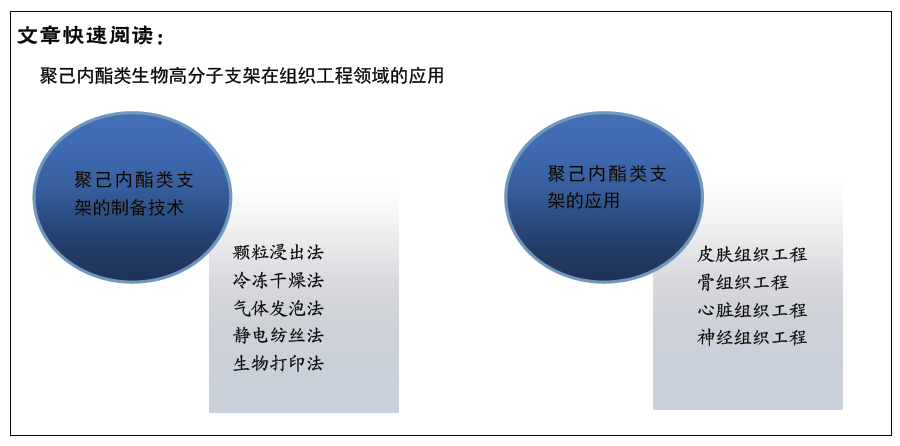
2.1 支架的制备 众所周知,聚合物支架的三维结构和性质对其在组织工程领域的应用至关重要,多孔结构是三维支架的重要特性之一,决定了支架的体积、比表面积、机械性能、表面性能、生物相容性、降解性等。为了调控支架的多孔结构,研究者们常用的方法包括颗粒浸出法、冷冻干燥法、气体发泡法、静电喷射纺丝、生物打印技术等[10-12]。
2.1.1 颗粒浸出法 颗粒浸出法是选择合适的致孔剂与聚合物材料混合制备成支架,用溶剂溶出致孔剂,从而获得具有孔隙结构的支架。常用的致孔剂包括食盐、糖、石蜡等,致孔剂的大小和几何形状、浓度决定了孔的大小、几何形状和孔隙率,这种制备方法简单,容易控制孔结构,但是不能制备相互连通的孔。
HOU等[13]通过加入氯化钠致孔剂制备了聚己内酯基多孔支架,考察了氯化钠的粒径、浓度对支架孔隙率的影响,结果表明支架的孔隙率和孔径可以由氯化钠的浓度和粒径控制,氯化钠浓度为80%-95%时支架孔隙率为65%-96%。
2.1.2 冷冻干燥法 冷冻干燥也称冻干,是指将聚合物溶液倒入模具、低温固化,然后采用冷冻干燥手段使溶剂升华,制得海绵状支架。支架的多孔结构可通过体系的pH值和释放速率决定,这种制备多孔支架的方式不需要致孔剂和浸出液,操作简单,孔隙均匀且孔洞相互连通。
FERESHTEH等[14]利用冷冻干燥方法制备了一种基于聚己内酯和玉米醇溶蛋白共混物的新型药物缓释多孔支架,通过调节聚己内酯和玉米醇溶蛋白溶液的浓度可以获得具有管状结构和孔隙率达89%的支架;通过盐酸四环素测试支架的药物缓释性能,结果表明与纯聚己内酯支架24 h的药物释放率为92%相比,添加玉米醇蛋白的聚己内酯支架24 h的药物释放率降低为62%,表明制备的复合支架具有较好的药物缓释作用。
刘华国等[15]认为对比单一的冷冻干燥法或颗粒浸出法,采用冷冻干燥/颗粒浸出复合法制备的聚己内酯支架具有更高的孔隙率和更均匀的孔隙结构,且孔径可控。通过控制预冷冻温度多孔支架可获得好的完整性和连通性,通过控制致孔剂的量可调节多孔支架的孔径。
2.1.3 气体发泡法 气体发泡法是指通过高压气体制备多孔支架的一种方法,常用高压二氧化碳进行发泡,通过控制气体压强调节支架材料的孔隙率。
CHEN等[16]采用超临界CO2对聚己内酯进行分批发泡制备了适宜骨组织工程的聚己内酯支架,发现孔的形态和结构明显受到发泡温度的影响,在40 ℃以上时,由结晶熔融温度(Tm)降低引起的聚己内酯熔融增强导致孔径分布更宽,即熔融态泡沫,并且变量对孔径的多米诺效应被放大;而在40 ℃以下时,泡沫表现出致密和小孔的形貌,即固态泡沫。通过调整工艺变量制造了直径为(12.5±0.1)-(344±54) μm且孔隙率为(60.8±3.2)%-(83.4±1.3)%的支架,支架的互连性大多在70%左右。
2.1.4 静电纺丝法 将聚合物以高浓度溶解在有机溶剂中,并使该黏性溶液经受高压(数十千伏),在临界电压下,静电荷克服液滴的表面张力形成稳定的射流,当带电的射流在电场作用下喷射时溶剂蒸发,形成支架。静电纺丝是一种用于制备多孔支架的通用技术,可稳定呈现细胞基质的亚微米纤维形态,支架纤维直径和纤维排列方式可以操作控制,进而调整组织支架的特异性,因此这种方法使用广泛。
王金茹等[17]以纤维纳米晶体为增强剂,采用静电纺丝法制备了纤维直径200-400 nm的聚己内酯/纤维纳米晶体支架,结果显示,当纤维纳米晶体添加量为5.25%时,复合支架达到最大应力4.2 MPa、断裂伸长率123%;成人胰腺导管癌细胞和肝细胞在复合纤维支架上均能正常生长,表明纤维纳米晶体没有增加纤维支架的细胞毒性,支架细胞相容性好,为该支架在组织工程上的应用提供了参考。
YOGANARASIMHA等[18]采用静电纺丝法制备了纳米纤维结构的聚己内酯支架,考察了不同灭菌方式对纤维支架纳米纤维结构、亲水性及机械性能的影响,发现体积分数20%乙醇稀释的5 000×10-6过氧乙酸处理后的聚己内酯支架具有更好的亲水性,接触角为0°;可以采用过氧乙酸进行快速、高效灭菌,同时纳米纤维的结构和机械性能保持不变。
2.1.5 生物打印法 生物打印技术被认为一种很有前途的快速原型设计技术,由于它能够生产高孔隙、互连性和精确控制材料结构,成为组织工程领域研究者们制作异质特性支架的常用手段。这种方法制备的支架,其纤维直径和孔径可以通过聚合物溶液黏度、操作压力和沉积速度这些打印参数进行调整。
TRACHTENBERG等[19]通过打印技术制备了聚己内酯多孔支架,当打印温度为60 ℃保持不变时,支架的孔隙率随着操作压力的增大而下降,打印速度增大孔隙率减小,当打印速度为300 mm/min时,支架的孔隙率为(40±13)%;当打印速度为400 mm/min时,支架的孔隙率为(36±12)%;支架的纤维直径则与压力有关,压力增大纤维直径增大;力学实验表明,该支架的压缩强度和压缩模量分别是(8.6±4.1) MPa和(42.0±20.7) MPa。
2.2 多孔支架在组织工程领域的应用
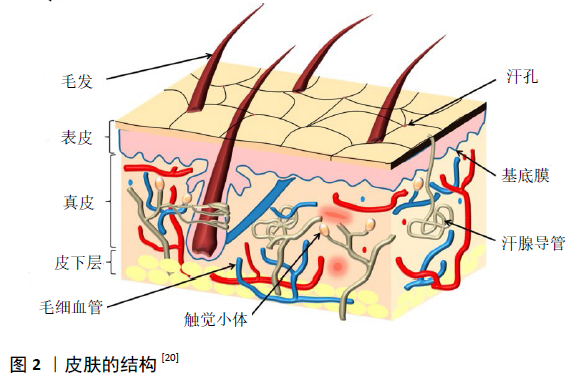
2.2.1 皮肤组织工程 皮肤是人体最大的器官,每一层皮肤的厚度、强度和生物组织都不同,其结构如图2所示,它们在微生物抵抗力、传感和温度调节中起着至关重要的作用[20-21],因此皮肤组织的修复、重建显得尤为必要且更有挑战性。
GAUTAM等[22]制备了一种用于皮肤工程和创面愈合的纳米纤维复合支架,首先采用静电纺丝制备了聚己内酯/明胶纳米纤维支架,然后采用Ⅰ型胶原蛋白接枝修饰聚己内酯/明胶,MTT实验结果表明成纤细胞在修饰后的支架上有较高的成活率和增殖率,场发射扫描电子显微镜分析显示成纤维细胞在支架表面可以黏附,该纳米纤维支架可用于皮肤创面愈合。
LIN等[23]制备了一种用于皮肤组织工程的聚己内酯/生物活性玻璃纳米纤维膜,并考察了其性能,结果显示,当生物活性玻璃添加量为4%时,纤维直径从700 nm增大到 1 100 nm,不同含量(2%-8%)活性玻璃添加时支架的孔隙率均在90%以上,断裂伸长率均有提高;当生物活性玻璃含量为6%时,复合支架表面细胞的增殖和黏附最佳,表明该支架在皮肤组织工程领域有广阔应用前景。
SHARIF等[24]制备了一种聚己内酯/胶原支架用于皮肤重建,该支架的纳米纤维直径为820 nm,适合干细胞生长,并考察了干细胞在支架上的附着、增殖、存活和分化,结果表明胶原包覆的聚己内酯支架可以作为干细胞的基质,可达到预期的皮肤愈合效果。
2.2.2 骨组织工程 理想的骨组织支架应具有生物活性、生物降解性、生物相容性、良好的力学性能、适宜的孔隙率等特性和物质传递的能力,而且随着新生骨组织的增殖生长支架逐渐降解,直至完全替代支架长成新骨[25]。聚己内酯在环境温度下具有稳定性,并且在期望的生理范围内具有机械性能及促进成骨细胞生长的能力;另一方面,聚己内酯的缓慢降解速率(相对分子质量为50 000,降解时间为3年)使其适用于骨组织工程领域的长期植入,因此聚己内酯是骨组织工程常用的生物高分子材料。
伍林招等[26] 以氯化钠为致孔剂,以聚己内酯、壳聚糖、磷酸钙骨水泥为原料制备了一种适合于骨组织工程的多孔支架,研究显示该复合支架具有柱状多孔海绵状结构,可以为营养物质输送提供通道;弹性模量为11.0 MPa,机械性能可以满足骨组织工程力学要求。
BHATTACHARJEE等[27]在模拟骨组织结构方面做了尝试,将磷酸钙以电沉积方式对非桑蚕丝素蛋白接枝的聚己内酯纳米纤维支架进行矿化,矿物层的形态可以通过沉积电势来调整,制备了骨组织替代品,结果显示,不同沉积电势条件下制备的磷酸钙沉积支架(5 V、3 V)具有与生物羟基磷灰石 (Ca/P=1.67)几乎相等的比例;与3 V沉积电势组相比,5 V沉积电势组的强度和细胞相容性更好,该支架模拟了天然骨细胞外基质的组成和结构,可以用作骨骼再生的合适生物相容性界面与进一步开发的平台。
WOODARD等[28]报道了一种聚左旋乳酸/聚己内酯-二丙烯酸酯半互穿型大孔形状记忆支架,该支架能够解决不规则颅骨缺损造成的自体移植物和周围组织之间存在界面不匹配的治疗难题。该研究结果显示,退火温度对支架的结构有显著影响,退火前的支架孔径为349 μm,退火后致支架密度增大、孔径减小,85 ℃退火时孔径减小,并且平均孔径随着聚己内酯/聚左旋乳酸比例的变化而变化;与聚己内酯-二丙烯酸酯对照的平均孔径(约231 μm)相比,相应的半互穿型支架平均孔径(247-338 μm)更大,随着聚左旋乳酸含量的增加而增加;在160 ℃退火时,不同比例的聚己内酯/聚左旋乳酸支架均表现出相似的平均孔径(214 μm)。
2.2.3 心脏组织工程 心脏是人体的重要组织,心脏病严重损害人体健康甚至生命,心脏病后期伴随着心脏组织的不可逆损伤是心脏病治疗的一大难题,传统的心脏移植伴随着供体受限、免疫排斥等弊端,而心脏组织工程的出现可一定程度解决这一难题。
吕丰等[29]以聚己内酯为原料制备了心肌内可降解药物支架,该支架可实现牛血清白蛋白持续释放30 d,具有药物缓释作用;可承受心肌压力,支架压缩80%时应力为 1.7 MPa,可实现透室壁性心肌血管重建术 后通道畅通,因此该支架具有临床应用前景。
CONSTANTINIDES等[30]采用颗粒浸出法(以氯化钠为致孔剂)制备了中长链聚羟基脂肪酸酯/聚己内酯支架,并研究了其在心脏组织工程中的应用,结果显示与纯中长链聚羟基脂肪酸酯支架相比,在中长链聚羟基脂肪酸酯/聚己内酯(95∶5)支架上心脏干细胞表现出更强的附着力和更强的增殖能力,因此该共混物在控制心脏干细胞的传递和心脏组织再生方面有巨大应用潜力。
HO等[31]采用3D打印技术制备用于心脏组织工程的聚己内酯-碳纳米管支架,并对支架性能进行了考察,MTT分析和荧光成像表明H9c2细胞可黏附在支架表面并健康生长;与其他支架相比,H9c2细胞在聚己内酯-碳纳米管(1%)支架上增殖最多,如图3所示,表明该支架具有H9c2细胞增殖的最适宜电导率和刚度;同时聚己内酯-碳纳米管支架可在心脏组织修复后被酶促生物降解。
2.2.4 神经组织工程 周围神经及脊髓损伤是神经组织修复和再生的一大难题,而神经组织支架因其特定的三维结构和生物活性可用于神经组织的修复和再生。理想的神经组织支架应具有可生物降解性、生物相容性、神经感应性及神经传导性等功能。人们在设计神经组织支架结构时主要从两方面考虑:一是导电性,增强支架的电活性,响应神经刺激;二是适宜的孔隙率和黏附性,能促进神经系统细胞生长、迁移、分化的支架。
宋学文等[32]制备了能促进大鼠坐骨神经损伤修复再生的红景天苷微球/胶原蛋白/聚己内酯复合神经导管,该支架的红景天苷累计缓释率达 76.59%,可持续缓释至16 d;动物体内实验术后6个月发现,胶原蛋白/聚己内酯的壳层大部分被降解,残留材料中有大量细胞侵入,提示构建的神经导管支架材料具有良好的组织相容性和可降解性,能够有效引导缺损神经的再生,显示其作为修复周围神经损伤的支架材料具有巨大潜力。
SHAFEI等[33]通过静电纺丝法制备了聚己内酯-聚吡咯导电支架,这是一种潜在的神经或肌肉组织工程支架,具有1.3-1.9 S/cm的电导率,孔隙率约为92%,可以满足组织工程支架的要求;对支架进行生物相容性评价的结果表明,该支架具有出色的生物相容性,且支持神经样细胞生长。
KO等[34]采用熔融静电纺丝制备了不同形态的聚己内酯超细纤维支架用于神经组织研究,考察了加工温度、收集距离、施加电压和喷嘴尺寸等工艺参数对支架形态和机械性能的影响,通过鼠R1胚胎干细胞系的神经元细胞考察支架的细胞相容性,结果显示神经细胞可以在聚己内酯支架上生存、迁移并分化为神经元,表明了熔融静电纺丝聚己内酯支架在神经组织工程应用中的潜力。