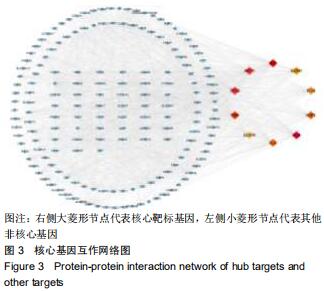
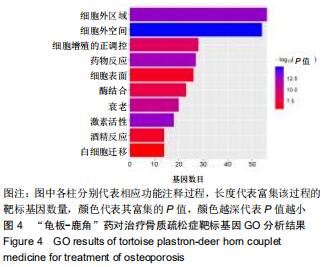
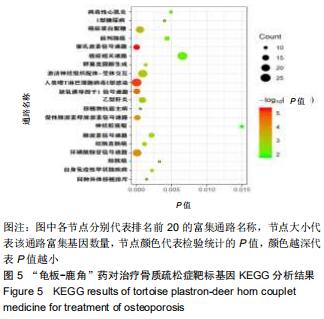
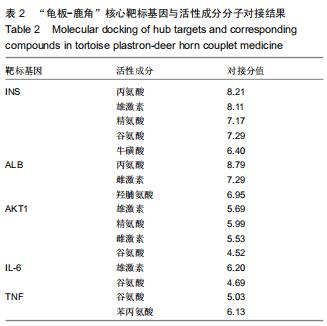
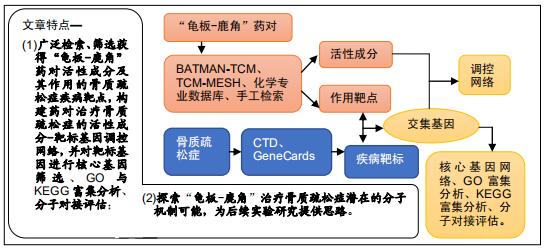
|
[1] 夏维波,章振林,林华,等.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(3):281-309.
[2] ZENG Q, LI N, WANG Q, et al. The prevalence of osteoporosis in China, a nationwide, multicenter dxa survey. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(10):1789-1797.
[3] MILLER PD. Management of severe osteoporosis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016;17(4):473-488.
[4] 闫慧明,郭静,安燕,等.分子信号通路在骨质疏松症发生机制中的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(10):1336-1340.
[5] FLORENCIO-SILVA R, SASSO GR, SASSO-CERRI E, et al. Biology of bone tissue: structure, function, and factors that influence bone cells. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:421746.
[6] 董冰子,孙晓方.骨质疏松症治疗新进展:从分子机制到药物靶点[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2018,11(6):620-627.
[7] 葛继荣,郑洪新,万小明,等.中医药防治原发性骨质疏松症专家共识(2015)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(9):1023-1028.
[8] 尹恒,王建伟,马勇,等.龟鹿二仙胶治疗原发性骨质疏松症60例疗效观察[J]. 国医论坛,2015,30(6):31-32.
[9] 牛素生,李楠,张燕,等.龟鹿二仙胶含药血清诱导大鼠骨髓基质干细胞成骨分化的作用及机制[J].中国医药导报,2015,12(31):8-12+169.
[10] 钱哲,王建伟,尹恒,等. 龟鹿二仙胶治疗骨质疏松症的机制研究[J].中华中医药学刊, 2017,35(4):1008-1013.
[11] 杨树华.龟鹿二仙胶及其拆方对体外培养破骨细胞骨吸收功能的影响[D].福州:福建中医药大学, 2015.
[12] AGUAYO-OROZCO A, AUDOUZE K, BRUNAK S, et al. In silico systems pharmacology to assess drug's therapeutic and toxic effects. Curr Pharm Design. 2016; 22(46):6895-6902.
[13] CHENG F, HONG H, YANG S, et al. Individualized network-based drug repositioning infrastructure for precision oncology in the panomics era. Brief Bioinform. 2017;18(4):682-697.
[14] ZHANG W, BAI Y, WANG Y, et al. Polypharmacology in drug discovery: a review from systems pharmacology perspective. Curr Pharm Design. 2016;22(21): 3171-3181.
[15] LIU Z, GUO F, WANG Y, et al. BATMAN-TCM: a Bioinformatics Analysis Tool for Molecular mechANism of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:21146.
[16] ZHANG RZ, YU SJ, BAI H, et al. TCM-Mesh: The database and analytical system for network pharmacology analysis for TCM preparations. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1): 2821.
[17] DAVIS AP, GRONDIN CJ, JOHNSON RJ, et al. The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database: update 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019; 47(D1): D948-954.
[18] STELZER G, ROSEN N, PLASCHKES I, et al. The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016;54:1.30.1-1.30.33.
[19] SZKLARCZYK D, GABLE AL, LYON D, et al. STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1): D607-613.
[20] SHANNON P, MARKIEL A, OZIER O, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13(11): 2498-2504.
[21] OTASEK D, MORRIS J H, BOUCAS J, et al. Cytoscape Automation: empowering workflow-based network analysis. Genome Biol. 2019; 20(1): 185.
[22] CHIN CH, CHEN SH, WU HH, et al. cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 2014; 8 Suppl 4:S11.
[23] The Gene Ontology Consortium. Expansion of the Gene Ontology knowledgebase and resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1): D331-338.
[24] KANEHISA M, GOTO S. KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(1):27-30.
[25] DENNIS G JR, SHERMAN BT, HOSACK DA, et al. DAVID: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 2003;4(5):P3.
[26] XIE C, MAO X, HUANG J, et al. KOBAS 2.0: a web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39: W316-322.
[27] GROSDIDIER A, ZOETE V, MICHIELIN O. SwissDock, a protein-small molecule docking web service based on EADock DSS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:W270-277.
[28] GROSDIDIER A, ZOETE V, MICHIELIN O. Fast docking using the CHARMM force field with EADock DSS. J Comput Chem. 2011;32(10): 2149-2159.
[29] UNIPROT CONSORTIUM. UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019; 47(D1): D506-515.
[30] 陈少军,陈宏降,郭章华.反向分子对接法预测丹参醇A的潜在靶点[J]. 中药药理与临床,2014,30(5): 58-61.
[31] 杨释岑,钟昌桓,易增兴,等. 薏苡素潜在靶点预测及正向分子对接验证[J]. 湖北民族学院学报(医学版),2018,35(4):1-4.
[32] 鲍悦,高久堂,孙佳明,等.中药鹿角胶的研究进展[J].吉林中医药,2016, 36(2):173-175+204.
[33] 方达任,张克兰,刘焱文. 龟板、鳖甲炮制前后化学成分的变化[J]. 中国药学杂志,1989,34(1):26-28+62.
[34] 李民,王春艳,李士栋,等.鹿角胶的研究进展[J].中国药物评价,2014,31(5): 310-312.
[35] 李阳春.龟甲有效成分及药理研究进展[J].科技视界,2017,14(6):291+300.
[36] 谢平,杨梅香. 龟上、下甲化学成分比较[J].中成药研究,1986, 9(3): 32.
[37] 杨清. 龟上、下甲化学成分及药理作用的比较研究通过鉴定[J]. 中国药学杂志,1987,32(5):298.
[38] 周芳妍,李婷,刘力,等. 鹿角胶中氨基酸类成分的HPLC指纹图谱[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2014,20(9):47-51.
[39] 郭鱼波,王丽丽,马如风,等. 骨质疏松的中医病因病机分析及其中医药治疗的前景探讨[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2015,17(4):768-772.
[40] 纪慧娇.几种抗氧化剂对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖分化的调控及纳米生物活性玻璃涂膜的骨诱导作用[D].杭州:浙江大学, 2012.
[41] ALMEIDA M, LAURENT MR, DUBOIS V, et al. Estrogens and Androgens in Skeletal Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiological Rev. 2017;97(1):135-187.
[42] FAYED HA, BARAKAT BM, ELSHAER SS, et al. Antiosteoporotic activities of isoquercitrin in ovariectomized rats: Role of inhibiting hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha [J]. European journal of pharmacology, 2019;865:172785.
[43] MIYAMOTO T. Mechanism underlying post-menopausal osteoporosis: HIF1alpha is required for osteoclast activation by estrogen deficiency. Keio J Med. 2015;64(3):44-47.
[44] ZHANG J, ZHANG X, XIE F, et al. The regulation of TGF-beta/SMAD signaling by protein deubiquitination. Protein Cell. 2014; 5(7): 503-517.
[45] ZHAO B. TNF and Bone remodeling. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017; 15(3):126-134.
[46] ZHA L, HE L, LIANG Y, et al. TNF-alpha contributes to postmenopausal osteoporosis by synergistically promoting RANKL-induced osteoclast formation. Biomed Pharmacothe. 2018; 102(3):69-74.
[47] EFTEKHARI H, HOSSEINI SR, POURREZA BABOLI H, et al. Association of interleukin-6 (rs1800796) but not transforming growth factor beta 1 (rs1800469) with serum calcium levels in osteoporotic patients. Gene. 2018; 671:21-27.
[48] JI Y F, JIANG X, LI W, et al. Impact of interleukin-6 gene polymorphisms and its interaction with obesity on osteoporosis risk in Chinese postmenopausal women. Environ Health Prev Med. 2019; 24(1):48.
[49] 宋囡. 基于MAPK/TGF-β1/Smads信号级联研究左、右归丸促骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨机制[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学, 2014.
|