沉默组较模型组升高,补骨脂提取物组较模型组降低,补骨脂提取物+骨保护蛋白沉默组较骨保护蛋白沉默组降低,较补骨脂提取物组升高(均P < 0.05);③模型组与空载组两组间各指标比较无明显变化(P > 0.05);④结果说明,补骨脂提取物可提高地塞米松诱导骨质疏松症大鼠的骨密度,改善其骨生物力学,可能是通过上调骨保护蛋白表达,下调RANKL表达实现的。ORCID: 0000-0001-9896-6214(周倚墨)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: