[1]PERUZZARO ST, ANDREWS MMM, AL-GHARAIBEH A, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells genetically engineered to overexpress interleukin-10 promotes alternative inflammatory response in rat model of traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation.2019;16(1):2.
[2]LI T, XIA M, GAO Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: an overview of their potential in cell-based therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15(9):1293-1306.
[3]HYDER AA, WUNDERLICH CA, PUVANACHANDRA P, et al. The impact of traumatic brain injuries: a global perspective. NeuroRehabilitation.2007;22(5):341-353.
[4]OBERMEIER B, DANEMAN R, RANSOHOFF RM. Development, maintenance and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Nat Med.2013;19(12):1584-1596.
[5]NEUWELT E, ABBOTT NJ, ABREY L, et al. Strategies to advance translational research into brain barriers. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(1):84-96.
[6]SUN P, LIU DZ, JICKLING GC, et al. MicroRNA-based therapeutics in central nervous system injuries. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018;38(7):1125-1148.
[7]BLENNOW K, HARDY J, ZETTERBERG H. The neuropathology and neurobiology of traumatic brain injury. Neuron. 2012;76(5):886-899.
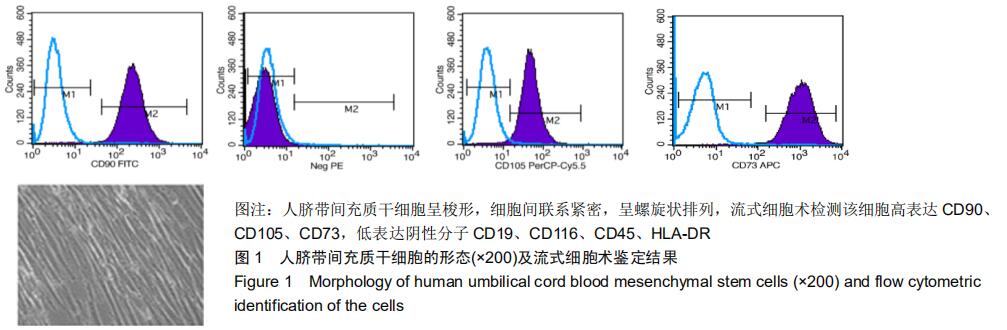
[8]韩潇,白海,赵强,等.人脐带间充质干细胞体外分离培养及其生物学特性的研究[J].重庆医学,2016,45(7):876-879.
[9]DONG HJ, ZHAO ML, LI XH, et al. Hypothermia-Modulating Matrix Elasticity of Injured Brain Promoted Neural Lineage Specification of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Neuroscience. 2018;377:1-11.
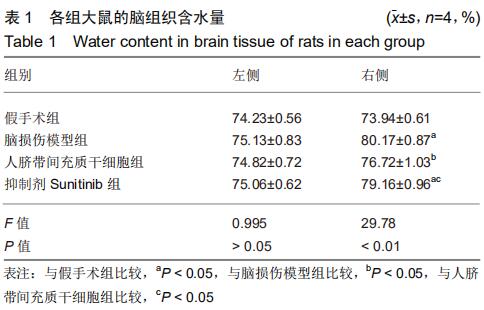
[10]傅兴宁,刘丽冰,张志杰,等.CART肽抑制缺血再灌注小鼠脑组织水通道蛋白4表达并减轻脑水肿[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2018, 34(8):1363-1367.
[11]BELL L, KOENIGER T, TACKE S, et al. Characterization of blood-brain barrier integrity in a B-cell-dependent mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Histochem Cell Biol. 2019;151(6): 489-499.
[12]LORENZO MF, THOMAS SC, KANI Y, et al. Temporal Characterization of Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption with High-Frequency Electroporation. Cancers (Basel). 2019; 11(12). pii: E1850.
[13]YOU Q, GONG Q, HAN YQ, et al. Role of miR-124 in the regulation of retinoic acid-induced Neuro-2A cell differentiation. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(6):1133-1139.
[14]许泽艳,杨志贤,廖承德,等.创伤性脑损伤与血脑屏障关系的研究进展[J].山东医药,2018,58(41):110-112.
[15]SHEN Q, YIN Y, XIA QJ, et al. Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Promote Neuronal Restoration in Rats with Traumatic Brain Injury: Involvement of GDNF Regulating BAD and BAX Signaling. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(2):748-762.
[16]PISCHIUTTA F, BRUNELLI L, ROMELE P, et al. Protection of Brain Injury by Amniotic Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Secreted Metabolites. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(11):e1118-e1131.
[17]LUO SY, LI R, LE ZY, et al. Anfibatide protects against rat cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via TLR4/JNK/caspase-3 pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;807:127-137.
[18]王义义,杨卓.血脑屏障的结构和功能[J].天津医药, 2010,38(3): 200.
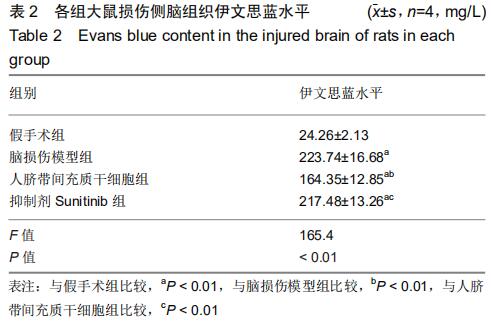
[19]张合鹏,杜爱玲,李磊,等. AG490对大鼠脑损伤后血-脑屏障通透性及白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α表达的影响[J].中国脑血管病杂志, 2015,12(3):134-139.
[20]GONÇALVES J, LEITÃO RA, HIGUERA-MATAS A, et al. Extended-access methamphetamine self-administration elicits neuroinflammatory response along with blood-brain barrier breakdown. Brain Behav Immun. 2017;62:306-317.
[21]ZHU X, CAO Y, WEI L, et al. von Willebrand factor contributes to poor outcome in a mouse model of intracerebral haemorrhage. Sci Rep.2016;6:35901.
[22]KUROSE T, TAKAHASHI S, OTSUKA T, et al. Simulated microgravity-cultured mesenchymal stem cells improve recovery following spinal cord ischemia in rats. Stem Cell Res. 2019;41:101601.
[23]SHIM AH, LIU H, FOCIA PJ, et al. Structures of a platelet-derived growth factor/propeptide complex and a platelet-derived growth factor/receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(25):11307-11312.
[24]GERHARDT H, BETSHOLTZ C. Endothelial-pericyte interactions in angiogenesis. Cell Tissue Res.2003;314(1): 15-23.
[25]SHEN J, ISHII Y, XU G, et al. PDGFR-β as a positive regulator of tissue repair in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2012;32(2):353-367.
[26]ARMULIK A, GENOVÉ G, BETSHOLTZ C. Pericytes: developmental, physiological, and pathological perspectives, problems, and promises. Dev Cell. 2011;21(2):193-215.
[27]DANEMAN R, ZHOU L, KEBEDE AA, et al. Pericytes are required for blood-brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis. Nature. 2010;468(7323):562-566.
[28]FARSHORI P, KACHAR B. Redistribution and phosphorylation of occludin during opening and resealing of tight junctions in cultured epithelial cells. J Membr Biol.1999; 170(2):147-156.
[29]BHOWMICK S, D'MELLO V, CARUSO D, et al. Impairment of pericyte-endothelium crosstalk leads to blood-brain barrier dysfunction following traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2019; 317:260-270.
|